Austria (Austrian Republic)
A country in Central Europe. Area — 83.9 thousand km². Capital — Vienna (1.6 million), largest cities: Graz (226 thousand), Linz (183 thousand), Salzburg (142 thousand). Administrative-territorial division — 9 federal states: Lower Austria, Upper Austria, Burgenland, Styria, Carinthia, Tyrol, Vorarlberg, Salzburg, and Vienna, which is equivalent to them in administrative terms. Population — 8 million (1995); about 98% are German-speaking Austrians, with Slovenes, Croats, Hungarians, Czechs, and Slovaks also residing. Official language — German. Religion: about 74% of believers are Catholics, 6% are Protestants (mainly Lutherans). Currency - euro = 100 cents.
National holiday — October 26 — Day of the adoption by the parliament of the Federal Constitutional Law on the permanent neutrality of Austria (1955).
According to the Federal Constitutional Law of 1920, as amended in 1929, Austria is a democratic parliamentary and federal republic. The head of state is the federal president, elected by the population for a term of 6 years (since 2004 — H. Fischer). The highest legislative body is the parliament, consisting of 2 chambers: the National Council and the Federal Council. The National Council (183 deputies) is elected by a proportional system, based on equal direct suffrage, through secret ballot for a term of 4 years; members of the Federal Council (63 deputies) are delegated by the Landtags (parliaments of the states) for the duration of their mandates according to a proportional system based on the population of individual states. Following the last extraordinary elections (November 2002), the seats in the National Council were distributed as follows: Social Democratic Party of Austria (SPÖ) - 69 seats, Austrian People's Party (ÖVP) - 79, Austrian Freedom Party (FPÖ) - 18, Green Party - 17. The highest executive body is the government headed by the federal chancellor. Since February 2003, this position has been held by V. Schüssel (ÖVP). The government is a coalition (formed in February 2003 by ÖVP and FPÖ).
In 2005, as a result of a split in the FPÖ, the party "Alliance for the Future of Austria" (BZÖ) was formed, led by J. Haider, which included all sitting cabinet members as well as an absolute majority of the parliamentary faction. The remaining part of the FPÖ retained its original name.
Political parties: The Social Democratic Party of Austria (SPÖ) — re-established in 1945 as the successor to the Social Democratic Party of Austria, founded in 1889 (from 1945 to 1991 — Socialist Party of Austria). It has over 500 thousand members, of which about 200 thousand belong to the Vienna organization. Workers in the party make up about 35%, civil servants — over 25%, housewives — 13%, retirees — about 15%. Social Democrats maintain a dominant influence over wage earners. Trade unions are within its sphere of influence. About 30 different organizations with a total membership of over 1 million are affiliated with or influenced by the SPÖ. It is a member of the Socialist International. In the elections to the National Council (November 2002), 36.51% of voters supported the SPÖ. The party chairman is A. Gusenbauer (since April 2000).
The Austrian People's Party (ÖVP) - established in 1945 as the successor to the conservative Christian Social Party, founded in 1887. It has about 850 thousand members. The social composition of the party: farmers - over 45%, entrepreneurs - up to 17%, intelligentsia, civil servants, and workers - up to 38%. It has influence in several mass organizations and maintains contact with Catholic organizations. The ÖVP is a member of the International Democratic Union (IDU) and the European Democratic Union (EDU). In the last parliamentary elections, the ÖVP received 42.3% of the votes. The party chairman is V. Schüssel.
The Austrian Freedom Party (FPÖ) - founded in 1955. It has about 60 thousand members. It is supported by small and medium-sized entrepreneurs, civil servants, students, intelligentsia, as well as some workers. In recent years, the right wing has dominated the FPÖ, advocating from nationalist positions. It is a member of the World Liberal International. In the last elections, about 10% of voters supported the FPÖ. It is represented in all 9 Landtags. The chairman of the remaining part of the FPÖ after the split is H.-C. Strache.
The Green Party — founded in 1987, a leftist movement leading a portion of the youth, civil servants, and intelligentsia. Its main area of interest is ecology. Nevertheless, the Greens strive to act actively in other areas of foreign and domestic policy. In the last elections, 9.4% of voters supported it. The party chairman is A. van der Bellen.
The Austrian Trade Union Federation (ÖGB) includes 14 sectoral trade unions, which have a total of 2 million members (about 60% of wage earners). The largest are the trade unions of private employees (345 thousand), metalworkers, miners, and energy workers (245 thousand), and civil servants (228 thousand). It is a member of the International Confederation of Free Trade Unions (ICFTU) and the European Trade Union Confederation (ETUC).
The name Austria is first mentioned in a document from 996. Since 1156, Austria has been a duchy, since 1453 — an archduchy, since 1804 — the Habsburg Empire, and from 1867 to 1918 — Austria-Hungary (a dualistic - dual monarchy). The Austrian Republic was formed in November 1918 after the collapse of the Austro-Hungarian monarchy. In 1938, Austria was forcibly annexed (Anschluss) to Nazi Germany. After Austria was liberated in 1945, its territory was divided into Soviet, American, British, and French occupation zones.
In May 1955, representatives of the USSR, USA, UK, France, and Austria signed in Vienna the State Treaty on the restoration of an independent and democratic Austria. In October 1955, the Austrian parliament adopted a constitutional law on the permanent neutrality of the country. Austria's foreign policy is based on its commitments under the State Treaty and its adopted status of permanent neutrality.
Austria is a member of the UN (since 1955), Council of Europe (since 1956), OECD (since 1960), EU (since 1995).
Austria is among the most developed countries in Europe. The country's GDP in 2004 amounted to 232.692 billion euros. The volume of industrial production increased by 3.3%. The largest foreign investor is Germany (about 80% of all investments). Mineral resources include magnesite, oil, natural gas, lignite, iron ore, copper, lead-zinc, and tungsten ores, bauxite, graphite, and table salt.
The leading industries are machine engineering, metallurgy, chemicals, pulp and paper, mining, textiles, and food. One-third of the volume of industrial production comes from the state sector of the economy.
Austria has a productive agricultural and forestry sector. Its share in GDP is 3.1%. Almost all types of agricultural products necessary for the population are produced. The most important sector of agriculture is animal husbandry.
Foreign tourism is one of the most profitable sectors of the Austrian economy. About 20 million people visit the country annually.
The length of the state railways is more than 5.8 thousand km, and the length of the roads is more than 34 thousand km. There are 6 international airports. The largest airline is "Austrian Airlines".
Austria trades with more than 150 countries around the world. About 70% of its foreign trade turnover is with EU countries. In second place are the countries of Central and Eastern Europe (14% of foreign trade turnover). Austria's main trading partners are Germany, which accounts for about 40%, as well as Italy (9%), France, and Switzerland (5% each). Russia accounts for about 1.5%.
In terms of income per capita (25 thousand dollars), Austria ranks 9th in the world. The unemployment rate at the beginning of 2005 was 4.5%.
Universal compulsory education begins at the age of 6 and lasts for 9 years. Education in public schools and higher education is free. There are 21 higher education institutions, including 12 universities. The University of Vienna (founded in 1365) is the oldest existing university in German-speaking countries.
In Austria, more than 20 daily newspapers are published. Their single issue circulation is nearly 3 million copies. The largest of them are "Die Presse" (about 1 million), "Kurier" (about 400 thousand), "Salzburger Nachrichten" (about 100 thousand), "Der Standard" (about 100 thousand), "Die Presse" (100 thousand). The official government publication is "Wiener Zeitung" (27 thousand). Television and radio broadcasting is carried out by the state company ORF. The national news agency is the Austrian Press Agency (APA).
Read also:

Republic of Palau
PALAU. Republic of Palau A state in Oceania, on an archipelago in the group of the Caroline...

Republic of Slovenia
SLOVENIA. Republic of Slovenia A state in the southern center of Europe, in the northwestern part...

Guyana. Cooperative Republic of Guyana
Guyana. Cooperative Republic of Guyana A country on the northeastern coast of South America. Area...

Republic of Kiribati
KIRIBATI. Republic of Kiribati A state in the central, equatorial part of the Pacific Ocean...

Belize
Belize A country in the southeast of the Yucatán Peninsula in Central America. Area - 23,000 km²....

Republic of Nauru
NAURU. Republic of Nauru A state in Oceania, located on the eponymous coral island in the...

Republic of Kenya
KENYA. Republic of Kenya A country in East Africa on the coast of the Indian Ocean. Area — 582.6...
Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda A state on the islands of Antigua, Barbuda, and Redonda, which are part of the...

Dominica. Commonwealth of Dominica
DOMINICA. Commonwealth of Dominica A state on the island of the same name in the Lesser Antilles...

Independent State of Samoa
SAMOA. Independent State of Samoa A state in the central part of the Samoa archipelago in the...

The State of Tuvalu
TUVALU A country in Oceania, in the southwestern part of the Pacific Ocean (includes 9 islands of...

Barbados
Barbados A state on the island of the same name in the Lesser Antilles archipelago in the Atlantic...

Republic of Trinidad and Tobago
TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO. Republic of Trinidad and Tobago A state on the northeastern coast of South...

Republic of Croatia
CROATIA. Republic of Croatia A country in southeastern Europe, on the eastern shore of the...

Federated States of Micronesia
MICRONESIA. Federated States of Micronesia An island nation in Oceania, including the center and...

Eastern Samoa. American Samoa, Territory of American Samoa
Eastern Samoa. American Samoa, Territory of American Samoa U.S. possession in the South Pacific,...

Gabon. Republic of Gabon
Gabon. Gabonese Republic A country in Central Africa. Area - 267.7 thousand km². Capital -...

Frankl Felix Isidorovich
Frankl Felix Isidorovich (1905-1961), Doctor of Physical and Mathematical Sciences (1931) and...

Ukraine
A state in Central-Eastern Europe. Area - 603.7 thousand km². Capital - Kyiv (2,630 thousand, as...

Republic of Iceland
ICELAND. Republic of Iceland A country in Europe located on the island of the same name in the...

Bahamas. Commonwealth of the Bahamas
The Bahamas. Commonwealth of The Bahamas A state located in the Atlantic Ocean on the archipelago...

Gambia. Republic of Gambia
Gambia. Republic of Gambia A country in West Africa on the Atlantic Ocean coast. Area — 11.3...

Jamaica
JAMAICA A state on the island of the same name and adjacent small islands in the Caribbean Sea,...

Principality of Monaco
MONACO. Principality of Monaco A state in Southern Europe, on the coast of the Mediterranean Sea,...

Republic of the Islands of Fiji
FIJI. Republic of the Fiji Islands A state located in Oceania, in the southwestern part of the...

Republic of Honduras
HONDURAS. Republic of Honduras A country in Central America. Area - 112,000 km². Capital -...

Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands
NORTHERN MARIANA ISLANDS. Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands A state in Oceania, in the...

Personal Exhibition of Asatilla Teshbaev "Origins of Time"
From October 16 to November 4, at the G. Aitiev National Museum of Fine Arts, there will be a...

Grenada
GRENADA A country on the eponymous island and two islands from the Grenadines group in the Lesser...

Ireland
IRELAND A country in Western Europe, occupying most of the island of Ireland. Area - 70.3 thousand...

Botswana. Republic of Botswana
Botswana. Republic of Botswana A country in southern Africa. Area - 600.4 thousand km², 80% -...
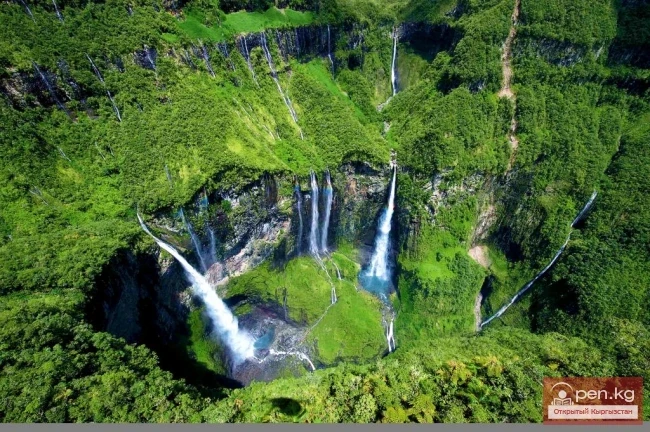

Réunion
RÉUNION An overseas department of France in the Indian Ocean, on the island of Réunion, located...
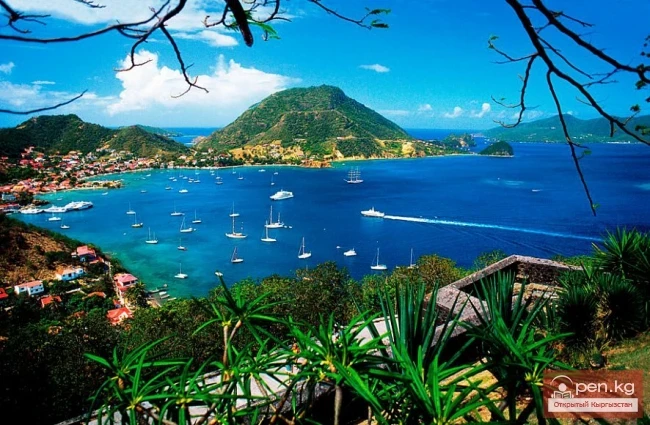

Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe - an overseas department of France in the Caribbean Sea in the Lesser Antilles...
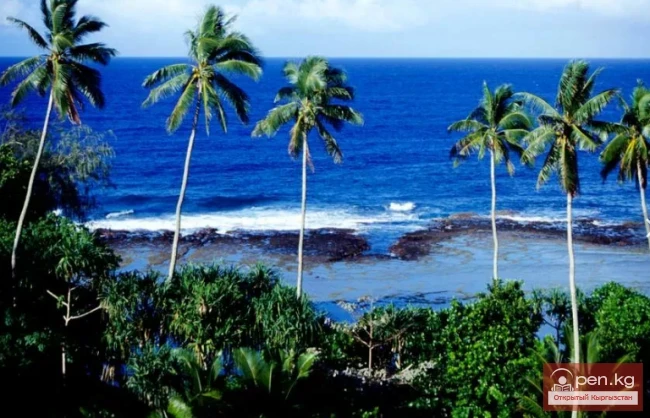

Wallis and Futuna Islands
WALLIS AND FUTUNA (ISLANDS) An overseas territory of France, located in Oceania, in the central...
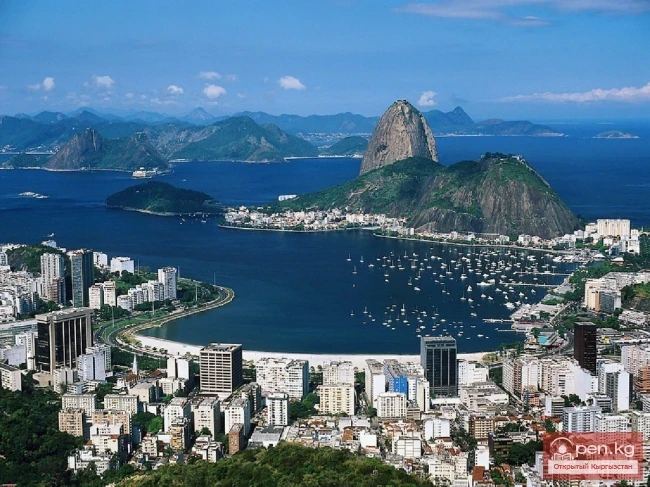

Cayman Islands
CAIMAN ISLANDS (Cayman Islands) A British territory located on the islands of Grand Cayman, Little...

Niue
NIUE An island in Oceania, in the central part of the Pacific Ocean. Area - 262.6 km²....

Republic of Guinea-Bissau
Republic of Guinea-Bissau A country on the Atlantic coast of Africa. It includes, in addition to...

Republic of Estonia
ESTONIA. Republic of Estonia A state in the northwest of Europe, on the coast of the Baltic Sea....

Hungary. Hungarian Republic
Hungary. Hungarian Republic A state in the southeastern part of Central Europe. Area - 93,03...

Republic of Namibia
NAMIBIA. Republic of Namibia A country in the southwestern part of Africa, bordered by the...

Republic of Senegal
SENEGAL. Republic of Senegal A state located on the Atlantic coast of West Africa. Area - 196.7...

Guatemala. Republic of Guatemala
Guatemala. Republic of Guatemala A country in the northwest part of Central America. Area - 109...

Vanuatu. Republic of Vanuatu
Vanuatu. Republic of Vanuatu A state in the southwestern part of the Pacific Ocean (in Oceania)....
