CAMBODIA. Kingdom of Cambodia
A state in Southeast Asia in the southwestern part of the Indochinese Peninsula. Area - 181,035 km². Capital - Phnom Penh (approx. 1.5 million, 2005). Administrative-territorial division - 21 provinces and 3 cities of central subordination (Phnom Penh, Sihanoukville, and Kep). Population - 13 million (1997); about 90% are Khmer, with over 40 national minorities, including significant communities of Chinese and Vietnamese. The official language is Khmer. The state religion is Buddhism, with about 4% of the indigenous population (Chams) practicing Islam. Currency - riel.
It has diplomatic relations with the Russian Federation (established with the USSR in 1956).
National holiday - November 9 - Independence Day (1953).
Cambodia is a constitutional monarchy. The political system of Cambodia is defined by the 1993 constitution as "multi-party liberal democracy." The king is the head of state and is elected by the Council of the Crown (heads of parliament, government, and senior clergy). In October 2004, Norodom Sihamoni was elected as the new king.
The highest legislative authority is a bicameral parliament. The term of office for parliament is 5 years. The upper house of parliament is the Senate (chairman - Chea Sim), which performs the duties of the head of state in the absence of the king. The lower house is the National Assembly (123 deputies, chairman - Prince Norodom Ranariddh). In July 2003, parliamentary elections were held in the country. The Cambodian People's Party (CPP) received 73 mandates in the National Assembly, the royalist FUNCINPEC party received 26, and the opposition Sam Rainsy Party (SRP) received 24. The highest executive authority is the Royal Government. Its composition is approved by the National Assembly. A new cabinet was formed in July 2004 after resolving inter-party disagreements regarding the structure of the government. The Prime Minister is Hun Sen.
The most influential parties are: the Cambodian People's Party (CPP, founded in 1951, chairman - Chea Sim, deputy chairman - Hun Sen), the National United Front for an Independent, Neutral, Peaceful, and Cooperative Cambodia (FUNCINPEC, active since 1992, leader - Prince Norodom Ranariddh), and the Sam Rainsy Party (SRP, formed in 1995, operated illegally until 1998, chairman - Sam Rainsy).
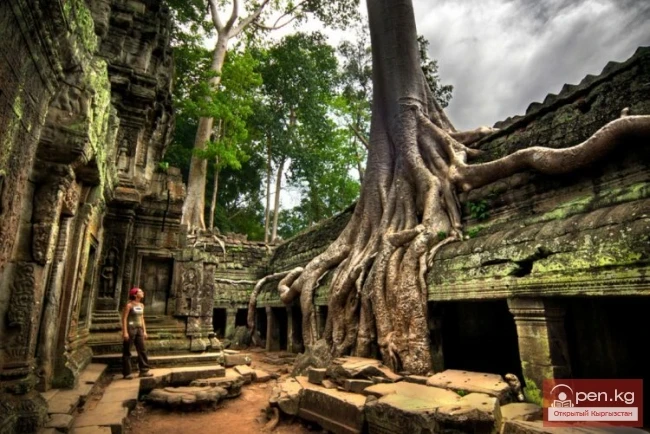
The first known state on the territory of Cambodia was Funan, founded in the early Common Era and existed until the 6th century. Cambodian statehood reached its peak during the Angkor Empire (9th-13th centuries).
In 1863, the country came under French protectorate, and from 1884 it effectively became a colony. From 1940 to 1945, Cambodia was occupied by Japan.
As a result of the national liberation struggle, Paris was forced to announce in 1953 the granting of independence to Cambodia, and in 1954 at the Geneva Conference on Indochina, it officially recognized its sovereignty. The monarchical regime of Norodom Sihanouk came to power. In March 1970, he was overthrown by General Lon Nol, who relied on U.S. support. The Khmer Republic was established.
In April 1975, power in the country was seized by the leftist extremist group "Khmer Rouge" led by Pol Pot, who declared the establishment of Democratic Kampuchea (the Khmer name for the country). A regime of genocide was established, resulting in the deaths of an estimated 1 to 3 million people in less than 4 years.
In January 1979, the armed forces of the United Front for the National Salvation of Kampuchea, with the support of Vietnamese troops, overthrew the Pol Pot regime. The People's Republic of Kampuchea was proclaimed. At the same time, a coalition government of Democratic Kampuchea was formed in Thailand under the slogan of opposing Vietnamese presence, which included FUNCINPEC - the party of supporters of King N. Sihanouk, the Buddhist Liberal Democratic Party, which represented the interests of republicans, as well as the "Khmer Rouge."
After the complete withdrawal of Vietnamese troops and as a result of the development of the national reconciliation process, it became possible to hold the International Paris Conference on Cambodia (July - August 1989). During its second phase (October 1991), the Paris Agreements on a comprehensive political settlement of the Cambodian conflict were signed, according to which a UN peacekeeping operation was conducted in Cambodia. After general elections in May 1993, organized under the auspices of the UN, a new parliament and government were formed, a constitution was adopted, and the Kingdom of Cambodia was established under King N. Sihanouk (September 1993).
In July 1997, armed clashes occurred in Phnom Penh between supporters of the CPP and FUNCINPEC, resulting in a political crisis. As a result, Cambodia lost its seat at the 52nd session of the UN General Assembly, and its admission to ASEAN was postponed.
The general elections held in July 1998, recognized by the international community as free and fair, opened opportunities for overcoming the negative consequences of the July 1997 crisis and normalizing the situation in the country. Preparations for the elections, along with other factors, contributed to the disintegration of the "Khmer Rouge" movement, which ceased to exist as a political and military force.
According to the UN classification, Cambodia is among the least developed countries in the world (GDP in 2004 - 4.5 billion dollars). Per capita income - 312 dollars. In 2004, the economic growth rate was 5%, and the inflation rate was 2%. Currency reserves are estimated at 780 million dollars.
Natural resources have been poorly studied. There are deposits of bauxite, iron, manganese, gold, phosphates, precious stones, and several other minerals, as well as significant reserves of valuable timber. Oil reserves have been discovered on the continental shelf in the Gulf of Thailand.
The main sector of the economy is agriculture, where 80% of the self-employed population is engaged and which produces 34% of GDP. The main food crop is rice.
The garment industry, which accounts for 80% of industrial production, is developing rapidly. Products are exported to the USA and EU countries.
There is also food, tobacco, woodworking production, and a rubber industry. Handicraft production is widespread. The country's energy needs are met only by one-third.
Cambodia's foreign trade turnover in 2004 amounted to 3.8 billion dollars (imports - 1.8 billion dollars, exports - 2 billion dollars). The main export items are ready-made clothing, rubber, timber, soybeans, rice, corn, and tobacco. Imported goods include petroleum products, equipment, vehicles, cement, and consumer goods. The main foreign trade partners are Singapore, Thailand, Malaysia, and China.
Among European partners, France and Germany are the leading ones. Relations with Australia are developing dynamically. The main investors are the USA, Malaysia, Taiwan, China, Singapore, South Korea, and Thailand. The main donors are Japan, France, Australia, as well as the Asian Development Bank, IMF, World Bank, UNDP, and the European Union. At the 7th meeting of the Consultative Group of Donors to Cambodia in 2004, a decision was made to allocate 504 million dollars to it in 2005.
Cambodia's external debt to Western countries for loans granted before 1975 amounts to 280 million dollars, while to Russia it exceeds 1.5 billion dollars. The Paris Club has decided to grant Cambodia a preferential debt repayment regime, including the cancellation of 67% of the total debt amount.
According to the constitution, Cambodia is an independent, sovereign, peaceful state that pursues a policy of neutrality and non-alignment; it is part of the group of founding states of the Non-Aligned Movement.
Cambodia has been a member of the UN since 1955, supports initiatives to strengthen peace and international security, establish arms control, has joined the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, and signed the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty.
Cambodia is focusing on developing ties with Southeast Asian countries (ASEAN), has joined the Bali Treaty on Friendship and Cooperation in the region, became a member of ASEAN in 1999, a participant in the ASEAN Regional Forum on Security (ARF), signed a treaty to create a nuclear-weapon-free zone in Southeast Asia, and is preparing for full-scale accession to the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) being formed.
Since 1952, it has been part of the Colombo Plan.
The country faces a complex health situation. Cambodia has the highest rate of AIDS incidence in Southeast Asia (over 120,000 HIV-infected individuals). There is a serious problem with the transit of narcotic drugs through the territory of the country.
Daily newspapers "Rasmey Kampuchea," "Koh Santepheap" are published in Khmer, as well as publications in English and French. Due to financial difficulties, the official news agency AKP mainly processes information from foreign agencies. There are radio and television stations owned by the government and individual political parties.