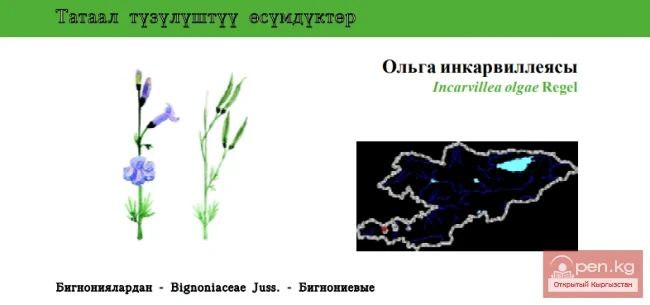
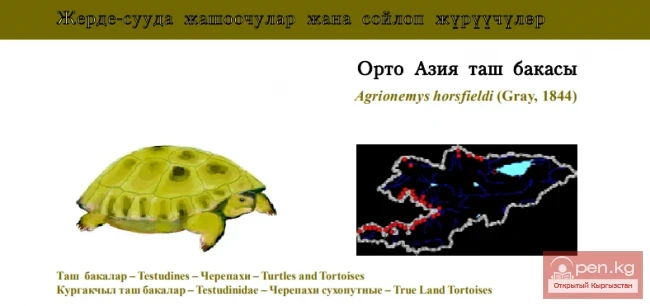
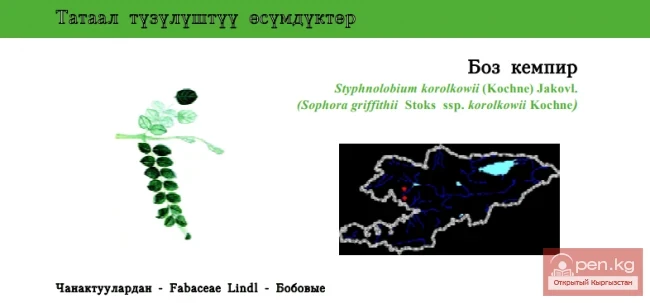
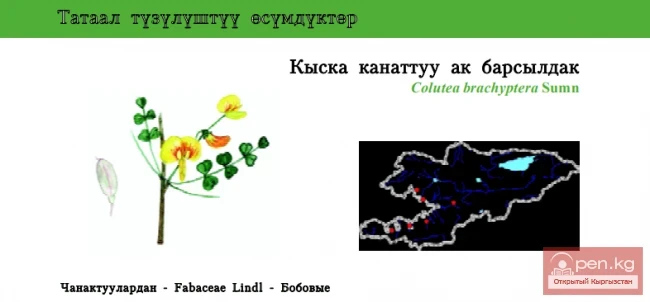
NORFOLK
An island in Oceania, in the south-western part of the Pacific Ocean, located 1676 km northeast of Sydney (Australia). Area — 34.5 km². The administrative center is Kingston. Population - 2.3 thousand (2004); consists of descendants of settlers from Pitcairn Island and partially from recent immigrants from Australia and New Zealand. The official language is English.
The currency is the Australian dollar.
A possession of Australia, it has the status of an "Australian external territory." It is administered by an administrator appointed by the Australian Governor-General. In 1957, an advisory body called the Island Council was established under the administrator, consisting of 8 members elected every 2 years. According to the 1979 Act, which defines the foundations of the legislative, administrative, and legal systems, internal self-government was expanded: a Legislative Assembly was created consisting of 9 members elected for 3 years. The Assembly forms the Executive Council of the island, which acts as the government.
Discovered by the English navigator J. Cook in 1774. From 1788 to 1813 and from 1825 to 1855, it served as a place of exile for convicts. In 1844, it was included in the colony of Tasmania. By the 1913 Act, it was declared a possession of Australia.
The economy is primarily based on tourism, agriculture, and fishing. Food products are imported from Australia and New Zealand.
Some types of industrial goods, palm and pine seeds are re-exported.
There are 90 km of roads, an airport, and maritime connections with Australia and New Zealand.
Radio and television services are available.