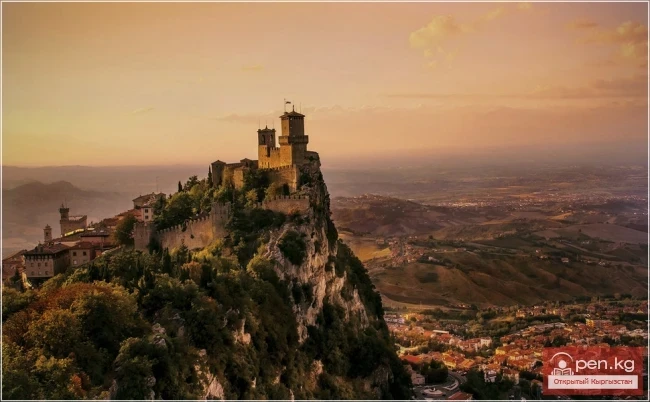
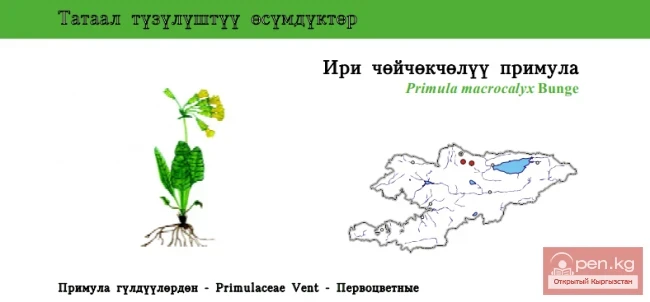
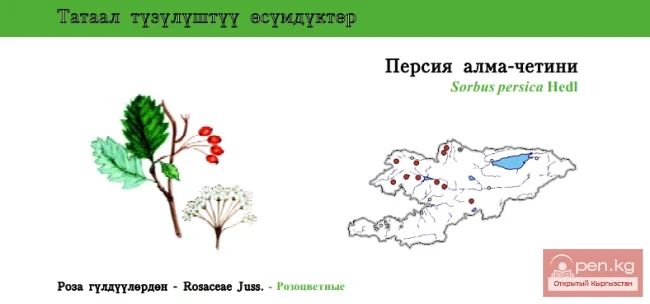
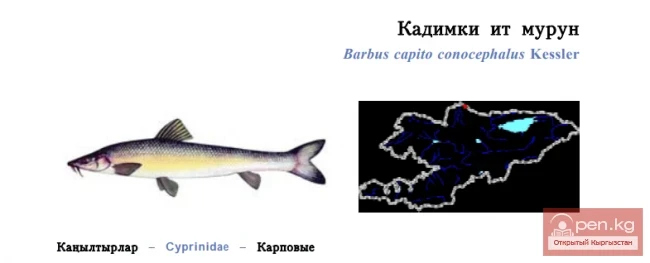
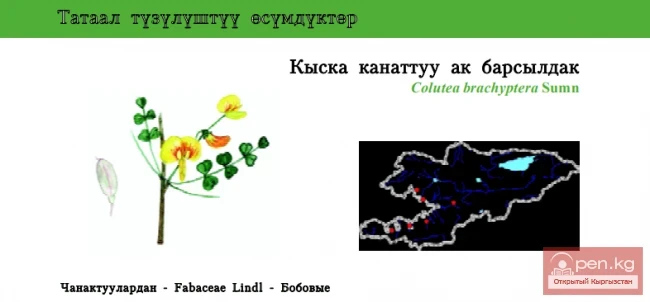
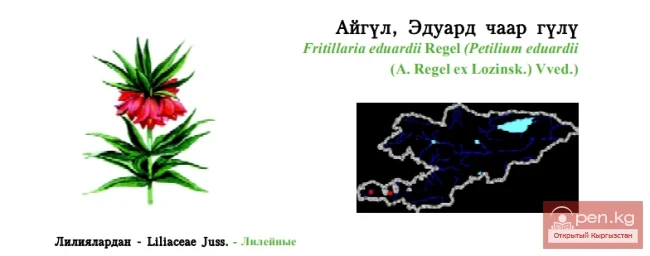
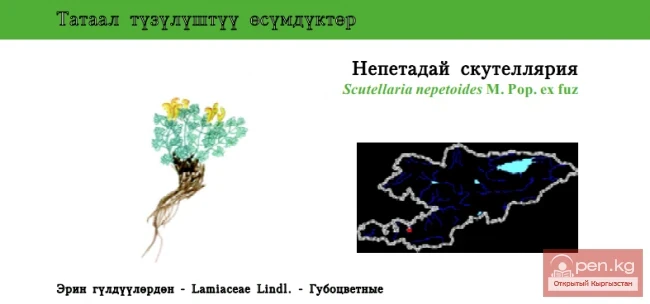
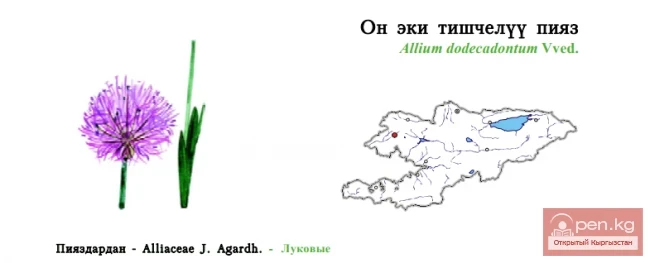
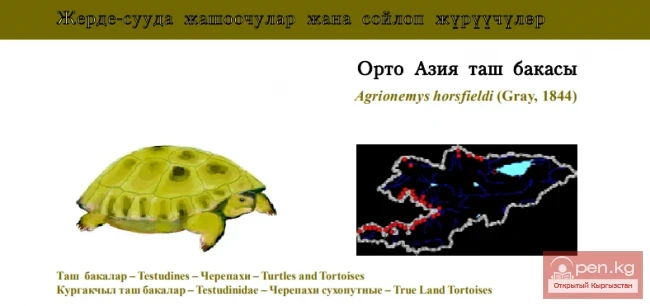
SAN MARINO. Republic of San Marino
A state in the northeastern part of the Apennine Peninsula on Mount Titano, surrounded by Italian territory. Area - 61 km². Capital - San Marino (approx. 4,500). Administratively divided into 9 districts: Serravalle/Dogana, Borgo Maggiore, Faetano, San Marino, Domagnano, Fiorentino, Chiesanuova, Acquaviva, Monte Giardino.
Population - over 28,000. A large number of San Marino citizens (about 13,000) live permanently outside the country, mainly in Italy, as well as in France, the USA, and Argentina. The official language is Italian. Religion - Catholicism.
Currency - Euro.
Has diplomatic relations with the Russian Federation (established in full on September 30, 1993).
National holiday - September 3 - Day of the Proclamation of the Republic (301 AD).
San Marino is a parliamentary republic. The constitution (Statute - a collection of laws on the system of state structure) of 1600 is in effect (with amendments).
The highest legislative body is the Grand General Council (unicameral parliament), which is elected for 5 years by universal and direct voting according to a proportional system. It consists of 60 deputies. The GGC elects the Captains Regent, members of the State Council (government), the Council of Twelve, government auditors, confers military ranks, ratifies international treaties, declares amnesty, grants citizenship, and approves the state budget. The functions of the head of state and executive power are performed by 2 equal Captains Regent, who serve as the collective head of state and government and are elected by the Grand General Council from among its members for 6 months (taking office on April 1 and October 1).
Each of them has the right to veto the decisions of the other. The Captains Regent preside over the Grand General Council, the sessions of the State Congress, and the Council of Twelve. The State Congress is formed by the Grand General Council from members of the coalition that has obtained the majority of seats in parliament. The Council of Twelve is the highest judicial body for civil, judicial, and criminal cases, resolves disputes within its jurisdiction, and serves as a court of third instance. It is elected by the GGC for 5 years. Government auditors represent the state in court in financial or property disputes.
Political parties: San Marino Christian Democratic Party (SMCDP) - founded in 1945, San Marino Socialist Party (SMSP) - established in 1986, Democratic Party - formed as a result of the transformation of a certain communist party in San Marino in April 1990, San Marino Party of Communist Revival - created by some former members of the San Marino Communist Party, San Marino National Alliance and People's Alliance of San Marino Democrats.
Trade unions: San Marino Confederation of Labor - founded in 1945, San Marino Democratic Confederation of Workers - founded in 1957.
San Marino is the oldest of the modern states in Europe, existing since 301 AD, the name "Republic of San Marino" appears in documents from the 10th century. Before gaining independence in 855 AD, it was under the protectorate of the neighboring Duchy of Urbino. After the invasion of Napoleon's army in 1797 into Italian territory, San Marino remained the only Apennine state free from occupation. Since 1862 - under Italian protectorate.
The last treaty of friendship and good neighborliness with Italy was concluded in 1953.
In conducting its foreign policy, San Marino adheres to the principles of neutrality and non-alignment. Main directions: relations with Italy, work within international organizations, addressing humanitarian issues. It participates in a number of international treaties and conventions, took part in the Helsinki Conference on Security and Cooperation in Europe, and is a member of the OSCE. In November 1988, the Republic of San Marino joined the Council of Europe. Since 1992 - a member of the UN. San Marino actively advocates for the development of cooperation with EU countries. Relations with EU countries are regulated by the Cooperation and Customs Union Agreement, signed on December 16, 1991, which recognizes San Marino's status as a third country, establishing a unified legal framework for its relations with EU countries, replacing the relevant bilateral agreements between San Marino and Italy.
Bilateral relations are most closely and diversely maintained by San Marino with Italy. In 1991, the Republic of San Marino concluded a monetary and financial agreement with Italy, which replaced the 1953 agreement on customs and postal union. Under this agreement, San Marino, forming a single monetary space with Italy, receives autonomy in monetary and financial matters, freedom of capital movement, and the ability to conduct operations in foreign currency. In exchange for refraining from issuing its own currency and organizing a customs service, as well as for the obligation not to allow the establishment of gambling houses on its territory, San Marino receives annual compensation from Italy.
The economy of San Marino is closely linked to the economy of Italy. San Marino is part of a single European monetary area, with the Euro introduced on January 1, 2002. The manufacturing industry is mainly represented by food, ceramics, and textiles. The food industry includes winemaking, milling, baking, and oil production enterprises. Several cotton factories and a silk spinning mill operate. The basis of San Marino's agriculture consists of grain production, viticulture and winemaking, growing peaches, figs, apricots, almonds, walnuts, olives, raising cattle, and sericulture. An important source of income is the production of postage stamps and coins for numismatists. Tourism makes a significant contribution to the economy: more than 3 million tourists visit San Marino annually.
In accordance with the Italian-San Marino agreement signed in the 1990s, San Marino has established its own radio and television networks. The main daily newspapers are "Tribuna Sammarinese" (founded in 1993) and "San Marino Oggi."
Periodic publications: "Argomenti" (founded in 1982), "Azione" and "Periscopio" (founded in 1967 and 1996, respectively), "Comunicato Stampa" (founded in 1990), "Nuovo Titano" (founded in 1903), "Proposta Sindacale" (publication of the Democratic Confederation of Workers, founded in 1958), "Progresso" (founded in 1990), "San Marino" (founded in 1948), "Giovane Titano."