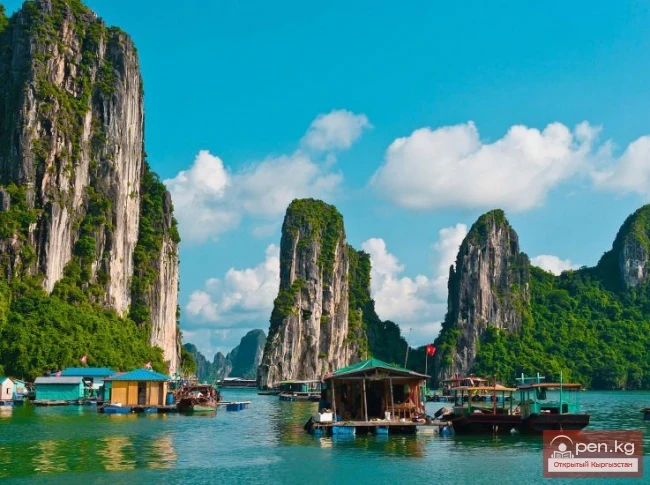
Vietnam. Socialist Republic of Vietnam
A state in Southeast Asia on the Indochina Peninsula. Area - 330 thousand km². Vietnam claims sovereignty over the Paracel and Spratly Islands in the South China Sea. The capital is Hanoi (with suburbs - about 3.1 million), major cities: Ho Chi Minh City (formerly Saigon until 1976, over 5.5 million), Hai Phong (1.8 million). Administrative-territorial division - 59 provinces and 5 centrally governed cities: Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City, Hai Phong, Da Nang, and Can Tho. Population - about 82 million (2004). The predominant nationality is Kinh (Vietnamese), making up 87.5% of the population. The country is also home to representatives of 54 ethnic groups and several ethnic minorities (Thai, Tay, Chinese, Khmer, Muong, etc.). The official language is Vietnamese. The main religions are Buddhism (10 million believers) and Catholicism (5.3 million). In the south of the country, the Caodai sect (2.3 million) and Hoa Hao sect (1.2 million) have significant influence. The currency is the dong.
It has diplomatic relations with the Russian Federation (established with the USSR on January 31, 1950).
National holiday - September 2 - Independence Day (1945).
The Socialist Republic of Vietnam is a parliamentary republic. According to the constitution adopted in 1992, the highest body of state power is the unicameral National Assembly (500 deputies, elected by universal, equal, and direct voting for a term of 5 years; elected in April 2002). The head of state is the president, elected for a term of 5 years by the National Assembly from among the deputies and accountable to it for their activities. The President of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam is Tran Duc Luong, re-elected in July 2002.
The executive power is exercised by the government (the Prime Minister is Phan Van Khai).
The current constitution establishes the leading role of the Communist Party of Vietnam (founded in 1930) in society. The General Secretary of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam is Nong Duc Manh, elected in April 2001. In 1977, the Vietnam Fatherland Front was established, uniting political and social organizations of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam.
The trade union association is the Vietnam General Confederation of Labor.
The oldest Vietnamese state was Van Lang. Its successors, Au Lac and Nam Viet, were conquered by China in the 2nd century BC. In the 10th century AD, during the liberation struggle, an independent Vietnamese state was proclaimed. From 1858 to 1884, Vietnam was conquered by France.
From 1941 to 1945, it was under Japanese occupation. As a result of the victory of the national democratic August Revolution, Vietnam was proclaimed an independent state in 1945 - the Democratic Republic of Vietnam. For more than 8 years (1945-1954), it defended its sovereignty in the anti-colonial war against France. On the territory controlled by France, the so-called State of Vietnam (South Vietnam) was created. In July 1954, the Geneva Accords were signed, confirming the independence, sovereignty, and territorial integrity of the country, and providing for its peaceful reunification. However, the implementation of the agreements was thwarted by the South Vietnamese administration with the support of the United States.
The Americans introduced their troops and allied forces into South Vietnam, and from 1964 to 1968 and in 1971-1972, subjected North Vietnam (the Democratic Republic of Vietnam) to massive air and naval bombardments. On January 27, 1973, an agreement was signed in Paris to end the war and restore peace in Vietnam. The troops of the United States and their allies were withdrawn from the country. On April 30, 1975, as a result of the operation of the People's Army and the uprising of the population, the South Vietnamese regime fell. On April 25, 1976, general elections were held for the National Assembly of a unified Vietnam, which on July 2, 1976, proclaimed the reunification of the country and the establishment of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam.
The continental shelf of Vietnam has large oil reserves. Coal, tungsten, zinc, lead, apatite, iron, and manganese ores, titanium, and tin deposits are mainly concentrated in the north and northwest. There are bauxite reserves. The country is rich in hydro resources.
The main industry is agriculture, where 70% of the self-employed population is engaged. The production of food crops is steadily increasing: in 2004, about 36 million tons of rice were harvested. In 2004, Vietnam ranked 2nd in rice exports (3.7 million tons).
The basis of industrial production consists of the oil industry (20 million tons of oil produced in 2004), coal industry (26.3 million tons), and electric power (46 billion kWh). The electrical engineering, chemical, textile, food industries, machine engineering, construction materials production, and tourism are also developing. The largest hydropower plant in Southeast Asia, "Hoa Binh," was built with Russian technical assistance.
The main export items are oil, coal, rice, sewing and knitwear, footwear, seafood, electronics and computing equipment, natural rubber, coffee, and tea.
74 countries and territories are implementing more than 4,000 investment projects worth about 40 billion dollars.
The main investors are Singapore, Taiwan, Japan, and South Korea.
During the implementation of the "Renovation" policy, Vietnam has achieved significant success in stabilizing the economy, which is developing at a high pace. GDP growth in 2004 was 7.7%. Vietnam is one of the world leaders in the supply of raw products (1st in the world in black pepper exports, 2nd in coffee exports). At the same time, serious imbalances remain in the national economy, and there is a sharp shortage of domestic savings. Against the backdrop of rising living standards for some categories of workers, property stratification of the population has intensified.
GDP per capita is about 470 dollars. The working-age population is about 37 million. The average life expectancy in Vietnam is 68 years (annual population growth is 1.7%). The literacy rate is about 94%.
Dynamic economic growth and the associated improvement in the well-being of the population have become the main stabilizing factors in public life. In turn, internal stability has created favorable conditions for the consistent and controlled implementation of market reforms. The country's leadership is taking measures to smooth out the contradictions arising during the transition to a market economy. A decision has been made to provide a number of tax and other benefits to low-income groups in cities and villages. A phased increase in salaries in the public sector is being implemented.
The campaign against corruption, smuggling, prostitution, and drug addiction continues.
In foreign policy, the Socialist Republic of Vietnam pursues a multi-vector course with an emphasis on regionalism. Its distinguishing features are pragmatism and de-ideologization, independence and autonomy, maintaining friendly relations with all countries, ensuring national interests and state security, and integration into the system of global economic relations. The Socialist Republic of Vietnam maintains diplomatic relations with 167 countries. Traditionally, an important direction of the foreign policy of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam remains participation in the activities of the UN (member of the UN since 1977) and its specialized agencies. Vietnam is an active member of regional and international organizations and forums: ASEAN, ARF, ASEM, APEC, and the Non-Aligned Movement. Cooperation with EU countries and the USA is dynamically developing. In March 2001, a Declaration on Strategic Partnership was signed between the Russian Federation and the Socialist Republic of Vietnam.
The country publishes over 100 newspapers and magazines (excluding provincial ones). The largest daily newspaper is "Nhan Dan" (190 thousand copies) - the central organ of the Communist Party of Vietnam.
The Vietnam News Agency (VNA) is located in Hanoi. There are radio and television services.