Geoecological Requirements for the Protection of Water Bodies
The intensive development of industry, transportation, and overpopulation in several areas of the Chui Valley has led to significant pollution of the hydrosphere. Pollution of surface waters is the process of changing the physical, chemical, or biological properties of natural waters upon the introduction of various substances that can have harmful effects on humans and nature. Any compound that disrupts norms and deteriorates water quality is considered a water pollutant.
Water quality is a characteristic of the composition and properties of water that determines its suitability for specific types of consumption. The main indicators of water quality include composition, total content, color, odor, taste, hardness, alkalinity, and the presence of iron, manganese, and some other elements.
The primary cause of the current degradation of natural waters is anthropogenic pollution. The main sources are:
• industrial wastewater;
• communal wastewater from cities and other settlements;
• runoff from irrigation systems, surface runoff from fields and other agricultural objects;
• atmospheric deposition of pollutants onto the surfaces of water bodies and watersheds.
Depending on the conditions of formation, wastewater is divided into three groups:
• domestic wastewater - runoff from showers, laundries, baths, canteens, toilets, floor washing, etc. Their average volume is 0.5-2 l/sec. From 1 hectare of residential development, they contain approximately 58% organic and 42% mineral substances;
• atmospheric wastewater, or stormwater. Their runoff is uniform: once a year - 100-150 l/sec per hectare; once every 10 years - 200-300 l/sec per hectare. Stormwater runoff from industrial enterprises is particularly dangerous. Due to their irregularity, the discharge and treatment of these effluents are complicated;
• industrial wastewater - liquid waste generated during the extraction and processing of raw materials. Water consumption in this case is calculated based on specific water consumption per unit of production.
The most dangerous pollutants include heavy metal salts, phenols, pesticides and other organic toxins, petroleum products, synthetic surfactants (SAS), and other detergents, as well as mineral fertilizers.
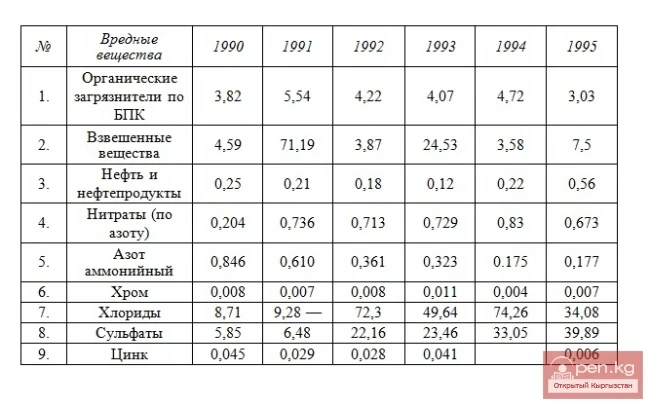
In the waters of the rivers in the Chui basin and major tributaries, there is an increased concentration of pollutants: petroleum products, phenols, pesticides, and heavy metals. In the water of the Chu River, in the upper reaches (village of Orto-Tokoy), the concentration of pollutants is at background levels, with phenols and petroleum products absent. In the waters of the Chu River, after the inflow of wastewater from Bishkek (village of Vasilyevka), the concentration of phenols increases 8 times compared to the upper reaches (village of Orto-Tokoy), and petroleum products increase 7 times, etc. It has been established that 1 m³ of untreated wastewater, on average, pollutes 10-15 m³ of clean water.
It should be noted that at the beginning of the century, science was aware of only 17 pollutants in natural waters, whereas now there are more than 2,500 worldwide. This has a detrimental effect on public health and leads to the death of fish, waterfowl, and other animals.
The dynamics of discharges into surface water bodies of the most characteristic harmful substances in thousand tons per year are presented in the table (for the Chui Valley according to the national report on the state of the environment for 1997)
A serious situation with nitrate pollution of groundwater has developed in the area of the Orto-Alysh water intake, which provides 60% of the capital with drinking water. Elevated concentrations of nitrates have been observed at a depth of 150 m. This pollution is associated with the placement of livestock facilities in the sanitary protection zones of the water intake, the development of irrigated agriculture, poor sanitary conditions in settlements, and the lack of water supply and sewage systems.
In the southwestern part of the city of Kara-Balta, groundwater pollution with nitrates and manganese is noted due to leaks from previously contaminated industrial effluents from the tailings storage of the Kara-Balta mining and metallurgical plant.
Geoecological requirements for the protection of water bodies
The most effective form of protection for water bodies from pollution is waste-free technology. The term waste-free technology was first proposed by Russian scientists N.N. Semyonov and I.V. Petryanov-Sokolov in 1982. According to the resolution of the UN Economic Commission and the Declaration on low-waste and waste-free technologies and waste utilization, the following formulation of waste-free technology (WFT) is accepted: "Waste-free technology is the practical application of knowledge, methods, and means to ensure the most rational use of natural resources and energy within the framework of human needs and to protect the environment."
Thus, waste-free technology should be understood as a set of measures in technological processes that allows minimizing harmful discharges and reducing the impact of waste on water resources to acceptable levels.
It is important to remember (L.A. Muravya, 2000) that assessing the degree of waste-free production is a very complex task, and there are no unified criteria for all industries.
The main principles for creating waste-free production (A.A. Muravya, 2000, p. 118) include the comprehensive use of raw materials, the creation of fundamentally new and improvement of existing technologies, the establishment of closed water and gas circulation cycles, cooperation between enterprises, and the creation of production-territorial complexes.
Passive methods of protecting water bodies include a set of measures to limit discharges of domestic wastewater, industrial, and agricultural runoff into water bodies.
Natural waters - rivers are capable of self-purification and establishing biological balance. This occurs as a result of the combined action of physical, chemical, and biological factors. Physical factors include the intense flow of rivers, which ensures good mixing and reduction of suspended particle concentrations, the settling of insoluble sediments, the impact of ultraviolet radiation from the sun, etc. Among the chemical factors, the oxidation of organic and inorganic substances should be highlighted. Aquatic biocenoses play a decisive role in the self-purification of water bodies. Aquatic organisms collectively ensure multi-stage mineralization of organic matter through trophic links and its transfer to bottom sediments.
However, the ability of water bodies to self-purify is not limitless. At a certain level of pollution, especially during emergency, pulse discharges of untreated wastewater, all biota in the water body can be destroyed. Technogenic pollution of rivers and lakes has reached such scales that in many areas it exceeds their self-purification capacities. Due to ineffective wastewater treatment, a significant portion of nutrients - nitrogen, phosphorus - enters water bodies. A large amount of soil, organic matter, and mineral fertilizers is washed into water bodies from agricultural areas during floods and after heavy rains. Excessive enrichment of water bodies with biogenic substances leads to their eutrophication, i.e., a sharp increase in biological productivity and mass reproduction of phytoplankton, primarily of unpretentious blue-green algae.
In addressing the issue of protecting surface and groundwater in the Chui Valley, a priority direction should be, first of all, the exclusion of the discharge of collector-drainage waters and domestic wastewater into water bodies and rivers. It is especially important to regulate water use in the most water-intensive sectors of the economy.
Hydrotechnical engineers and irrigation specialists in farms need to develop and control irrigation regimes, avoid excessive moisture, and secondary soil salinization. They must strictly monitor the norms of water consumption by users, as they pay money for water use.
Read also:

Geoecological Condition and Requirements for the Protection and Rational Use of Water Resources
Water resources are surface and groundwater that are suitable for use in a given territory. The...

Use of Water in Human Economic Activities
By the nature of water use, all modern sectors of the economy in the Chui Valley are usually...
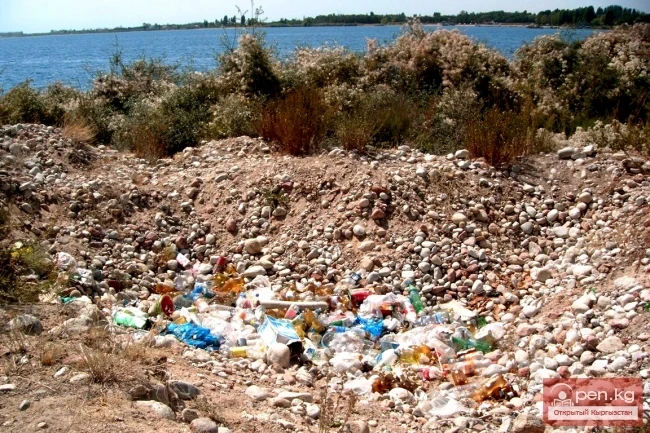

Land Pollution
Pollution, in a broad sense, is understood as the introduction of new (usually non-characteristic...

Nanostructures for Better Water Purification
A research associate at the University of Navarra (UPNA) recently announced the development of...

Mineral Waters
Groundwater is one of the main water resources of the Kyrgyz Republic (KR). They are characterized...

Airtash Warm Waters
Airtash Warm Waters were brought to the surface by wells drilled by the Makmal Geological...

What are mineral waters, and what types are available in Kyrgyzstan?
The components and indicators that provide grounds for assessing water as mineral can include the...

Who is turning the Naryn River into a sewage ditch?
It is unlikely that any of us has seriously thought about where the water goes when it is poured...

The first "Water Museum" - Aquatarium in Central Asia has opened in Bishkek.
In the city of Bishkek, based on the Kyrgyz National Agrarian University named after K. I....
The State of the Environment in the Kyrgyz Republic in 2008-2012.
As of January 1, 2013, the territory of the Kyrgyz Republic, according to the State Registration...

Aksuyskoe Deposit of Carbonated Mineral Waters
The Aksu mineral water deposit is the most intensively exploited deposit of therapeutic table...

Iodobromine waters
Among thermomineral waters, waters of this type occupy a special place; as a rule, being...

Sulfide Waters
While the identification of most mineral waters requires various water analyses, and radon waters...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 17:00 is 94 AQI (smog map)
According to IQAir, as of October 21, 2025, in Bishkek at 17:00, the air quality index is 94 AQI....

Alamedin Deposit
The Alamedin Deposit is located 28 km south of Bishkek city in the middle reaches of the Alamedin...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 16:00 is 96 AQI (smog map)
According to IQAir data, as of October 22, 2025, at 16:00, the air quality index in Bishkek is 96...

Measures for the Protection and Regulation of Air Pollution
To regulate emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere, individual norms are used for...

Carbonated Water in the Chayek Well
Carbonated water in the Chaek well. For now, this is the only well of its kind in the republic...

Pollution of the Atmosphere and Its Consequences
Geoecological Condition and Requirements for Air Protection....

Mineral Waters Without "Specific" Components
Waters without 'specific' components are distinguished only from a balneological point...

Geoecological condition of the land
Currently, in the Chui Valley, with the formation of numerous small farms, peasant and other...

Field Filter. Part - 2
Hiking Filter. Part - 2 Viruses are extremely rare in natural water sources, but they are smaller...

Beshbelchir-Arashan Deposit
Beshbelchir-Arashan Deposit has the warmest water among all manifestations of carbonated mineral...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 11:00 is 90 AQI (smog map)
As of October 23, 2025, at 11:00, the air quality index in Bishkek is 90 AQI. This value is...

Fishing on the Kekemeren River
Approximately a 2-hour journey from the Susamyr River is the Kekemeren River. The Kekemeren River...

Methods of Additional Water Disinfection. Part - 6
Water Disinfection Sometimes a water source can raise significant concerns — what if there is a...

Thermal Waters of Ugut
Thermal waters of Ugut are located on the left bank of the Naryn River, 110 km west of the city of...

Drinking Water and Glaciers
Water resources are vital for the economy, humans, and the environment; they are the most...

The Hunter Ashir and the Living Water
Water - The Basis of Life The peoples of Central Asia and Kazakhstan, who roamed the endless...

Attention! There will be no water in part of Bishkek on October 23
On October 23, 2025, the supply of drinking water will be temporarily suspended in some areas of...

In Bishkek, there will be no water in the residential areas "Ala-Too 1" and "Ala-Too 2" on October 21.
On the specified day, residents of the mentioned areas should take into account the temporary...

Tortkul Reservoir
Tortkul Reservoir is a unique structure. It is located in the Batken region on the Isfara River....
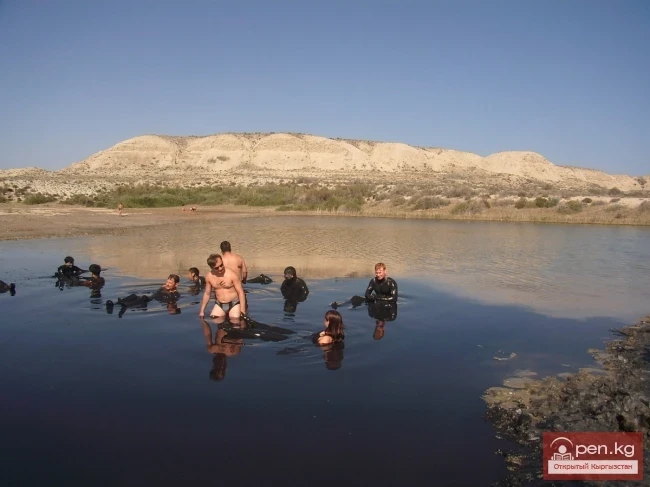

Mineral Waters, Healing Mud, and Resorts of Kyrgyzstan
Therapeutic Resources of Kyrgyzstan Currently, more than 120 natural mineral water springs have...

Carbon Dioxide Springs of Uselek
Uselik Carbonated Springs are the highest located outlets of carbonated mineral waters in...

Geoecological Requirements for Land Protection and Rational Use
It has been noted above that a significant part of the territory of the republic is subject to...

Groundwater
As a result of non-tectonic movements, intermountain depressions and mountain uplifts were formed....

Tan-mosho (spinning tops in Kyrgyz)
Tan-mosho Ingredients: 0.5-1 liter of liquid (milk, water, or a mixture of both), 1/2 cup of...
In the Kyrgyz Republic, the yield of certain crops in 2025 decreased due to a lack of irrigation water, - Ministry of Economy
- In the first nine months of 2025, the gross agricultural output of the country reached 348.4...

Therapeutic Use of Mineral Waters
No matter how interesting the composition and properties of water manifestations may be, it is...

The title translates to: "Kacharaltur and Konurtyube Site"
Kacharaltur Area is located on the same left bank of the Yassy River as Kara-Shoro, but 200 meters...

Carbonated Water of Kara-Kiche
The carbonated water of Kara-Kiche is the most sulfate-rich among the carbonated mineral waters of...

The title "Источник Аркаршур" translates to "Source of Arkarshur" in English.
Source Arkarsur is the most frequently visited outlet of carbonated waters by wild animals. Not to...

Karimov Tashmukhamed Khalmukhamedovich
Karimov Tashmukhamed Khalmukhamedovich Candidate of Technical Sciences. Born in 1958. Graduated...

Radon Waters of Kyrgyzstan
Of all the gases found on Earth, radon is the rarest and most expensive, although it is difficult...
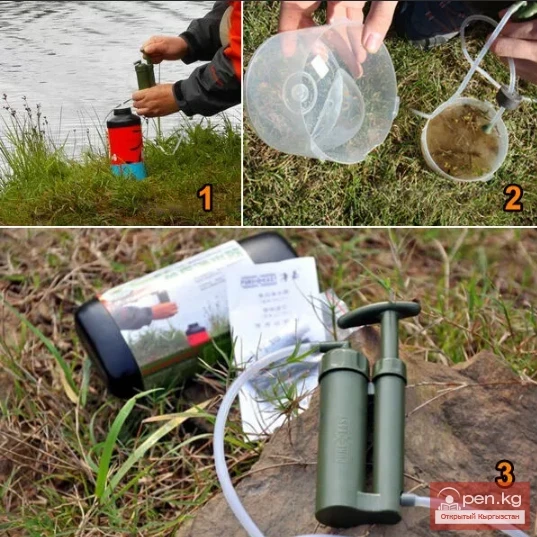

Field Filter. Part - 1
How to Choose a Hiking Filter. When hiking, you often have to drink water from unclear rivers and...
On October 24, there will be no hot water on Gogol Street in Bishkek.
From 9:00 AM to 4:00 PM on October 24, hot water supply will be temporarily suspended on Gogol...

Natural Resources of the Chui Region
All elements and conditions, as well as phenomena and bodies of nature, can be used in public...

Agriculture, Land Resources of Kyrgyzstan
Land Resources of Kyrgyzstan The climatic features dictate the development of agricultural sectors...