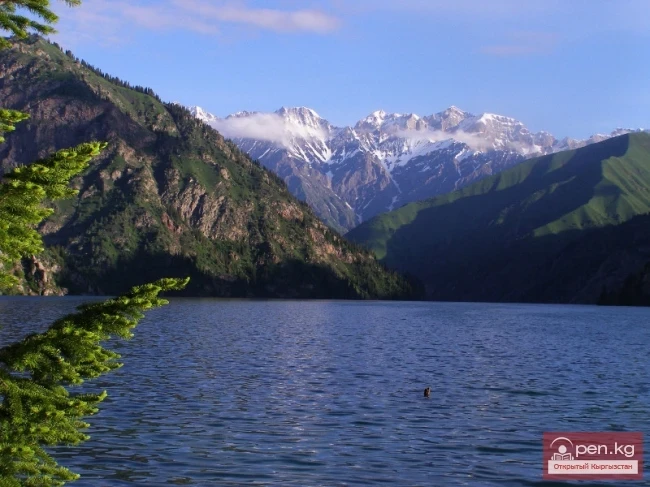
Geoecological Condition and Requirements for the Protection and Rational Use of Water Resources
Water resources are surface and groundwater that are suitable for use in a given territory. The boundaries of the territory can be administrative (district, region, republic) or geographical (river basin, continent). The determination of the volume of water resources is based on the calculation of the water balance of the territory.
The main component of water resources consists of surface waters - waters that are found on the Earth's surface in solid and liquid states (waters of rivers, lakes, reservoirs, swamps; glaciers, snow cover).
Water is the most abundant substance on Earth and, at the same time, the most important for sustaining organic life on it. Water is necessary for all areas of human activity without exception.
Water is the medium of life for many organisms, a necessary component of the habitat of living organisms on land. Modern social production is based on the extensive use of water, which is used in the process of energy production.
Water truly permeates all aspects of human life. A lack of water is a severe disaster for people. Water on Earth is in continuous motion - a cycle. There is almost no mineral or living organism that does not contain water.
Academician A.E. Fersman rightly called water the most important mineral on Earth, without which there is no life on Earth. This issue becomes particularly relevant due to the sharp increase in anthropogenic impact on the environment, especially on water resources. Water consumption doubles every 10-12 years. At the same time, water pollution increases, i.e., there is a qualitative deterioration of water. Therefore, in our time, water has become one of the most scarce natural resources in many countries of the world.
The Kyrgyz Republic has significant water resource reserves: 50 billion m³ per year of surface river runoff, 13 billion m³ per year of potential groundwater reserves, 1745 billion m³ per year of lake water, and 650 billion m³ of glaciers (National Report on the State of the Environment 1997, p. 25). The total water resources of the Chui Valley, according to specialists, amount to 3034 million m³.
Read also:

Attractions of Naryn Region
Historical-Architectural and Modern Attractions, as well as Natural-Ecological Complexes Cities...

Attractions of Batken Region
Mountains: Ak-Suu - Karavshin (Asian Patagonia)...
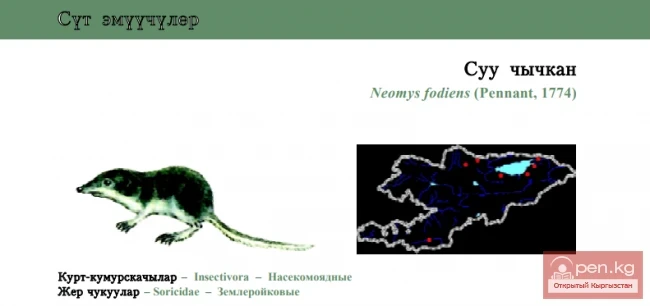
Common Water Shrew / Eurasian Water Shrew
Common Water Shrew Status: Category VI, Near Threatened, NT: R. A rare species for Kyrgyzstan,...
The Bishkek City Hall and K-water Company Signed a Memorandum on Reducing Carbon Emissions
Negotiations were held in the municipality with a delegation from a South Korean corporation...

Attractions of Osh Region
Attractions of the city of Osh...
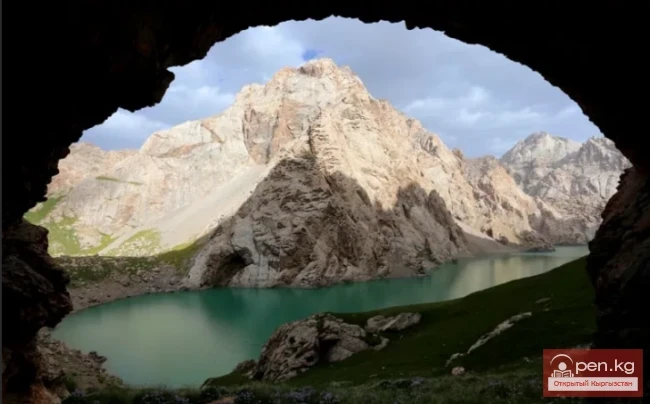

Lake Kel-Suu
Lake Köl-Suu in Kyrgyzstan: a fairy tale of mountains, a song of ice Lake Köl-Suu...
The Beautiful Country Known as Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan is a small country bordering Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, and Russia. The main attractions...

Chuya Sharp-wing / Uchtoo Kanat / Eastern Ostroluchka
Chuy Ostroluchka Status: 2 [CR: C]. Possibly already extinct in Kyrgyzstan, an endemic...
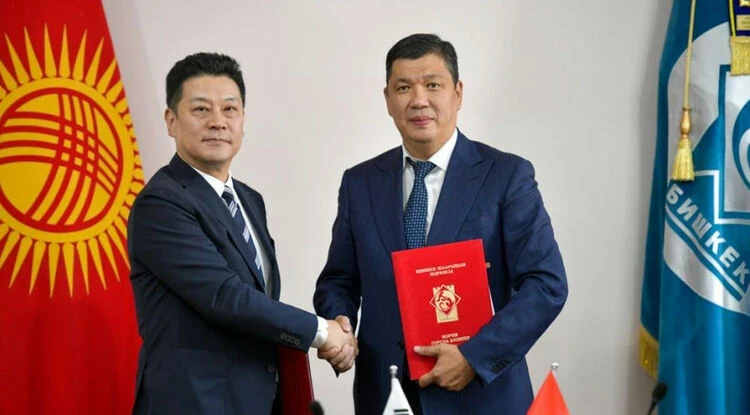

A Korean company will help Bishkek reduce carbon emissions
Photo of the City Hall The meeting of Bishkek Mayor Aibek Junushaliev with the K-water delegation...
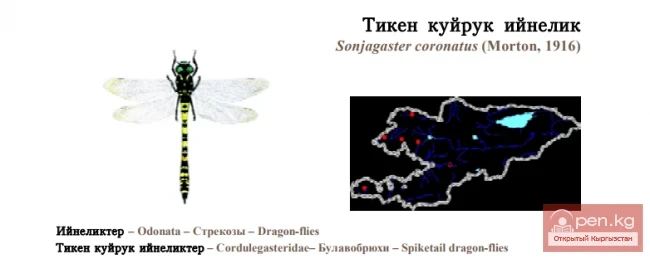
Crowned Bulbous-Body / Tiken Tail Needle / Coronate Spiketail
Coronate Spiketail Status: Category II (VUA4bc; B2b(iii,iv); D2). A locally occurring species with...

Waterfall "Find Me"
Sarala-Saz (Yellowish Swamp). Naryn Region. Located 55 km northwest of the town of Kochkor is the...

Kochergin Vladimir Pavlovich
Kochergin Vladimir Pavlovich (1927), Doctor of Physical and Mathematical Sciences (1975),...

Pike Asp / Kashka / Pike Asp
Pike Asp Status: 2 [CR: A]. Listed in the Red Book of the Kyrgyz SSR in 1984. A rare...

Turkestan Catfish / Turkestan Zhayany, Zhayany Fish, Lakka
Turkestan Catfish Status: 2 [VU: E]. The only representative of the genus in Kyrgyzstan....

Usuni in Prissykul
Usuns This text will discuss the people of the Usuns. Few Central Asian-Kazakh ethnonyms have such...

Crane Beauty / Karkyra / Demoiselle - Crane
Demoiselle Crane Status: Category VI, Near Threatened, NT: R. One of two species of the genus in...

Lake Kara-Suu
Lake Kara-Suu is located in the Toktogul district. It is a dam-type lake, and its level depends on...

Vitaly Antonovich Stavinsky
Stavinsky Vitaly Antonovich (1936), Doctor of Geological and Mineralogical Sciences (1997),...
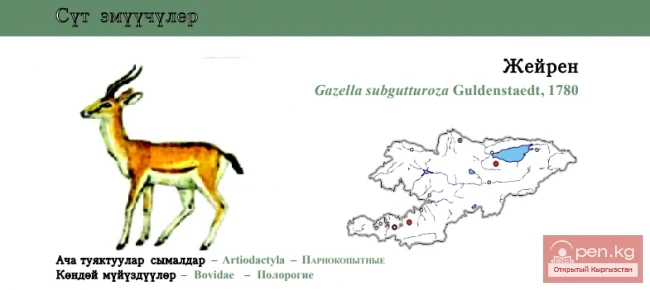
Jayran / Zheiren / Goitered gazelle
Dzhayran Status: Category III, Critically Endangered, CR: R, Cl. An endangered or possibly extinct...

Aral Catfish / Tenge Fish / Aral Barbel
Aral Barbel Status: 2 [CR: C]. Species extinct in Kyrgyzstan....

Sako-Usun Period (5th century BC)
Late Medieval Period (14th—15th centuries). Saka-Usun Period (5th century BC). This period is...
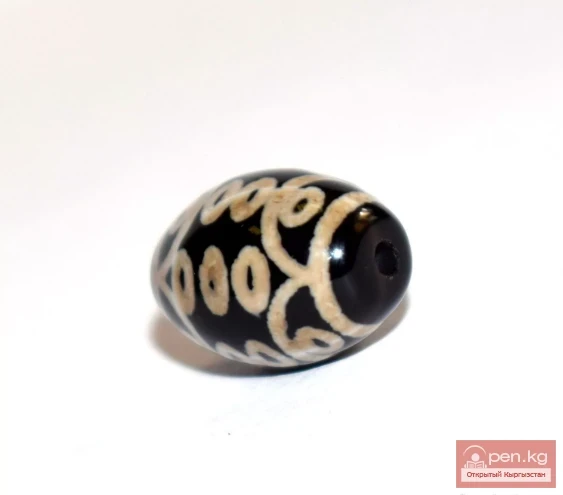

Sarybulun Bead
Little Guest Such finds are not anticipated. They come from a fairy-tale land and are always...
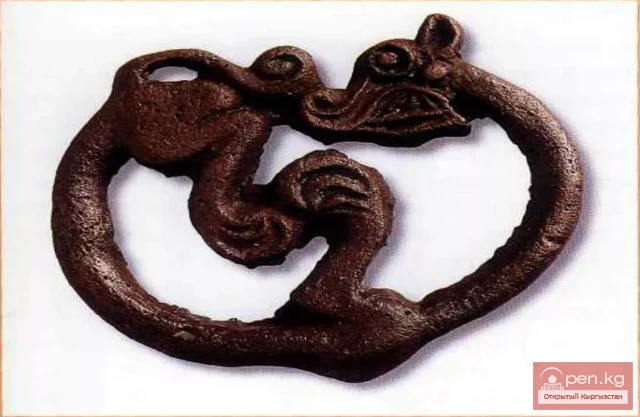

Early Saka Finds from the Issyk-Kul Region of the VIII—VI Centuries B.C.
Early Saka Period (VIII—VI centuries BC). It is represented by metal artifacts: an amulet with a...

Natural Resources of Kyrgyzstan
Mineral Resources of the Republic of Kyrgyzstan The subsoil of Kyrgyzstan is truly a gigantic...

Rivers of Kyrgyzstan
The formation of runoff and the hydrographic network in the territory of Kyrgyzstan is greatly...
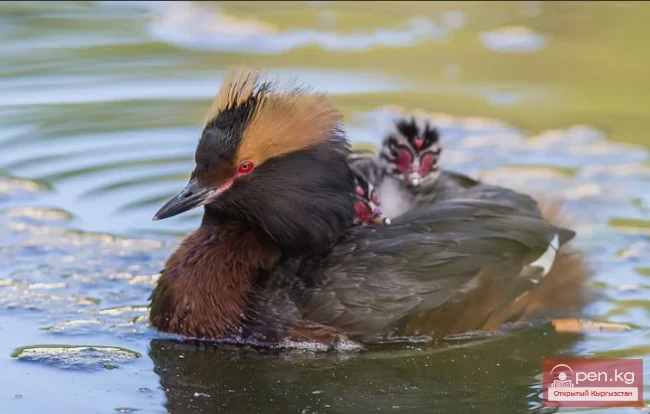

The title translates to "The Coot - The Aaram Duck."
Grebes — Family Podicipedidae (little grebe, black-necked grebe, red-necked grebe, gray-cheeked...

Unknown Saka Settlement on the Shores of Issyk-Kul?
Hypothesis—1985 At the bottom of the Tyup Bay of Issyk-Kul during the field season of 1985, we...

White-bellied Sandgrouse / Actor Black-headed / Pin-tailed Sandgrouse
Pin-tailed Sandgrouse Status: VI category, Near Threatened, NT: R. A species with low numbers,...
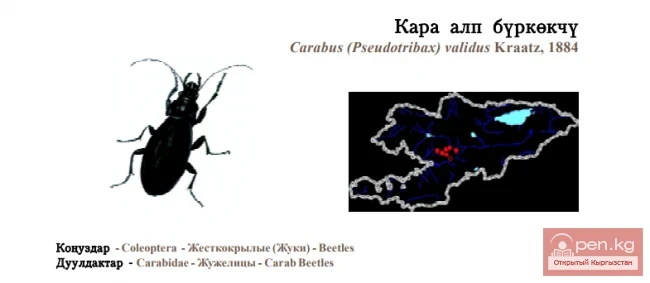
Vigorous Ground Beetle / Кара алп буркёкчу / Брызгун могучий
Vigorous Ground Beetle Status: Category II (VUBlb(iii)+2b(iii,iv); C2b). A narrowly distributed...
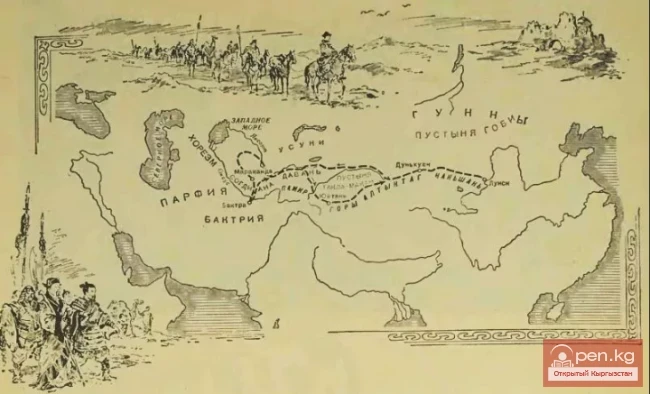
Zhang Qian - "The Asian Columbus"
The Little-Known "Columbus of Asia" The name Zhang Qian is almost unknown to the general...

Toktosopiev Alymbai Moldokmatovich
Toktosopiev Alymbai Moldokmatovich (1953), Doctor of Physical and Mathematical Sciences (1999),...
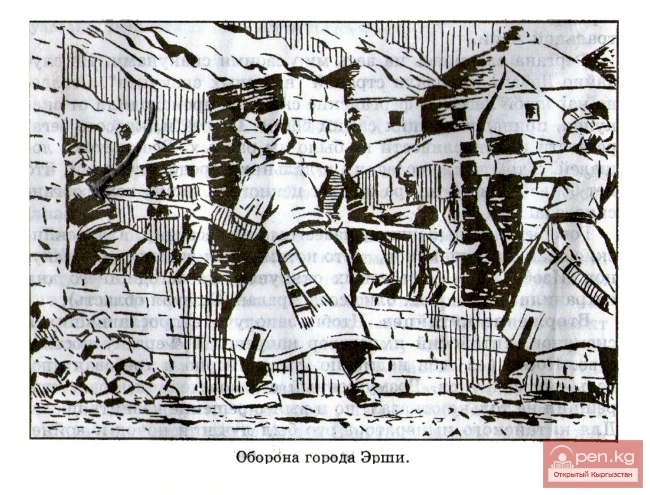

The State of Dawan
Davan. In the Fergana Valley, a powerful state emerged in the 1st millennium BC. In Chinese...
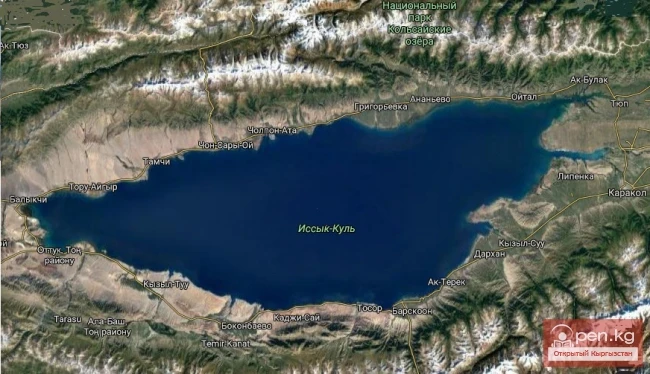
Transgressions and Regressions at Issyk-Kul
What fate awaits modern culture? We have talked about the tragic fate of just one sunken city in...
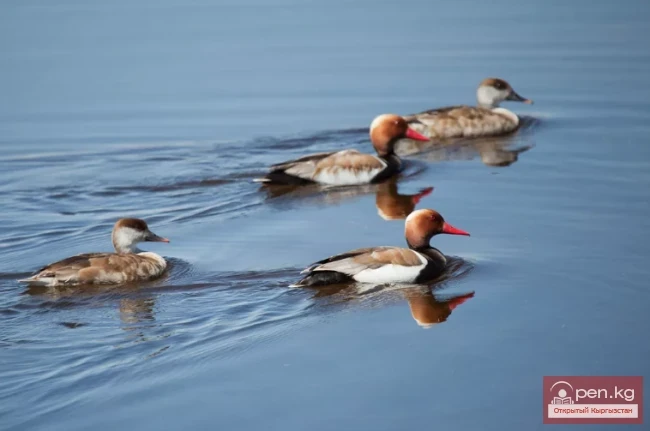

Red-nosed Dive - Kyzyl-ordok
Red-nosed Diving Duck. A rather peculiar duck, biologically considered a transitional form between...
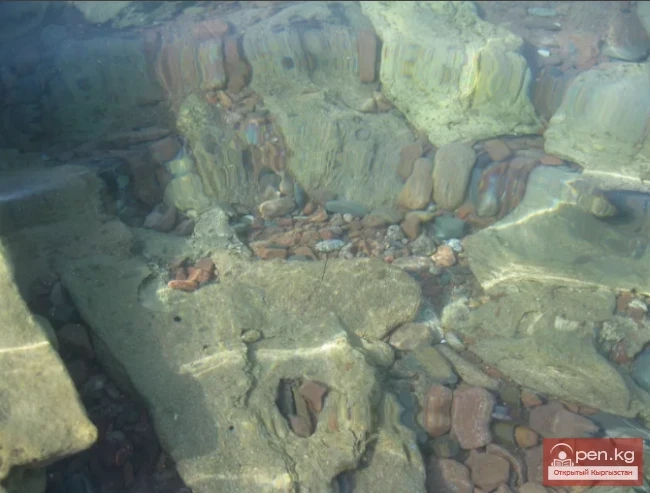

Is Sarabulun not the ruins of Chigu?
On which shore of Issyk-Kul was the ancient Chigu located? Sarybulun is the only known large...
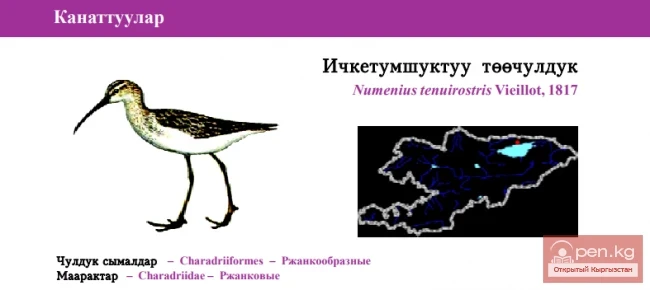
Slender-billed Curlew
Slender-billed Curlew Status: III category, Critically Endangered, CR, C2a(ii); D. One of 3...
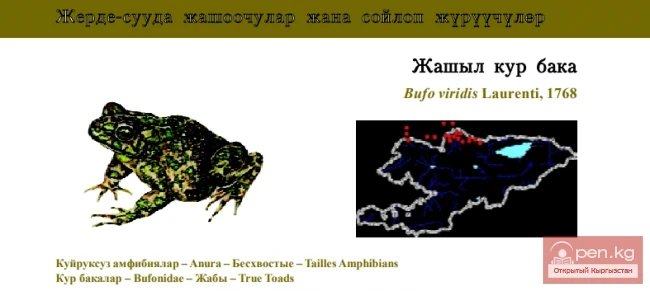
Central Asian Frog / Kyzyl Koltuk Frog / Middle Asia Wood, or Asiatic Brown, Frog
Central Asian Frog Status: Category VUB1ab(iv). A mosaic-distributed species with a disjunct and...
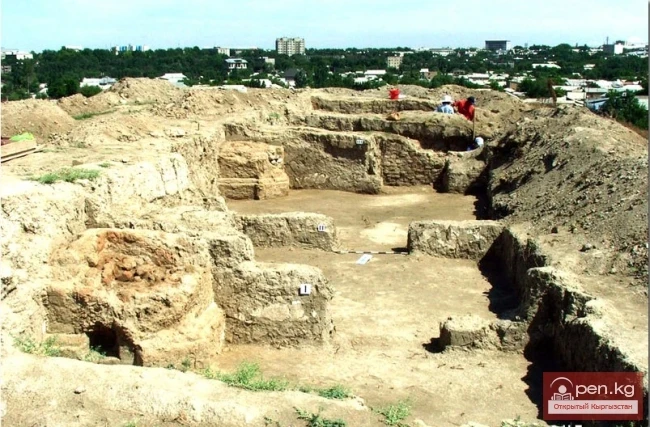

Archaeological Finds in the Territory of Kyrgyzstan
Archaeological Finds of Kyrgyzstan In the summer of 1960, parts of the skeleton of a large mammal,...

Periods of Habitation of the Sarabulun Settlement
When was life flourishing? Even a brief overview of the material culture with a short excursion...

Arguments in Favor of Identifying the Settlement of Sarybulun with Chigu
“The City of the Red Valley” In connection with the discovery of a large settlement from the 1st...

Black-headed Gull / Great Black-headed Gull
Great Black-headed Gull Status: VI, Near Threatened, NT: R. One of 6 species of the genus in the...
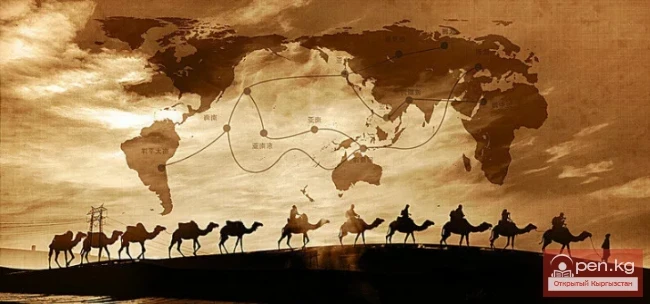
Hymn to the Great Silk Road
1600 Years of the Great Road In the decades following the death of Zhang Qian, his plan of...

Water Resources of Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan: A Country of Heavenly Lakes Kyrgyzstan can confidently be called a country of heavenly...

From the History of Geographic Research in Kyrgyzstan
Researchers of Central Asia Throughout the centuries of studying the Tian Shan, it has been...

Findings Indicating the Construction of a Palace-Type Structure at the Issyk-Kul Settlement of Sarybulun
Sarybulun Palace at the Issyk-Kul Settlement The "Jianhanpu" contains significant...
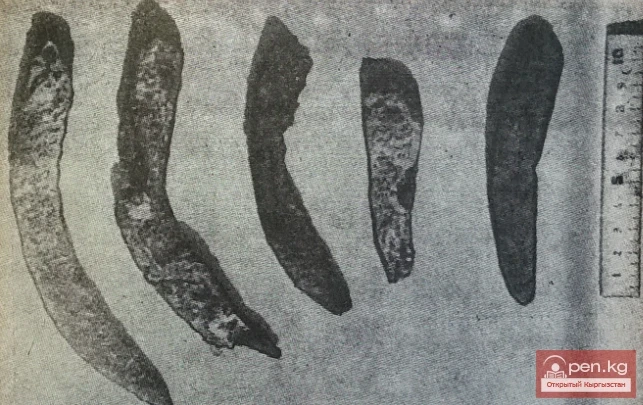
Stone Tools of Sarabulun
Stone Tools of Sarybulun Even in the best books about the culture of ancient pastoralists, which...
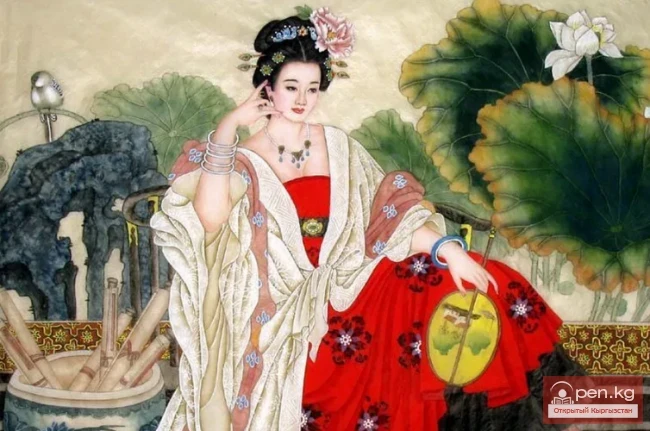

The Bride of Kunbaga. Part - 1. The Lotus Flower
The Choice of the Bride Whose chest was adorned with such a precious and exotic bead? Was it not...
