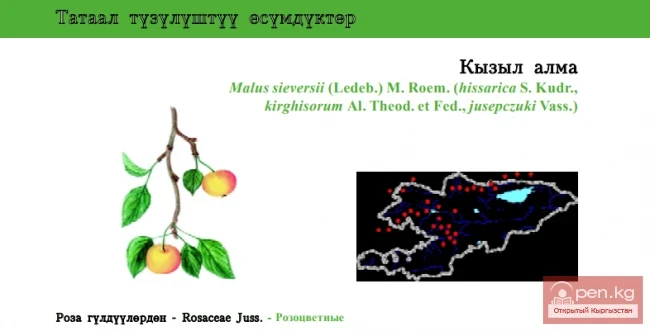
Sievers’s Apple-tree \ Kyzyl Alma \ Sievers’s Apple-tree
Sievers’s Apple-tree
Status: LC category. A polymorphic species of the mountain-central Asian region, a valuable element of the gene pool, one of the secondary forest-forming and fruit-bearing species [61, 21, etc.]. The only species from the flora of Kyrgyzstan included in the International Red List (IUCN RLTS, category VU B1+2c) [87].
Description. Trees up to 3-5 m tall, with a compact crown. Branches with reddish-brown bark, or gray, peeling. Shoots lighter than those of M. niedzwetzkyana. Leaves from dense to thin, up to 10 cm long. Flowers in clusters of 2-5, pale pink, 5.5-6.0 cm in diameter. Apples in clusters of 2-3, flattened-spherical, 3-7 cm in diameter, green or yellowish, often with a purple blush. Sweet-sour, dry.
Biological features. Blooms in late April - early May, fruits in July-September. Propagates by seeds and root suckers. The species is usually low-growing but winter-hardy and relatively undemanding [61, 55, etc.].
Distribution general and in the country. Mountains of Central Asia (Kyrgyzstan, Southern Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan), Northern Afghanistan, Xinjiang, and the Tarbagatai Range [61, 81, 23, 35, 20, 18]. In Kyrgyzstan - the Kyrgyz Range (northern slope), Talas Range (west) [35], Suusamyr-Too (southern slope), Kavak-Too [61], Chatkal, Uzun-Akhmat, Atoinok, Fergana, basins of the Chatkal, Kichi, and Chon-Kemin Rivers [20]; absent in the Alai and Turkestan Ranges, except for the Turok area [61].
Habitat. In the black forest zone, along the bottoms and slopes of gorges, at altitudes from 900 (in Kyrgyzstan usually from 1200) to 2400 m above sea level [61, 81, 23, 18].
Population. Trees are found both individually and in relatively large groups in forest masses, almost throughout the species' range in Kyrgyzstan. The apple forests managed by the forestry authorities of the Republic, where Sievers’s apple-tree is the main species, are estimated to cover about 16,700 ha as of the year 2000 [21].
Limiting factors. Economic activity, excessive grazing. In some habitats, trees are cut down for fuel, and are periodically heavily affected by harmful insects [35]. Cultivation. Widely cultivated in Central Asia and in the countries of the former USSR (north to Moscow and Kaliningrad [35]), sometimes grown by local residents in household plots in Kyrgyzstan. Cultivated in the Botanical Garden of the National Academy of Sciences of the Kyrgyz Republic since 1953 from seeds, began to bear fruit at 8 years [55].
Existing conservation measures. The species was listed in the IUCN RLTS in 1994 [87] as vulnerable on a global scale, and also in the Red Book of Kazakhstan in 1981 as decreasing in number [23]. Several habitats are located in protected areas in the Western Tien Shan [18, 35] (in Kyrgyzstan - in the reserves of Padysha-Ata, Sary-Chelek, and Besh-Aral, as well as in the nature reserves of Dashman, Uzun-Akhmat, Iyrisuy, etc.).
Recommended conservation measures. Control marginal populations (in the Suusamyr-Too, Kavak-Too, Alai Ranges), increase fines for the destruction of trees as objects protected by IUCN.
Kyzyl alma
Sievers’s Apple-tree
Malus sieversii (Ledeb.) M. Roem. (hissarica S. Kudr., kirghisorum Al. Theod. et Fed., jusepczuki Vass.)
Status: LC. This species is polymorphic and spread mainly in the mountains of Central Asia, a valuable food plant for apple selection. It is the only species from the flora of Kyrgyzstan which is listed in IUCN RLTS (category VU B1+2c). The area of the species in the country includes the Alexander (western part of the northern macroslope), Talas (western part), Suusamyr-Too (southern slope), Uzun-Akhmat, Chatkal, Atoinok, Fergana, and Alai (northeastern part) Mountain Ranges, and the basins of the Chatkal, Kichi-Kemin, and Chon-Kemin Rivers. Trees occur individually and in groups in the forest belt at 1,200-2,400 m above sea level. The period of flowering is from the end of April to the beginning of May, and fruiting occurs from July to September, with propagation occurring both generatively and vegetatively. The apple forests in Kyrgyzstan (with M. sieversii as the main component) are managed by forest governmental authorities and occupy about 16,700 ha. Limiting factors include economic activity in inhabited areas, felling (firewood cutting), fruit collection by people and consumption by animals, and excessive pasturage; the hybridization factor for genetic purity is unstudied. However, at present, this species is not endangered in the country. The species is widely cultivated in world arboretums, and in the Bishkek Botanical Garden since 1953. Special monitoring for some small isolated marginal natural populations is recommended to protect this species, along with monitoring and educational work for people and fines for illegal felling.
Read also:

Niedzvetzki’s Apple-tree \ Red-leaved Apple
Niedzvetzki’s Apple-tree Status: VU. Very rare, endemic, endangered species with a small...

Korzhinski's Pear / Korzhinski Almurutu / Korzhinski's Pear
Korzhinski’s Pear Status: VU. One of three species growing in the territory of the Kyrgyz...
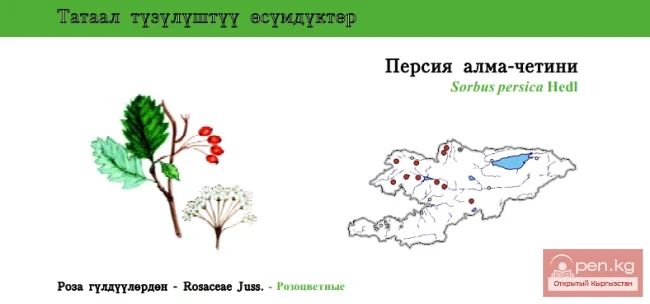
Persian Rowan \ Persia Alma-Chetini \ Persian Rowan
Persian Rowan Status: VU. Endemic, ornamental species....

Strange (Paradoxical) Honeysuckle / Укмуштуу шилби / Paradoxical Honeysuckle
Paradoxical Honeysuckle Status: Category CR B2ab(iii). A relict endemic species with a disjunctive...

Petunnikov's Almond
Petunnikov’s Almond Status: VU. One of 40 species growing from the Mediterranean to Central Asia....
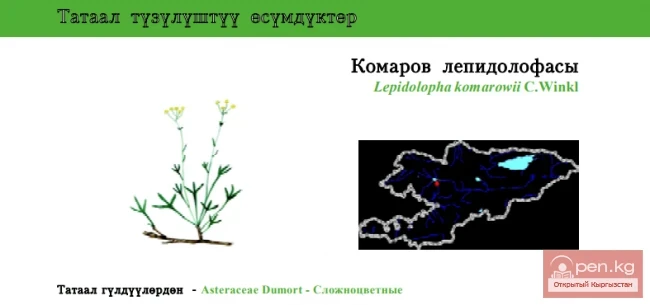
Lepidolopha Komarov / Komarov's Lepidolopha
Lepidolopha Komarovii Status: EN. An endemic species of mountainous Central Asia, representative...

Dwarf Ammopiptanth / Baibiche Chekey / Ammopiptanth Dwarf
Dwarf Ammopiptanth Status: EN. A rare species with a disjunctive range. One of two known...
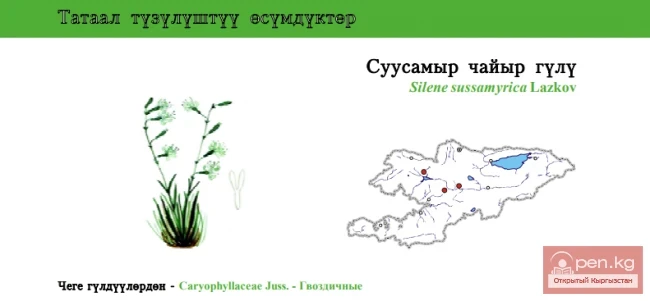
Susamyr Catchfly
Susamyr Catchfly Status: EN. A rare species found in small numbers and in a limited area, which...
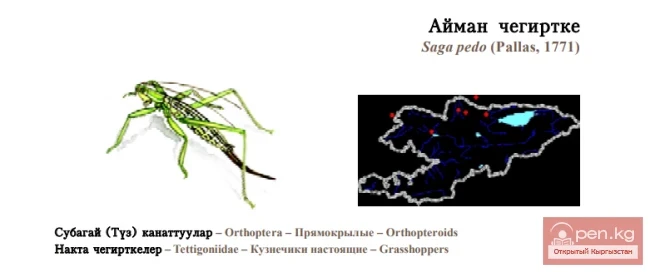
Steppe Dybka / Ayman Katydid / Matriarchal Katydid, Predatory Bush Cricket
Steppe Katydid Status: Category II (VU Alc; B2ab(iii,iv); D1+2). A relic steppe species with...

Types of Insects Listed in the 2004 IUCN RLTS Not Included in the Red Book of Kyrgyzstan
Insect species listed in the 2004 IUCN RLTS, not included in the Red Book of Kyrgyzstan 1....
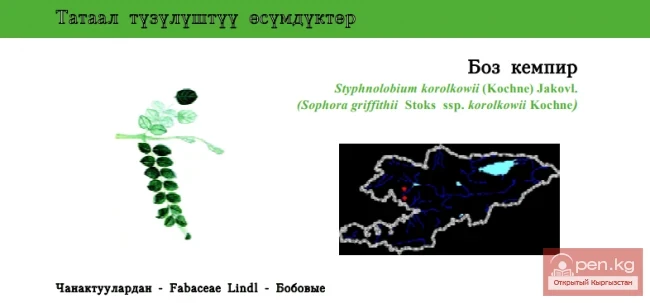
Sofora Korolkova / Boz Kempir / Korolkov’s Pagoda-tree
Korolkov’s Pagoda-tree Status: CR. The only species of the genus found in Kyrgyzstan....
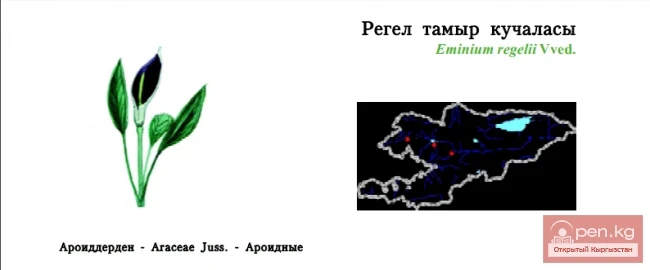
Regel's Eminium / Regel's Root Cluster / Regel's Eminium
Regel’s Eminium Status: VU. A rare endemic species of the Western Tien Shan....

Kashgarian Bean Caper
Kashgarian Bean Caper Status: VU. Rare, little-studied endemic species....

Aulie-Ata Stemmacantha Centaury / Aulie-Ata Stemmacantha / Aulie-Ata Centaury
Aulie-Ata Stemmacantha Centaury Status: EN. A very rare species, critically endangered....

Hairy Flowering Golden / Yellow Trichanthemis / Golden Trichanthemis Centaury
Golden Trichanthemis Centaury Status: VU. A rare narrowly endemic species of the Alai Ridge, an...
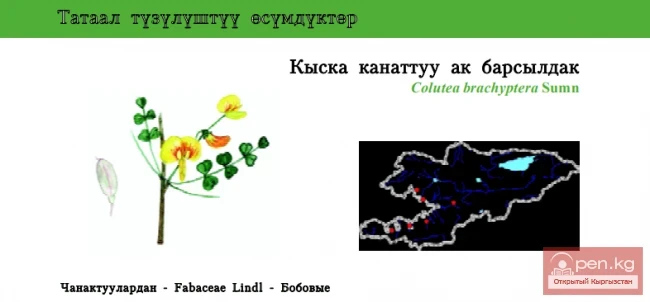
Short-winged Bladder-senna / Baibiche Chekey
Short-winged Bladder-senna Status: VU. One of three very rarely occurring species of this genus in...
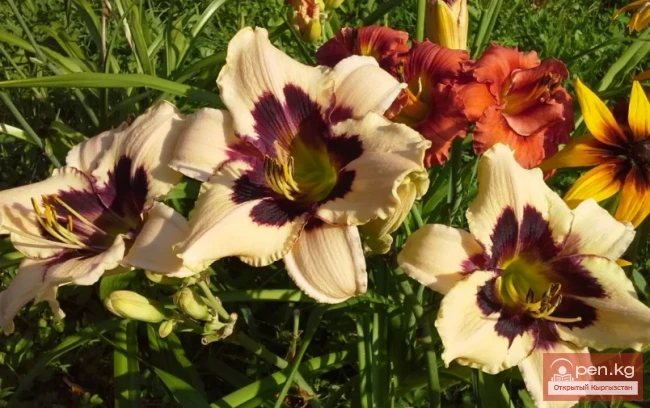

Daylily, Marsh Marigold. Perennial Herbaceous Plants Wintering in the Soil of Kyrgyzstan
Daylily, Hemerocallis (Hemerocallis L.). In nature, it is found on the edges of forests, among...

Kashgarian Barberry
Kashgarian Barberry Status: VU. Rare species....

Red-headed Falcon / Shaheen / Barbary Falcon
Barbary Falcon Status: Category III, Critically Endangered, CR: R. Kyrgyz ornithologists believe...

Wrapped Alpine Saw-wort
Wrapped Alpine Saw-wort Status: VU. Rare species. Found in Kyrgyzstan at the edge of its range....

Greig's Tulip, Variegated Tulip / Greig Mandalagy, Chaar Mandalak / Greig’s Tulip
Greig’s Tulip / Тюльпан Греига, тюльпан пестролистный Status: EN. A species with declining numbers...

Lily of the Valley, Poppy, Small-leaved Aster, Monarda. Rhizomatous Perennials Wintering in the Soil of Kyrgyzstan
May Lily (Convallaria majalis L.). Has long been used in decorative gardening. Beautiful not only...

Siberian Tien Shan / Tien Shan Sibericus \ Tien Shan Sibiraea
Tien Shan Sibiraea Status: CR. An endemic, decorative, and rare northern Tien Shan plant....

Kostychev's Pasque Flower
Kostychev’s Pascueflower Status: VU. A narrowly endemic and very beautiful plant, deserving...
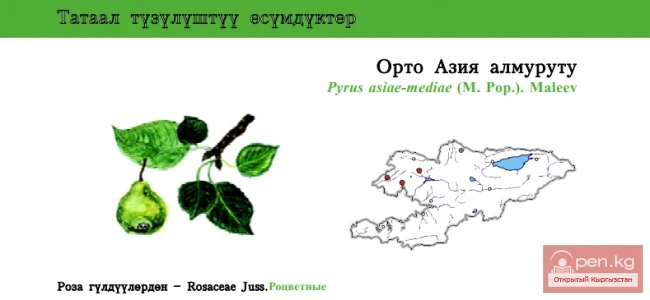
Middle Asian Pear
Middle Asian Pear Status: EN. The species is little-known and narrowly localized, endemic to the...
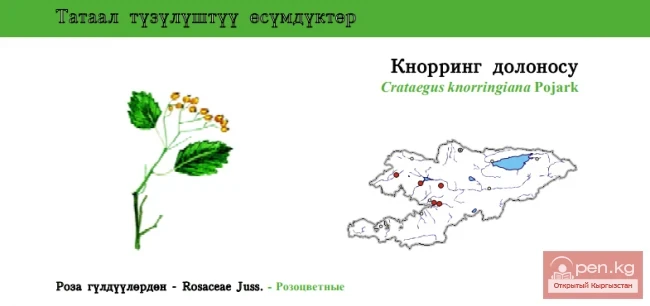
Knorring's Hawthorn / Knorring's Dolenos / Knorring’s Haw-tree
Knorring’s Haw-tree Status: VU. A narrowly endemic species....
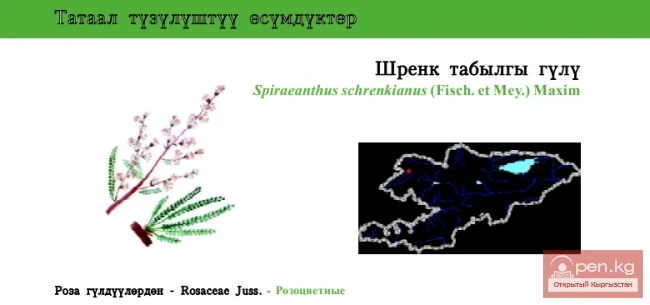
Schrenk's False Spirea / Schrenk's Tavolga Flower / Spireanthus
Schrenk’s False Spirea Status: CR B2ab(iii). Endemic, ornamental, and rare plant with a decreasing...
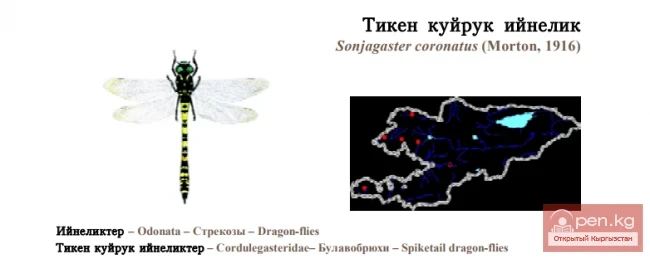
Crowned Bulbous-Body / Tiken Tail Needle / Coronate Spiketail
Coronate Spiketail Status: Category II (VUA4bc; B2b(iii,iv); D2). A locally occurring species with...

Vvedensky's Sage / Vvedensky Sage, Vvedensky Kyok Bashy / Vvedensky’s Sage
Vvedensky’s Sage Status: VU. A very rare narrowly endemic species. An ornamental plant....

Schennikov's Otostegia
Schennikov’s Otostegia Status: VU. A rare endemic species, endemic to Kyrgyzstan with a disjunct...

Uzun-Akhmat Grape \ Uzunakmat Grape
Uzun-Akhmat Grape Status: VU. Endemic species of Western Tien Shan....

Hairy-flowered Aulie-Ata / Oluyaata Trichanthera / Aulie-Ata Pseudoglossanthis Centaury
Hairy Flowering Plant Aulie-Ata Status: EN. A representative of a monotypic section, a narrowly...

Alai Bubblefish / Alai Physocline / Alai Physochlaina
Alai Bubblewort Status: VU. A rare narrowly endemic species....
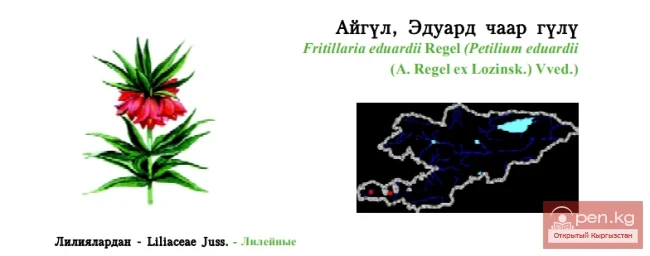
Eduard's Imperial Crown
Eduard’s Imperial Crown Status: EN B1ab(i,ii,iv,v). In Kyrgyzstan - the only one of three very...

Honey Plants of the Forests, Meadows, and Shrub Thickets of Kyrgyzstan. Part 1
Honey Plants of Forests, Meadows, and Shrub Thickets The honey flora in the forests, meadows, and...
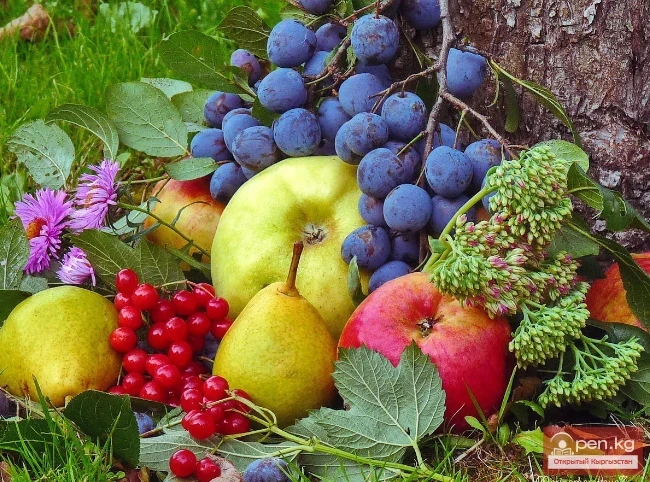

Honey-bearing fruit trees and berry shrubs of Kyrgyzstan
Honey-bearing Fruit Trees and Berry Bushes Fruit trees and berry bushes hold special value among...
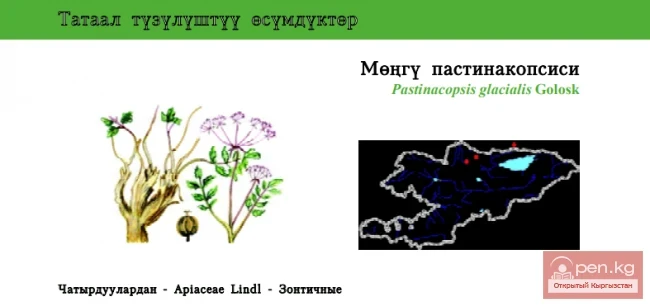
Pasternak's Glacier / Miongu Pastinacopsis / Pastinacopsis
Glacial Pastinacopsis Status: EN. A rare endemic species of a monotypic genus in the Northern Tien...
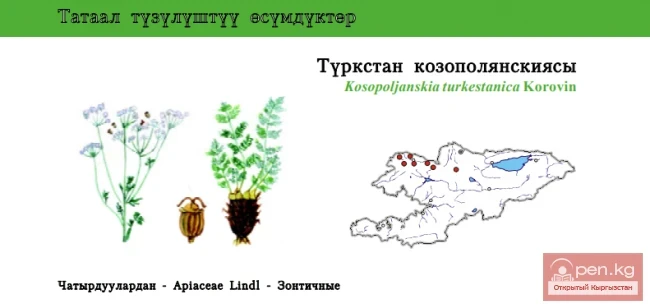
Kosopolyan Turkestan / Turkestan Kosopoljanskia
Kosopoljanskaya Turkestanian Status: VU. One of the two endemic species of this genus found in...

Acantholimon Dense / Nyk Työ Tamán / Dense Prickly-thrift
Acantholimon compactum Status: VU. A very rare narrowly endemic species....

Eugenia's Primrose
Eugenia's Primrose Status: VU. A narrow endemic rare, highly ornamental species. Found in...
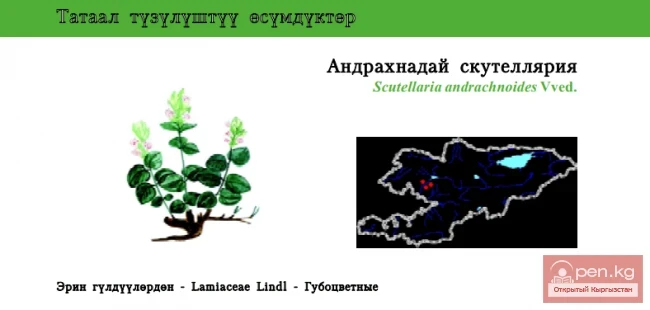
Andrachne-like Scullcup / Andrachne-like Helmet
Andrachne-like Scullcup Status: VU. A very rare rocky species, narrowly endemic to a small section...

Saker \ Bakharyn ылaaчыны / Peregrine Falcon
Peregrine Falcon Status: Category VII, Least Concern, LC. One of 10 species of the genus in the...

Mountain hiking routes by regions of the republic
It can be confidently said that there is no gorge in the republic that is "unsuitable"...