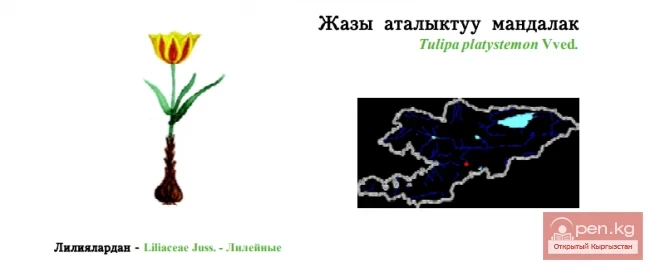
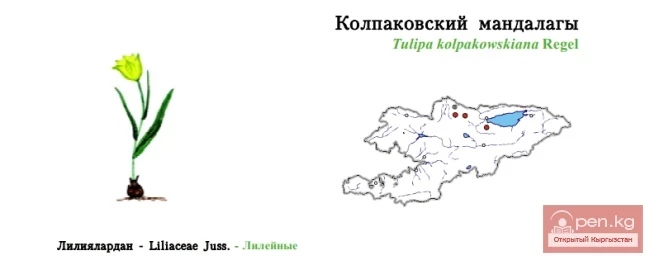
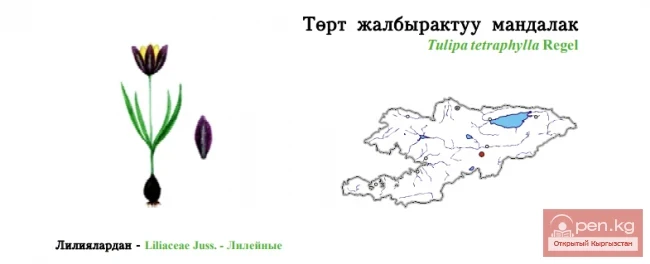
Daylily, Hemerocallis (Hemerocallis L.).
In nature, it is found on the edges of forests, among shrubs, near water bodies. In the wild, it is distributed in the Far East, Eastern Siberia, China, and Japan.
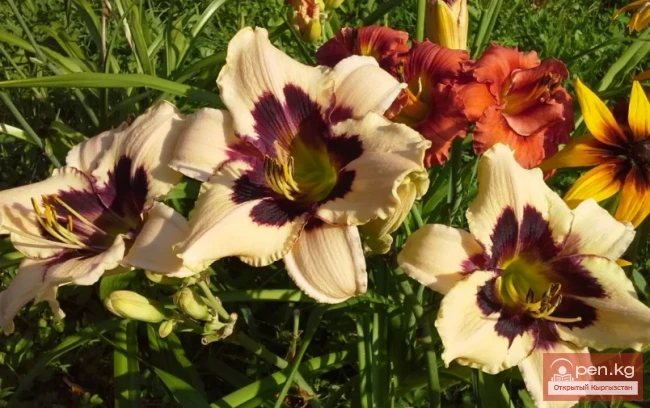
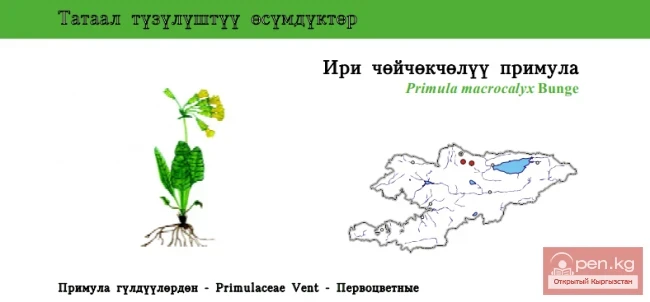
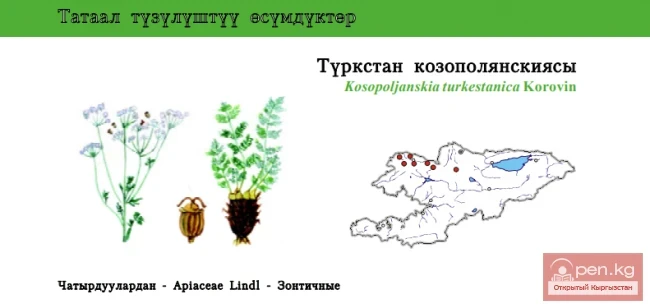
The plant is rhizomatous, with some species having thickened, spindle-shaped roots. The leaves are basal, sessile, linear, straight, or arching. The flower stalks rise above the leaves, sturdy, 50—100 cm tall, ending in a clustered or spreading inflorescence. The flowers, in groups of 2—8, are large, funnel-shaped, in shades of yellow and orange-red. The plant is undemanding, moisture-loving, grows well even in poor soils, shade-tolerant, spreads quickly, displacing weeds, and is winter-hardy. In cultivation, wild species are used:
Yellow daylily (H. flava L.). The stem is leafless, elastic, up to 50 cm tall. The leaves are broad-linear, persisting throughout the growing season. The inflorescence is branched, with 8 bright yellow fragrant flowers. It blooms from late May to early July;
Orange daylily (H. fulva L.). The stem is up to 80 cm tall. The leaves are narrow and pointed. The inflorescence contains 6—12 yellowish-orange flowers, each up to 14 cm in diameter.
It blooms from mid-June for 30—35 days;
Middendorff's daylily (H. Middendorffii Trautv. et Mey.). The bush height is up to 80 cm. The flowers are bright orange, up to 9 cm in diameter, gathered in globular inflorescences, fragrant. It blooms in May—June.
The best varieties include:
Aprico. Stem height up to 100 cm. The inflorescence contains up to 18 bright orange flowers, each up to 10 cm in diameter. The leaves are basal, numerous, and wide.
It blooms from June 10—15 for 35—40 days;
Golden Belle. Stem height 70 cm. The inflorescence contains up to 10 golden-yellow flowers, each up to 10 cm in diameter.
Golden Dust. Bush height up to 80 cm. The flowers are bright yellow, 6 cm in diameter.
Daylilies are propagated by dividing the bush, offsets, and wild species by seeds. Seeds are sown in the fall or after stratification in early spring in open beds, in well-fertilized soil. Uniform and vigorous young shoots appear in spring. In the second year of life, they are planted in a permanent place.
Daylilies are propagated by division and offsets in spring, autumn, and immediately after flowering. To achieve lush and abundantly flowering bushes, plants are planted 50 cm apart. Planting holes are dug 30X30X30 cm and filled halfway with a mixture of soil and peat or compost. Before planting, a quarter bucket of water is poured into each hole, and the plants are planted in the resulting slurry. The first watering is done after 7—10 days, subsequent waterings as needed.
Complete mineral fertilizer is applied annually in autumn or spring at a rate of 150—170 g per 1 m².
Daylily rightfully deserves wide application in gardens, parks, and private plots. Its flowers resemble lilies in shape, have a pleasant aroma, and possess a golden, extraordinarily pure color.
Marsh Marigold, Trollius (Trollius L.).
It grows wild in the cold and temperate zones of the Northern Hemisphere. Depending on the species, it blooms from April to August.
It grows lushly and develops well in soils enriched with compost and peat with regular watering. It blooms longer and retains green leaves in shaded areas during midday hours. The following species are of the greatest interest: Asian marsh marigold (T. asiaticus L.). Plant height 70—80 cm. The leaves are basal, long-petioled, palmately five-lobed, stem leaves are sessile and glossy. The flowers are bright, reddish-orange, up to 5 cm in diameter, almost spherical. In a three-year-old bush, up to 30 buds form with 5—7 flowers blooming simultaneously. It blooms in April—May for 30—35 days;
Altai marsh marigold (T. altaicus C. A. M.). Widely distributed in Altai and Central Asia. This species is similar to the Asian marsh marigold but is brighter. It blooms from mid-April to late May. Soon after cutting the flowers, new shoots and secondary flowering are noted;
Chinese marsh marigold (T. chinensis Bge.). Bush height 80—100 cm. It differs from the previous species in that the nectar petals are almost half longer than the sepals, giving the flower an unusually attractive shape. It blooms in May;
European marsh marigold (T. europaeus L.). It grows wild in the European part of the USSR. A highly decorative plant. Its flowers resemble rose buds in shape and size. They are quite large, spherical, and lemon-yellow in color. The bushes are robust, forming 5—7 stems with 3—5 flowers up to 5 cm in diameter.
There are many hybrids of the European marsh marigold with the Altai and Asian marsh marigolds, differing in growth strength, shape, size, color, and flower double-ness.
Some varieties bloom in summer (July-August).
Marsh marigolds are propagated by dividing bushes and seeds. Bushes are divided in the 4th-5th year of life. The planting conditions are the same as for daylilies, but the best place is considered to be partial shade, where the plant retains beautiful foliage until late autumn. Seeds are sown in the fall. Uniform sprouts appear in spring, with the onset of consistently positive air temperatures.
Marsh marigolds are beautiful in flower beds, group, solitary plantings, and for cutting.
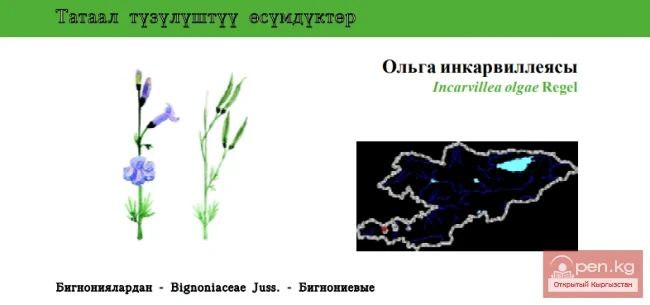
Incarvillea and irises. Perennial plants with rhizomes, wintering in the soil of Kyrgyzstan