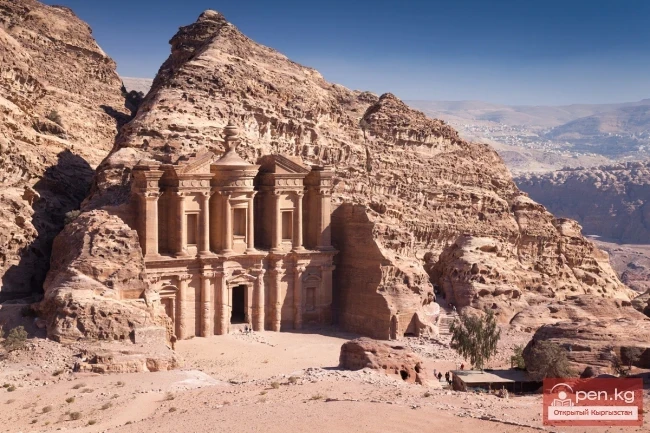
JORDAN. Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan
A state in the Middle East in the western part of Asia. Area - 96,188 thousand km². Capital - Amman (approximately 1.6 million). Administrative division - 12 governorates (muhafaz). Population - 5.7 million (2005); predominantly Arabs, as well as Circassians (approximately 30 thousand), Chechens (4 thousand), Armenians (2 thousand), and others. More than 50% of the population are Palestinian Arabs, including 1.5 million officially registered Palestinian refugees. The official language is Arabic. The state religion is Sunni Islam. More than 90% of the population are Muslims, 8% are Christians. The currency is the Jordanian dinar = 1000 fils.
It has diplomatic relations with the Russian Federation (established with the USSR in August 1963).
National holiday - May 25 - Independence Day (1946).
Jordan is a constitutional monarchy. The head of state is the king (since February 1999, Abdullah II bin Al-Hussein), who has broad powers in the legislative and executive branches. The highest legislative body is the National Assembly (parliament), consisting of a Senate and a House of Representatives. The Senate is appointed by the king for a term of 4 years (its composition, which includes 55 members, is renewed every 2 years).
The chairman of the Senate (since June 1997) is Z. Rifai.
The House of Representatives is elected for 4 years through universal direct and secret elections (110 deputies were elected in June 2003). In December 2003, A. Majali was elected speaker of the house. The executive body is the government headed by the prime minister (since November 2005 - Maaruf Bakhit).
From 1957 to 1992, the activities of political parties and organizations in Jordan were banned. Despite this, the Jordanian Democratic Party of National Unity, the Jordanian Communist Party, the Jordanian Arab National Democratic Organization (which includes the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party), the Islamic Action Front, and some other organizations operated semi-legally in the country. Since 1988, a program of gradual democratization of society has been implemented in the kingdom.
In 1992-93, emergency laws were repealed, and the activities of political parties were legalized. The largest opposition party, the Islamic Action Front, is represented in the lower house of parliament as an independent faction (17 deputies).
The trade union movement, represented by the General Federation of Trade Unions of Jordan, plays a significant role in the social life of the country.
Since late 2003, Abdullah II has initiated the implementation of a large-scale national dialogue project on issues of democratic development in the country, including topics such as expanding civil rights and freedoms, increasing the role of women in socio-political life, liberalizing the media, combating corruption, etc.
The territory of Jordan, since the 7th century, was part of the Arab Caliphate, from the early 16th century until 1918 it was part of the Ottoman Empire, and after its collapse, by the decision of the San Remo conference (1920), it was included in the British Mandate territory of Palestine. In 1921, this territory was designated as a special mandatory unit - the Emirate of Transjordan, headed by Emir Abdullah.
In 1946, it became an independent state and received its modern name, Jordan. Emir Abdullah was proclaimed king. The treaties of 1946 and 1948, however, retained significant rights for England (in particular, to keep its troops here) and the ability to influence the country's policy. At the same time, American penetration increased.
In March 1957, the Anglo-Jordanian treaty of 1948 was annulled, and on November 2, 1958, British troops were withdrawn from the territory of the kingdom.
Jordan is a member of the UN (since 1955), the League of Arab States (since 1945), the Organization of Islamic Cooperation, the Non-Aligned Movement, the WTO, a participant in the Kyoto Protocol, the Pan-Arab Free Trade Agreement, and other international and regional organizations and agreements.
Jordan advocates for a comprehensive settlement of the Middle Eastern conflict and recognized the State of Palestine, proclaimed in November 1988 by the 19th session of the Palestinian National Council in Algiers. On October 26, 1994, the kingdom signed a peace treaty with Israel. The parties established diplomatic relations at the embassy level; connections in trade, economic, cultural, and other spheres are developing. The main vector of Jordanian efforts in Palestinian-Israeli affairs is aimed at ending violence from both sides, stabilizing the situation, and the prompt implementation of the "road map" for the peace process.
The USA and the UK are viewed in Jordan as the main external guarantors of safe and sustainable development. In 2000, Jordan became the 4th country in the world to sign a free trade agreement with the USA.
In recent years, Jordan has participated in NATO dialogue with several southern Mediterranean countries. Its cooperation with Turkey in the fields of security, military relations, etc., is being established. In 1997, an association agreement was concluded between Jordan and the EU (ratified in 1999).
Since 1999, an economic recovery program has been implemented in the kingdom under the auspices of the IMF. As part of this program, restructuring and privatization of the public sector, which previously accounted for up to 80% of the national economy, and a fundamental modernization of economic legislation are being carried out.
In 2004, Jordan's GDP grew by almost 1 billion dollars and amounted to 10.995 billion dollars (2003 - 9.96 billion dollars). Due to the government program to encourage investment projects for the development of specialized industrial zones, in accordance with the free trade agreement with the USA and Israel, there was an increase in foreign trade turnover (42.9%). Exports increased by 31.5% compared to 2003, amounting to 3.541 billion dollars, while imports increased by 37.2% (6.891 billion dollars). The negative trade balance (in 2004 - about 3.4 billion dollars) increased even more. Inflation remained at a stable level (2.4%). Unemployment remained one of the main social problems, with independent estimates suggesting it was up to 25-30% of the working-age population. The average income per capita in 2004 was 1,750.6 dollars.
The budget deficit in 2004 amounted to 413.9 million dollars, or 3.9% of the country's GDP.
The main creditors of Jordan remain the USA, Japan, Germany, the UK, the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, and the International Monetary Fund. In the form of foreign grants, Jordan received 833 million dollars in 2004. Jordan's external debt amounted to 7.598 billion dollars in 2004, internal debt - 2.711 billion dollars, and gold and foreign currency reserves - 5.283 billion dollars. In 2004, 592.8 million dollars were spent on servicing the external debt. The most attractive sectors of the economy for investors are trade (40%) and the service sector (34.8%).
Jordan has significant deposits of phosphates, ranking 4th in the world in reserves (over 1.5 billion tons). There are also deposits of potash and mineral salts from the Dead Sea, copper, and manganese.
The share of industry in GDP is about 26%. The main industries are mining, cement, and oil refining. Agriculture (about 2.4% of GDP) only partially meets the population's needs for basic food products. Animal husbandry is mainly extensive.
The service sector has developed the most, accounting for 71.5% of GDP. Despite the difficult situation in the region, the tourism sector is developing rapidly, with revenues in 2004 exceeding 600 million dollars.
Jordan imports almost all industrial and many types of food products; it exports phosphates, cement, and some agricultural products.
The main trading partners of the kingdom are the USA, China, Saudi Arabia, Germany, Iraq, India, and Israel.
There are about 600 km of railways and 9,000 km of roads. The cargo turnover of the only seaport in the country, Aqaba, is about 20 million tons.
The largest daily newspapers are "Al-Rai" (120 thousand copies), "Ad-Dustour" (90 thousand), "Jordan Times" (in English), and weekly publications "Ash-Shihan", "Al-Majd". The official Jordanian news agency Petra operates (a bilateral agreement was signed with RIA Novosti in 2002), as well as national radio and television broadcasting services. There are developed telecommunications systems, including the Internet.