Snow Leopard / Ilbirs / Snow Leopard
Snow Leopard
Status: III. Critically Endangered, CR C2a(i): R, C1.
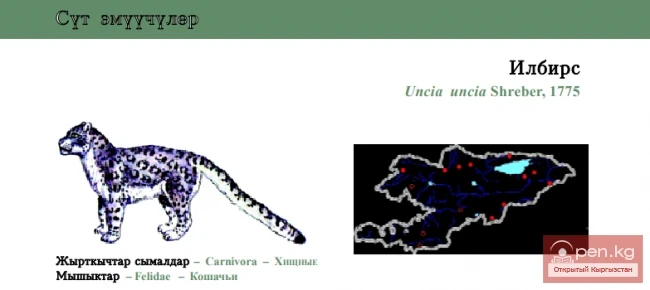
Distribution overall and in the country. Found in 12 mountainous countries of Asia. In Kyrgyzstan - in the Pskem, Chandalash, Talas, Kyrgyz, Suusamyr, Chatkal, Fergana, Turkestan, Alay ridges, as well as in Kungei and Teskei Ala-Too, Naryn-Too, Moldo-Too, At-Bashi, Sary-Jaz, and Kokshaal-Too [19].
Habitat. In alpine and subalpine landscape zones at altitudes of 3,000 to 4,000 m, prefers moderately rugged terrain with individual elevations for observation and hiding spots in the form of stones and thickets of shrubs (Caragana, Juniper). Typically visits the forest belt when moving from one river valley to another. In winter, it is also found in the upper forest zone, following mountain goats.
Population. Previously considered a common species in many mountain ranges, the total population was estimated at 1,400 individuals at the beginning of the 1980s [9], according to E. Koshkarev - 600-700 individuals, but no more than 1,000 [19]. Over the last 10-12 years, the population has decreased by 5-10 times [9, 20] and continues to decline, currently not exceeding 150-250 individuals [20]. The highest density is in the high mountains of Northern Tien Shan, approximately the same in Alay, Inner and Central Tien Shan, and the lowest in Western Tien Shan [19]. The global population of the species is estimated at 5-7 thousand individuals.
Life style (life cycles). Lives a sedentary lifestyle. Active during twilight and nighttime, in winter and spring, when ungulates are active during the day, it is also encountered during daytime. Breeding occurs in February-March, gestation lasts 98-103 days, with 1-3 cubs in a litter (very rarely up to 5). The female gives birth once every 2 years, and sexual maturity is reached at two years of age. Main prey includes mountain goats, argalis, marmots, and less frequently - roe deer, marals, wild boars, hares, snowcocks, and chukars. Diseases are poorly studied, with known cases of rabies and mange [4, 19].
Limiting factors. Anthropogenic: permitted hunting (late 19th-early 20th century); development of sheep farming and mountain exploitation, poaching.
Breeding (keeping in captivity). Successfully bred in many zoos around the world, with a total population of at least 700 individuals, including in 6 zoos of the CIS.
Existing conservation measures. Hunting in Kyrgyzstan has been prohibited since 1948, and since 1959, legal responsibility has been established for hunting and trapping without licenses. Included in the International Red List and Appendix 1 of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora. Since 1975, it has been included in the List of specially protected species of Kyrgyzstan. Protected in the Sarychelek, Besharal, Naryn, Karatal-Japyrik, and Sarychat-Ertash (established in 1993 primarily for this species) reserves, as well as in Ala-Archa, Karakol, and Chon-Kemin national parks. Since 1999, a joint Kyrgyz-German project "Snow Leopard" has been operating, and since 2002, a joint Kyrgyz-American project for monitoring and protecting leopards based in the Sarychat-Ertash reserve.
Recommended conservation measures. Establishment of a protected area in Alai. Strengthening public awareness of species conservation among local populations, enhancing protection, and implementing relevant articles of the Law on Wildlife Conservation of Kyrgyzstan (2000).
Ilbirs
Snow Leopard
Uncia uncia Shreber, 1775
Status: III, Critically Endangered, CR, C2a(i): R. Occurs in Pskem, Chandalash, Talas, Kyrgyz, Suusamyr, Chatkal, Fergana, Turkestan, Alay, Kungei, Teskei, Naryn-Too, Moldo-Too, At-Bashi, Sary-Jaz and Kokshaal-Too Mountainous Ridges. Inhabits in subalpine and alpine belts: 3,000-4,000 m (9,800-13,100 feet) above sea level. Prefers partitioned relief with hills for observations and hiding spots among stones and bushes (Caragana, Juniperus). Visits forest belt only during roaming from one river valley to another. Occurs in forest zone in winter following wild goats. It was a common species in the past, total numbers were up to 1,400 animals. For the last decade, the Leopard’s numbers drastically reduced and do not exceed 150-200 individuals. The highest density is in Northern Tien Shan. World’s total numbers are 5-7,000 animals. Resident species are most active in dusky and nighttime. Heating season begins in February-March, pregnancy lasts for 98-103 days, female delivers 1-3 cubs, rarer - up to 5, once in two years. Uses for food wild goats, sheep, marmots, and relatively rare deer, hares, snowcocks, chukars. Diseases poorly investigated, rabies and mange are well known. Limiting factors are reduction in numbers of wild goats and sheep populations, poaching. Hunting is prohibited in Kyrgyzstan since 1948. Protected in all zapovedniks (protected areas), Sarychat-Ertash protected area was established with the major purpose to conserve Snow Leopard. Several international projects are designed to introduce protection interventions: Kyrgyz-German and Kyrgyz-American ones. It is recommended to establish a protected area in Alai Ridge, increase public awareness among local communities, better implementation of Kyrgyz Law about Wildlife Conservation.
Read also:

Tourist Area Management Program
The project "USAID Business Development Initiative" (BGI), within the tourism...

Types of Higher Plants Listed in the "Red Book" of Kyrgyzstan (1985)
Species of higher plants removed from the "Red Book" of Kyrgyzstan (1985) Species of...

Types of Insects Excluded from the Red Book of Kyrgyzstan
Insect species excluded from the Red Data Book of Kyrgyzstan Insect species excluded from the Red...

Types of Insects Listed in the 2004 IUCN RLTS Not Included in the Red Book of Kyrgyzstan
Insect species listed in the 2004 IUCN RLTS, not included in the Red Book of Kyrgyzstan 1....

The Poet Jumakan Tynymseitov
The poet J. Tynymseitova was born on 11. 1929—29. 07. 1975 in the village of On-Archa in the...

Prose Writer, Critic Dairbek Kazakbaev
Prose writer and critic D. Kazakbaev was born on June 20, 1940, in the village of Dzhan-Talap,...

Poet, Critic, Literary Scholar Omor Sooronov
Poet, critic, literary scholar O. Sooronov was born in the village of Gologon in the Bazar-Kurgan...

The title translates to "Poet Soviet Urmambetov."
Poet S. Urmambetov was born on March 12, 1934, in the village of Toru-Aigyr, Issyk-Kul District,...

Prose Writer, Journalist Djapar Saatov
Prose writer, journalist Dzh. Saatov was born on February 15, 1930, in the village of Alchaluu,...

Poet, Prose Writer Tash Miyashev
Poet and prose writer T. Miyashev was born in the village of Papai in the Karasuu district of the...

The Poet Baidilda Sarnogoev
Poet B. Sarnogoev was born on January 14, 1932, in the village of Budenovka, Talas District, Talas...

Poet, Prose Writer Medetbek Seitaliev
Poet and prose writer M. Seitaliev was born in the village of Uch-Emchek in the Talas district of...

Salamatov Zholdon
Salamatov Zholdon (1932), Doctor of Physical and Mathematical Sciences (1995), Professor (1993)...

The Poet Gulsaira Momunova
Poet G. Momunova was born in the village of Ken-Aral in the Leninpol district of the Talas region...

The Poet Subayilda Abdykadyrov
Poet S. Abdykadyrova was born in the village of Sary-Bulak in the Kalinin district of the Kirghiz...

Prose Writer Kachkynbay (KYRGYZBAI) Osmonaliev
Prose writer K. Osmonaliev was born on March 5, 1929, in the village of Chayek, Jumgal district,...

The Poet Akbar Toktakunov
Poet A. Toktakunov was born in the village of Chym-Korgon in the Kemin district of the Kyrgyz SSR...

Literary scholar, prose writer, poet Dzaki Tashtemirov
Literary scholar, prose writer, poet Dz. Tashtemirov was born on October 15, 1913—October 7, 1988,...

Critic, Literary Scholar Abdyldazhan Akmataliev
Critic and literary scholar A. Akmataliev was born on January 15, 1956, in the city of Naryn,...

Poet Abdilda Belekov
Poet A. Belekov was born on February 1, 1928, in the village of Korumdu, Issyk-Kul District,...

Poet, Prose Writer Dzhenbap Mambetaliev
Poet and prose writer D. Mambetaliev was born on December 18, 1938, in the village of Ottyk,...

The Poet Tenti Adysheva
Poet T. Adysheva was born in 1920 and passed away on April 19, 1984, in the village of...

Poet Abdravit Berdibaev
Poet A. Berdibaev was born on 9. 1916—24. 06. 1980 in the village of Maltabar, Moscow District,...

Chorotegin (Choroev) Tynchtykbek Kadyrmambetovich
Chorotegin (Choroев) Tynchtykbek Kadyrmambetovich (1959), Doctor of Historical Sciences (1998),...

Poet Dzholdoshbay Abdykalikov
Poet J. Abdykalikov was born in the village of Tashtak in the Issyk-Kul district of the Issyk-Kul...

Poet Karymshak Tashbaev
Poet K. Tashbaev was born in the village of Shyrkyratma in the Soviet district of the Osh region...

Critic, Literary Scholar, Poet Kachkynbai Artykbaev
Critic, literary scholar, poet K. Artykbaev was born in the village of Keper-Aryk in the Moscow...

Poet Mariyam Bularkieva
Poet M. Bularkieva was born in the village of Kozuchak in the Talas district of the Talas region...
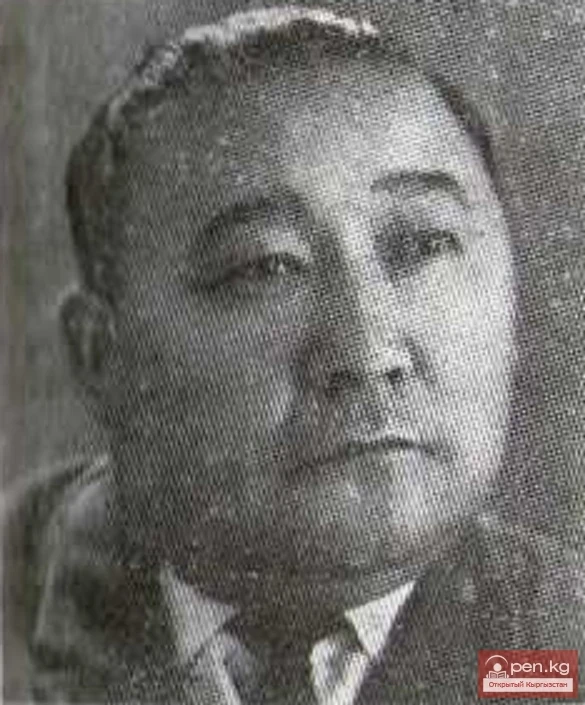

The Poet Kubanych Akaev
Poet K. Akaev was born on November 7, 1919—May 19, 1982, in the village of Kyzyl-Suu, Kemin...

Poet, storyteller-manaschi Urkash Mambetaliev
Poet, storyteller-manaschi U. Mambetaliev was born on March 8, 1934, in the village of Taldy-Suu,...

Poet Akynbek Kuruchbekov
Poet A. Kuruchbekov was born on December 5, 1922 — November 29, 1988, in the village of Eryktu,...

Poet, Prose Writer Isabek Isakov
Poet and prose writer I. Isakov was born on September 1, 1933, in the village of Kochkorka,...

The Poet Sooronbay Jusuyev
Poet S. Dzhusuev was born in the wintering place Kyzyl-Dzhar in the current Soviet district of the...

Poet, Journalist Barktabas Abakirov
Poet and journalist B. Abakirov was born in the village of Kum-Dyube in the Kochkor district of...
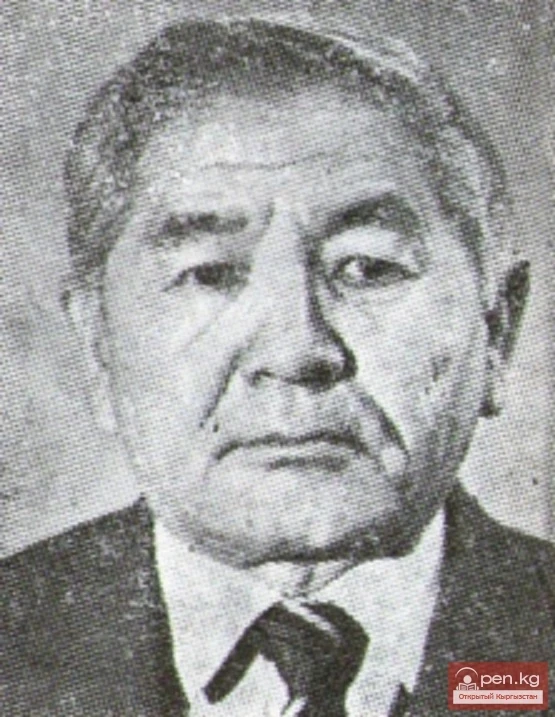

Poet Dzhaparkul Alybaev
Poet Dzh. Alybaev was born on October 12, 1933, in the village of Birikken, Chui region of the...

Kasymbekov Beishabay
Kasybekov Beyshabay (1933), Doctor of Veterinary Sciences (1991), Professor (1998) Kyrgyz. Born in...
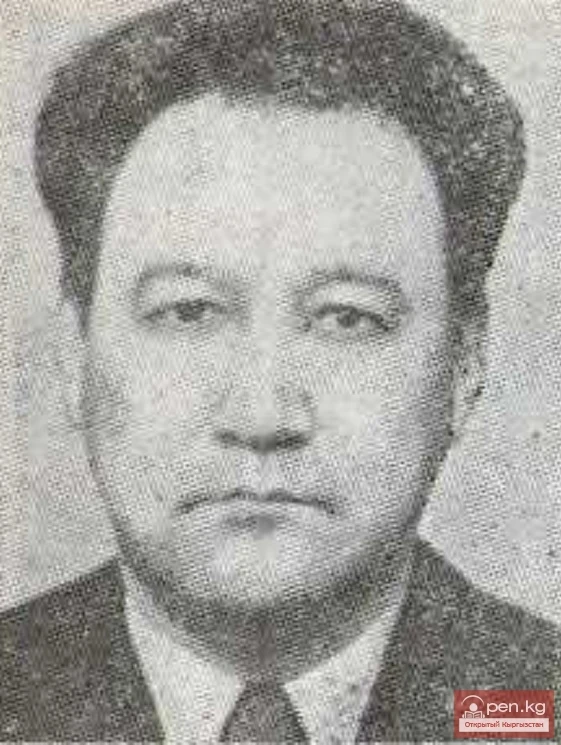

Poet Esengul Ibraev
Poet E. Ibraev was born on March 16, 1934, in the village of Chet-Nura, Tian-Shan district of...

Poet, Prose Writer Abdrasul Kylychev
Poet and prose writer A. Kilychev was born in the village of Orto-Sai near the city of Naryn in...

Poet Mukambetkalyy Tursunaliev (M. Buranaev)
Poet M. Tursunaliev was born on January 11, 1926, in the village of Alchaluu, Chui region of the...

Poet Mederbek Akimkodzhoev
Poet M. Akimkodzhoev was born in the village of Bazar-Turuk in the Jumgal district of Naryn region...

Prose Writer Duyshen Sulaymanov
Prose writer D. Su laymanov was born in the village of Jilaymash in the Sokuluk district of the...

Zhorobekov Zholbors
Zhorobekov Zholbors (1948), Doctor of Political Sciences (1997) Kyrgyz. Born in the village of...

The Poet Turar Kodzhomberdiev
Poet T. Kodzhomberdiev was born on October 15, 1941—January 30, 1989, in the village of...

Poet, Art Historian Sarman Asanbekov
Poet and art critic S. Asanbekov was born in the village of Aral in the Talas region of Kyrgyzstan...

Poet Mayramkan Abylkasymova
Poet M. Abylkasymova was born in the village of Almaluu in the Kemin district of the Kirghiz SSR...

Prose Writer Kudaibergen Dzhaparov
Prose writer K. Dzhaparov was born in the village of Saz in the Sokuluk district of the Kyrgyz SSR...

Kerimzhanova Bubu Dyikanbaevna
Kerimjanova Bubu Dyikanbaevna (1920-1993), Candidate of Philological Sciences, Corresponding...

Population of Kyrgyzstan as of January 1, 2013
Population of Kyrgyzstan Thanks to the fundamental changes that occurred in Kyrgyzstan after the...