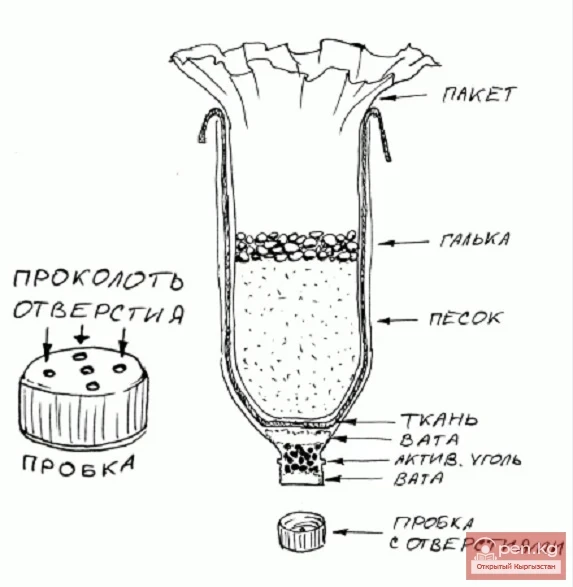
Water Disinfection
Sometimes a water source can raise significant concerns — what if there is a high risk of viral infections? Usually, this applies to non-flowing water bodies in densely populated areas and places where a lot of livestock graze, meaning the water may be contaminated with sewage or animal feces. In these cases, already filtered water should be additionally disinfected, for which there are at least three reliable methods. Each of them can be used independently, provided that the water is already sufficiently clean. However, it is better to use them in tandem with a portable microfilter. This way, you will obtain the cleanest and safest drinking water.
UV Water Treatment
Ultraviolet radiation with a medium wavelength can penetrate the cell walls of microorganisms and be absorbed by the nucleic acids of DNA and RNA, which carry all the information about the cell. As a result of this process, microorganisms lose their ability to reproduce and become harmless to humans. UV radiation is actively used in municipal water treatment facilities, as it is effective against all pathogens — viruses, bacteria, and protozoa. However, today there are also compact portable ultraviolet disinfectors. The most well-known are the portable SteriPen lamps, which are submerged in a container of purified water.
Ultraviolet is effective against viruses and microorganisms, but for it to work effectively, the water must be as clear as possible.
Unfortunately, this method can only be applied when treating clean, clear water without any mechanical impurities. Otherwise, these impurities scatter UV rays, reducing their effectiveness. Additionally, compact UV lamps used in hiking practices are not capable of disinfecting large volumes of water.
Chemical Water Treatment
Chemical compounds create an aggressive environment for harmful microorganisms, thereby destroying them. Such agents are most often available in the form of drops or tablets. The most advanced products are based on chlorine dioxide (Aquamira) or sodium hypochlorite (MSR SweetWater Solution), which not only disinfect water but also normalize its taste. Moreover, these agents are inexpensive and very lightweight, making them very popular among backpackers.
Popular in the USA, Aquamira drops for chemical water disinfection are also effective only in clean water: mechanical impurities can bind the active chemical and precipitate along with it. Additionally, chemical disinfectants can spoil the taste of water, and disinfecting water can take a long time — up to four hours. This process can also slow down in cold water. Some agents are unable to destroy cryptosporidium — parasites that cause intestinal disorders known as cryptosporidiosis, so be sure to read the instructions carefully. Another drawback is that it is impossible to purify a "convenient" volume of water, as it is important to adhere to the dosages specified in the instructions for the product.
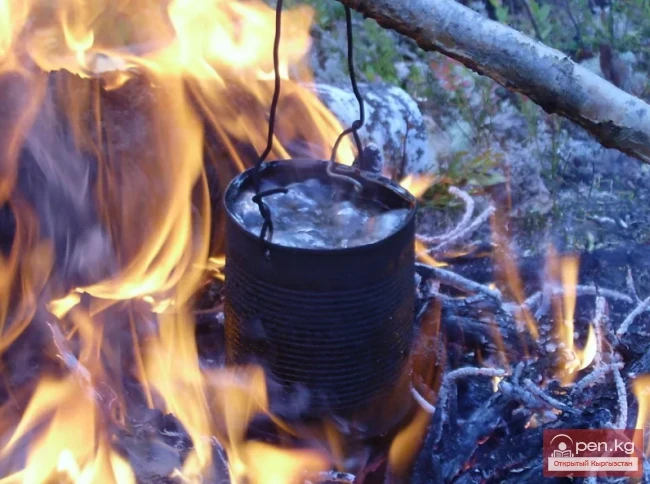
Boiling Water
The oldest method of water disinfection. Effective against all pathogenic microorganisms and parasites.
Boiling does not protect against chemical contamination of water and mechanical impurities. Additionally, it is the most labor-intensive method, which also leads to additional fuel consumption and time loss on the route.
Boiling requires a large amount of fuel but is a reliable method to disinfect water.
To avoid spending the entire hike in the bushes, follow two basic rules: drink only clean water and wash your hands thoroughly. For the first, comprehensive purification with the help of a filter and disinfectants will assist you, and for the second — your own discipline and established personal hygiene habits.
Maintenance of a Portable Filter. Part - 5