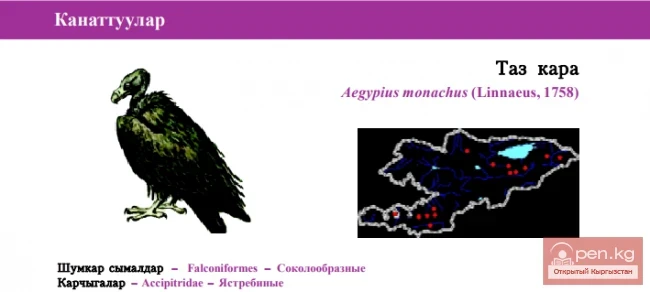
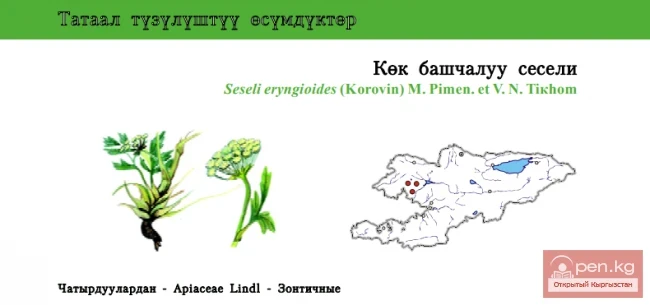
GRENADA
A country on the eponymous island and two islands from the Grenadines group in the Lesser Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean Sea, between North and South America. Total area - 344 km². Capital - St. George's (35 thousand). Administrative division - 7 districts. Population - 89 thousand (estimate); over 90% are blacks and mulattoes, the rest are Indians and people of European descent. The official language is English. The main religion is Catholicism. The currency is the East Caribbean dollar = 100 cents.
Diplomatic relations between the USSR and Grenada were established in September 1979. In November 1983, the Soviet embassy left Grenada due to the intervention of U.S. troops. The Governor-General of Grenada announced the severance of diplomatic relations with the USSR in November 1983. Relations were restored with the Russian Federation on September 17, 2002.
National holiday - February 1 - Independence Day (1974).
Grenada is an independent state, part of the Commonwealth led by Great Britain. According to the constitution, the head of state is the Queen of Great Britain, represented on the island by a Governor-General (since August 1996 - D. Williams). The legislative authority is vested in a bicameral parliament, consisting of a Senate (13 appointed members) and a House of Representatives (15 deputies elected by the population for a term of 5 years). The executive power belongs to the government, headed by the Prime Minister (since June 20, 1995 - K. Mitchell, leader of the New National Party).
Main political parties: New National Party (NNP) - founded in 1984, ruling (8 seats in the House of Representatives).
National Democratic Congress (NDC) - founded in 1987, leader - T. Thomas (7 seats). United Labor Party of Grenada (ULPG) - founded in 1950, leader - G. Benfield.
There is a Grenada Trade Union Council - established in 1955 (5,000 members), part of the ICFTU.
The island was first seen by Europeans by Christopher Columbus in 1498. From 1650 to 1783 - a colony of France, from 1783 - a colony of England. From 1958 to 1962 - part of the West Indies Federation. In 1967, Grenada received the status of "associated with Great Britain." Independence was proclaimed on February 7, 1974.
In March 1979, the regime of E. Gairy, who had been Prime Minister since 1967, was overthrown. All legislative and executive power passed to the government led by Prime Minister M. Bishop. Disagreements that arose in the leadership of the ruling party, the New Jewel Movement (NJM), led to an armed confrontation on October 19, 1983. Prime Minister M. Bishop and several of his supporters were killed. On October 25, 1983, the U.S., with the support of the Organization of Eastern Caribbean States, launched a military intervention, which also involved military contingents from Jamaica, Barbados, and several other island states.
In December 1984, elections were held in the country. The right-center coalition - NNP won them. It was led by G. Blaze, who had twice held the position of head of government under the English colonial regime. In 1987, a split occurred in the NNP. Several figures who disagreed with G. Blaze's political course formed their own party - the NDC, which was in power from 1990 to 1995 (Prime Minister N. Brathwaite). As a result of the 1995 elections, the ruling party became the NNP again.
Grenada is a member of the UN (since 1974), OAS (since 1975), ALBA (since 1975), Caribbean Community, and is part of the Non-Aligned Movement.
The main sectors of the economy are services and agriculture. Bananas, cocoa beans, coconuts, nutmeg (2nd in the world - 2,500 tons per year), cotton, citrus fruits, and sugar cane are grown. Industry is represented by small enterprises. In recent years, foreign tourism has begun to develop.
Main export items - nutmeg, cocoa beans, bananas; imports - food, fuel, machinery and equipment, mineral fertilizers, clothing. Main trading partners: the USA, EU countries, Caribbean Community, Canada.
External debt - 200 million USD (2000). Unemployment - about 10%. 85% of the adult population is literate.
The length of the roads is about 1,000 km, of which 638 km are paved. The main seaport is St. George's; there is an international airport.
A faculty of the University of the West Indies has been opened on the island. Several small circulation weekly newspapers are published. There is a state radio station, as well as a small television station built in 1986. Television broadcasts are received from Trinidad and Tobago, as well as Barbados.