Belgium. Kingdom of Belgium
A state located in the west of Europe, on the coast of the North Sea. Area - 32,545 thousand km². Capital - Brussels (951 thousand), other largest cities: Antwerp (469 thousand), Ghent (230 thousand), Charleroi (over 200 thousand), Liège (200 thousand). Administrative structure: 3 economically autonomous regions (Brussels-Capital, Wallonia, Flanders) and 3 linguistic communities (French, Flemish, and German-speaking), corresponding in status to federal subjects. The territory is divided into 10 provinces (5 each in Flanders and Wallonia) and 589 municipalities. Population - 10.36 million (2003), mainly Flemish and Walloons, as well as about 860 thousand permanently residing foreigners (Italians, Moroccans, French, Turks, Dutch, Spaniards, etc., totaling about 8% of the population). Official languages - French, Dutch (Flemish), and German.
There are 4 constitutionally established linguistic regions of distribution: the Dutch-speaking region - in the north of the country, in Flanders (5 provinces, 5.97 million, or 59% of residents); French - in the southern part, Wallonia (5 provinces, 3.35 million, or 31.2% of residents), between them runs the so-called "linguistic" border (legislatively defined in 1963); the bilingual Brussels region (19 municipalities of the Brussels agglomeration, 960 thousand, about 80% Francophones and 20% Flemish); in eastern Wallonia, there is also a region of German-speaking distribution (9 municipalities), where 71.3 thousand people live. The main religions are: Catholicism (75% of the population), Islam (500 thousand), Protestantism (about 150 thousand, including the Anglican Church - about 50 thousand), Judaism (34 thousand), and since 1988 - Orthodoxy (40 thousand). Currency - euro (since January 1, 2002).
Belgium has diplomatic relations with the Russian Federation (established with Russia in full in 1853, with the Soviet Union on July 12, 1935, interrupted in July 1940, restored on August 7, 1941).
National holidays - July 21 - Day of King Leopold I's oath to the Belgian Parliament to uphold the constitution (1831) and November 15 - Day of the Royal Dynasty (1866).
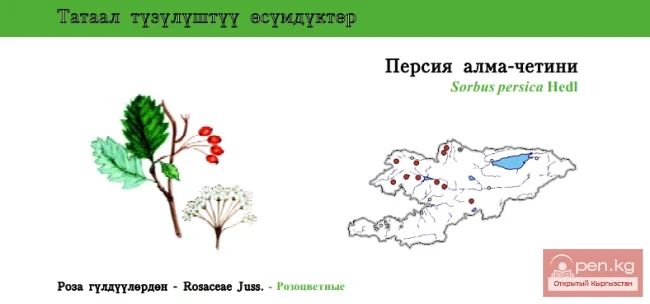
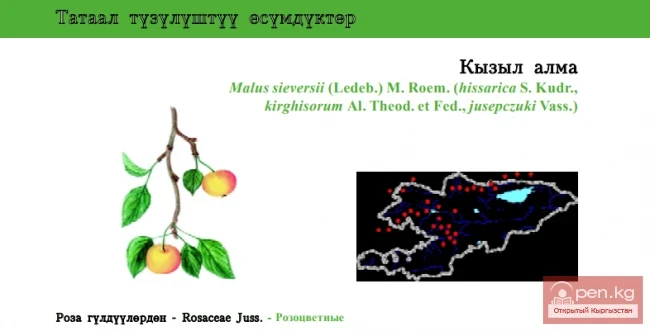
The name Belgium comes from the name of the tribes of the Belgae, who lived in the territory of the country in ancient times. In the 3rd-4th centuries AD, Germanic tribes of Franks invaded. Up to the present time, this remains the root cause of the linguistic division of the country. In the Middle Ages, Belgian territories were part of the Netherlands, within which they came under Spanish rule in the 16th century. During the War of the Spanish Succession, they became possessions of the Austrian Habsburgs (1714). From 1815 to 1830, they were part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The Brabant Revolution of 1830 led to the creation of an independent Belgian state. During World War I and World War II, Belgium was subjected to German occupation.
After World War II, the national-linguistic problem forced unitary Belgium to embark on the path of federalization. The constitutional reform, which began in 1970, led to the transformation of Belgium into a federal state (formally since January 1, 1989). The peculiarity of the current federal structure of the country, which was finally established by the beginning of 1995, consists in the parallel functioning of 2 types of federal subjects - communities and regions, which have equal rights with the federal state.
The federal state is responsible for all matters related to the Belgian nation, such as: defense, international affairs, social security, finance and most taxation, justice, law enforcement, public safety, postal and telecommunications, public transport, energy, most public health issues, and other matters not within the competence of communities and regions.
Communities have autonomy in the fields of culture (art, cultural heritage, media, sports, and tourism), education, as well as in matters related to health care, social support for citizens, scientific research, development cooperation, and international cooperation in these areas. Regions exercise territorial-economic autonomy and have broad powers in the fields of economy, energy, agriculture, employment, public works, transport, land use, environment, water resource policy, rural development, and nature conservation, housing, fishing, foreign trade, as well as scientific research and international relations in these areas.
Legislative bodies of regions and communities are parliaments, executive bodies are governments. The legislative and executive bodies of the Flemish community and region are merged into a single Flemish Regional Parliament and Government.
The process of regionalization in Belgium continues, with its main vector being the expansion of the autonomy of federal subjects at the expense of narrowing the powers of the central federal authority. In 2001, as a result of the next (5th) stage of federal reform, comprehensive measures were defined to change the funding scheme for communities and expand the tax independence of regions, regionalization of provincial and municipal legislation, and full transfer of agricultural policy and foreign trade (except for the representation of the country in international economic structures) to the regions.
In terms of governance, Belgium is a parliamentary monarchy. The head of state is the king, who has limited power. Since August 9, 1993, the King of the Belgians has been Albert II (from the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha). According to the constitution, which was adopted on February 7, 1831, and subsequently revised several times (last time in 1994), legislative power is exercised by the king and parliament.
The federal parliament is bicameral, elected for a 4-year term (the last elections were held in 2003). It consists of the House of Representatives and the Senate. A feature is the official division of deputies by linguistic principle into 2 groups - Dutch-speaking and French-speaking, which is taken into account when adopting special (so-called community) laws. The House of Representatives: 150 deputies, elected in one round by direct universal secret and mandatory voting based on proportional representation from the lists of political parties or their associations operating in the country. Senate: 71 senators; 40 senators (25 Dutch-speaking and 15 French-speaking) are elected based on direct nationwide elections; 21 senators (10 Dutch-speaking, 10 French-speaking, and 1 German-speaking) are delegated to the Senate by the parliaments of the respective communities. Both linguistic groups jointly co-opt an additional 10 senators into the Senate (6 Dutch-speaking and 4 French-speaking). The children of the king are members of the Senate by right. The parliaments of federal subjects are unicameral, elected for 5 years simultaneously with the elections to the European Parliament (the last took place on June 13, 2004) and, unlike the federal parliament, cannot be dissolved.
Executive power is exercised by the king and the government, which is accountable to the lower house of the federal parliament. The federal government coalition, formed in June 2003 and called the "purple" coalition, includes representatives of liberals and socialists. The government is headed by G. Verhofstadt (Flemish Liberals and Democrats).
Since the 60s-70s of the 20th century, political parties have operated on a national-linguistic basis. The parties represented in the federal parliament are subsidized by the government. The liberal movement consists of the Flemish Liberals and Democrats (VLD) and the Francophone Reform Movement (MR). Social democrats are organized into the Francophone Socialist Party (PS) and the Flemish Social, Progressive, and Alternative Party (SPA). The Christian democratic movement is represented by the Christian Democrats and Flanders (CD&V) and the Francophone Center for Democratic Humanism (cdH). Partners of the federal "purple" ruling coalition are the moderately nationalist New Flemish Alliance (N-VA) and the Social, Progressive, International, Regional, Integral-Democratic, Future-Oriented - left-liberal Flemish Party (SP.A). The "Greens" are united in the Flemish party "Groen!" (until November 2003 - "Agalev") and the Francophone "Ecolo". The "Flemish Interest" (until autumn 2004 - "Flemish Block") - a nationalist party of the far right - holds quite strong positions in Flanders.
After the regional elections on June 13, 2004, which resulted in the formation of parliaments and governments of regions and communities for the next 5-year period, political asymmetry emerged in Belgium - a mismatch of the party composition of the ruling majority between the federal authority (where the "purple" coalition of liberals and socialists remains) and the federal subjects (a three-party coalition of Flemish Christian Democrats, liberals, and socialists in Flanders; a coalition of Francophone socialists and Christian democrats in the Francophone part of Belgium). This complicates state governance and interregional interaction, putting the Belgian state structure system to the test.
Trade unions are a significant force in society. In Belgian trade unions, 80% of all workers and employees in the country are members. The largest of them: the Confederation of Christian Trade Unions - exists since 1912, uniting 18 different sectoral trade unions, influenced by the Christian democratic political "family," with more than 1.6 million members; the General Labour Federation of Belgium - created in 1945, has about 1.2 million members, includes 12 sectoral trade unions, oriented towards social parties; the General Center of Liberal Trade Unions - has 220 thousand members, oriented towards liberal parties (VLD, MR).
Belgium is a member of the UN (since 1945), the Council of Europe (since 1949), the OECD (since 1960), the EU (since 1957), Euratom (since 1957), the ECSC (since 1954), and NATO (since 1949).
In terms of living standards, Belgium ranks among the leading countries in the world. The economic development of the country is characterized by moderately low GDP growth rates, which in 2004 amounted to 2.7% compared to 2003, with a total GDP of 282.97 billion euros (in 2004). Per capita income reached 27,250 euros in 2004, with an inflation rate of 2.1%. The unemployment rate is 7.7% of the economically active population, with an employment rate of 62%. Unlike neighboring countries, Belgium has seen a decrease in the volume of government debt (96.9% of GDP) over the past 10 years; from 1999 to 2004, the government managed to maintain a balanced or even surplus budget. According to OECD data, Belgium ranks 12th in purchasing power index among member countries of this organization. In 2004, the average labor productivity in Belgium was 37.5 euros per hour (4th place after Norway, Luxembourg, and France).
In terms of external trade turnover and exports per capita, Belgium is a world leader. In 2004, there was a rapid growth in its external trade turnover. According to the Belgian Foreign Trade Agency, Belgian exports grew by 9.1% (in 2003 - by 1.2%) and amounted to 246.4 billion euros; imports increased by 10.6% (in 2003 - by 1.5%) and reached 229.5 billion euros. The positive balance of the external trade balance amounted to 16.9 billion euros. Belgium exports 80% of the products produced in the country. The main partners of Belgium are EU countries, which account for 75% of external trade turnover. The leading importers of Belgian goods are Germany (34.4 billion euros), France (34.2 billion euros), and the Netherlands (25 billion euros), outside the EU - the USA, Switzerland, Israel, India, and Sweden. The main exporters to Belgium are the Netherlands (38 billion euros), Germany (31 billion euros), and France (26 billion euros). The leading positions in Belgium's exports are held by chemical products (31 billion euros), vehicles (29 billion euros), as well as machinery and equipment (26 billion euros). In imports, machinery and equipment (31 billion euros), chemical products (27 billion euros), and vehicles (25 billion euros) prevail. The country's share in world trade in goods is 3.4% (10th place), and in services - 3.6% (11th place). The volume of trade between Russia and Belgium in 2004 amounted to 3 billion dollars.
In terms of living standards, Belgium ranks 4th in the world, and 11th in terms of attracted foreign investments (however, their inflow, according to UNCTAD, decreased from 29 billion dollars in 2003 to 7 billion dollars in 2004).
Belgium's industry is the foundation of its economy and is characterized by a high technical level of production. The share of industry in GDP is about 25% (in 1970 - 42%). In terms of industrial production, Belgium ranks 12th in the Western world. In industrial policy, priority is given to the introduction of new technologies, active promotion of exports, support for small and medium enterprises, which form the basis of Belgium's industrial potential, and attracting foreign investments. The most developed sectors of industry are machine engineering (especially automotive assembly), chemical, metalworking, electrical engineering, electronics, building materials production, textiles, food, woodworking (furniture, paper), and jewelry (diamond cutting). Industrial production growth in 2004 was 3.5%.
About 1.9% of Belgium's GDP comes from intensive, highly productive agriculture. Its foundation consists of medium-sized farms, which cover 4/5 of Belgium's needs for food and agricultural raw materials. The leading sector is animal husbandry, which accounts for over 60% of total agricultural production. For most types of products, production exceeds domestic needs by 1.5-2 times. The horticultural sector (fruits, vegetables, flowers, live plants, etc.) has been actively developing in recent years, accounting for about 1/4 of agricultural production. Cereals, potatoes, sugar beets, flax, hops, and tobacco account for about 12%. The main share of imported agricultural products belongs to grains and fruits. Since 1993, agricultural management has been transferred to the regions within the framework of federalization in Belgium.
Belgium ranks 1st in the world in terms of railway density (total length - about 35,180 km) and road network. The transport fleet includes 1.7 thousand locomotives, 1.8 thousand passenger cars, and 27.3 thousand freight cars. Freight transport by rail amounts to over 61 million tons per year. The length of roads (provincial, regional, and highways) is about 16 thousand km. The vehicle fleet exceeds 6 million cars, including 4.87 million passenger cars (2004). The main seaports are Antwerp (annual turnover - 151.6 million tons in 2004), Bruges-Zeebrugge (about 31.8 million tons), Ghent (about 24.9 million tons), Ostend (about 5.9 million tons). About 40 thousand ships enter Belgian ports annually. The length of inland waterways is 1515 km, with about 1300 vessels operating on them. Since 2002, the largest ship lift in the world (lifting capacity of 1350 tons) has been in operation on the Central Canal in the Belgian province of Hainaut.
The education sector has been under the competence of communities - subjects of the Belgian federation - since 1988. Education from ages 6 to 18 is compulsory and free in Belgium. In addition to state and municipal schools, many Catholic and private secular schools operate. Higher education is provided by 7 academies and 8 universities, several university centers, institutes, higher technical schools, and conservatories.
The number of the Belgian armed forces is 41 thousand people, of which more than 2 thousand are women. The military budget is 2.6 billion dollars (1.9% of GDP). In 1994, universal conscription was abolished, and a contract system was introduced. The Belgian armed forces are integrated into NATO. The headquarters of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization is located in Brussels; near the city of Mons is the headquarters of the Supreme Allied Commander Europe (SHAPE).
There are 33 daily newspapers published in French, Dutch, and German with a total circulation of 1.5 million copies, and 28 weekly magazines. There are many specialized city and municipal newspapers. The largest newspapers are: "Laatste Nieuws" (Dutch, about 290.6 thousand copies), "De Standaard" (Dutch, 79.8 thousand), "De Morgen" (Dutch, 51.4 thousand), "Gazet van Antwerpen" (Dutch, 117 thousand), "Het Laatste Nieuws" (Dutch, 35 thousand), "Le Soir" (French, 102.3 thousand), "Libr Belgique" (French, 50 thousand), "Dernière Heure" (French, 86.1 thousand), "Eko" (French, 18 thousand), "Metro" (bilingual free, 275 thousand).
Radio and television are divided into 2 independent networks in French (RTBF) and Dutch (VRT). The 3rd largest audiovisual media group in the country is the joint Belgian-Luxembourg private company RTL-TVI. There are about 12 private broadcasting companies, as well as more than 30 regional and municipal television studios. Cable television is dominant throughout the country. The Belgian Telegraph Agency (a joint-stock company of the largest Belgian newspapers) is the Belga Agency.