The doctor named the key risk factors for the transmission of hepatitis B from mother to child
This study emphasizes that vertical transmission of the hepatitis B virus remains a serious issue in perinatal medicine, as it can lead to the development of chronic HBV infection in newborns.
As part of a retrospective analysis, data were collected on 231 pregnant women suffering from chronic HBV infection. Serological and molecular biological indicators were assessed, as well as laboratory results, including the APRI index, which indicates the degree of liver fibrosis.
The results of the study showed that pregnant women with an elevated APRI index significantly increase the risk of HBsAg-positive newborns. This underscores the importance of assessing liver condition to predict vertical transmission of the virus.
The study also confirmed the high effectiveness of combined prevention: vaccination of newborns along with the administration of specific immunoglobulin (HBIG) provided complete protection against the virus. At the same time, when only the vaccine was used, hepatitis B virus was detected in 13.1% of children.
The article notes that vertical transmission of the virus can occur at all stages of chronic HBV infection, even with low viral load. Early application of antiviral therapy with tenofovir in combination with vaccination demonstrated high effectiveness and may be an alternative to regimens using HBIG.
The author of the study is confident that the best strategy for reducing the risk of hepatitis B transmission from mother to child is a combination of antiviral treatment for the mother and specific immunoprophylaxis for the newborn.
Read also:

Alymbaeva Damira Beishekeevna (1953)
Alymbaeva Damira Beyshekeevna (1953), Doctor of Medical Sciences (1997), Professor (1998)...

A Dangerous Virus Discovered in the Emirates
The Department of Tourism under the Ministry of Culture, Information, and Tourism of the Kyrgyz...

Usmanov Rafik Karimovich
Usmanov Rafik Karimovich (1947), Doctor of Medicine Tatar. Born in Frunze....
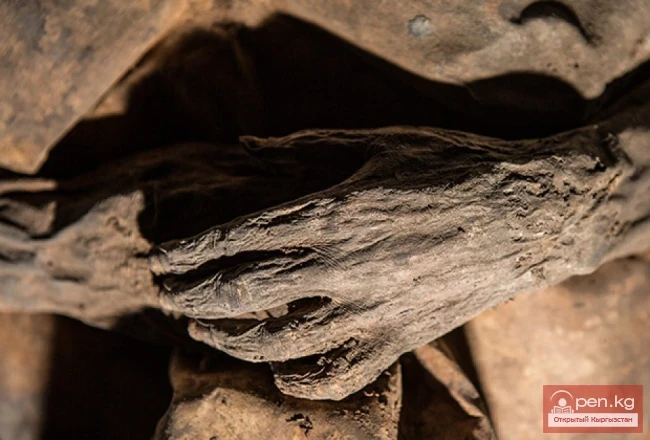

"The Case of the Mummy"
"The Case of the Mummy" The Minister of Culture of Kyrgyzstan, Tugelbay Kazakov, who...
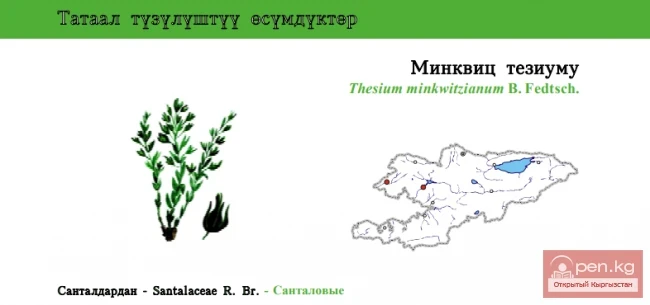
Minkwitz's Bastard Toad-Flax
Minkwitz’s Bastard Toad-Flax Status: CR. Subendemic. An extremely rare relict plant that is...
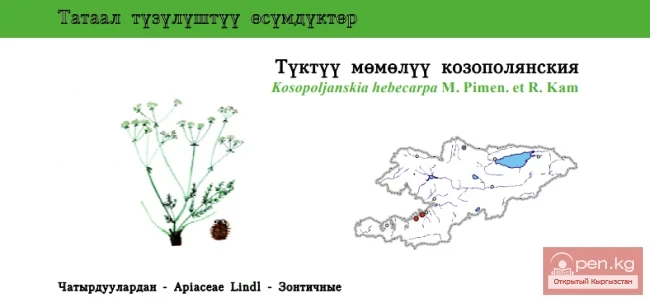
Wolly-fruited Kosopoljanskia
Wolly-fruited Kosopoljanskia Status: EN. Endemic. One of the two species that are sub-endemic to...

Toktosopiev Alymbai Moldokmatovich
Toktosopiev Alymbai Moldokmatovich (1953), Doctor of Physical and Mathematical Sciences (1999),...
Unhealthy. The air quality in Bishkek at 5:00 PM is 183 AQI (smog map)
According to IQAir data, as of 5:00 PM on December 2, 2025, the air quality in Bishkek is recorded...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 16:00 is 75 AQI (smog map)
As of 16:00 on November 13, 2025, the air quality index in Bishkek is recorded at 75 AQI. This...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 16:00 is 79 AQI (smog map)
As of 16:00 on November 3, 2025, the air quality index in Bishkek is recorded at 79 AQI. This...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 11:00 is 58 AQI (smog map)
According to IQAir, as of 11:00 on November 4, 2025, Bishkek has an AQI of 58. This level of air...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 5:00 PM is 80 AQI (smog map)
As of 5:00 PM on November 19, 2025, the air quality index in Bishkek is 80 AQI, indicating...
Unhealthy. The air quality in Bishkek at 11:00 is 174 AQI (Bishkek smog map)
According to information from IQAir, as of 11:00 on November 23, 2025, Bishkek recorded an AQI of...
Unhealthy. The air quality in Bishkek at 11:00 is 162 AQI (smog map)
According to IQAir, the air quality in Bishkek on December 1, 2025, at 11:00 was recorded at 162...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 11:00 is 94 AQI (Bishkek smog map)
According to IQAir, as of 11:00 AM on January 2, 2026, the air quality level in Bishkek is 94 AQI....
Unhealthy. The air quality in Bishkek at 5:00 PM is 167 AQI (smog map)
According to IQAir, as of 5:00 PM on November 24, 2025, the air quality in Bishkek is reported as...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 11:00 is 94 AQI (smog map)
According to IQAir, as of 11:00 on November 9, 2025, the air quality level in Bishkek is 94 AQI....
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 5:00 PM is 67 AQI (smog map)
According to IQAir, as of January 10, 2026, at 5:00 PM, the air quality level in Bishkek is 67 AQI....
Harmful for vulnerable groups. The air quality in Bishkek at 11:00 is 102 AQI (Bishkek smog map)
According to IQAir data, as of 11:00 on November 16, 2025, the air quality level in Bishkek is 102...
Unhealthy. The air quality in Bishkek at 10:00 is 184 AQI (smog map)
According to IQAir data, as of 10:00 on November 7, 2025, the air pollution level in Bishkek is 184...
Harmful to Vulnerable Groups. Air Quality in Bishkek at 11:00 is 107 AQI (smog map)
As of 11:00 AM on November 19, 2025, the air quality index in Bishkek reached 107 AQI. This level...
Unhealthy. The air quality in Bishkek at 11:00 is 155 AQI (smog map)
According to IQAir information, as of January 7, 2026, at 11:00, the air pollution level in Bishkek...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 5:00 PM is 71 AQI (smog map)
According to information from IQAir, as of November 20, 2025, at 5:00 PM, the air quality index in...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 11:00 is 86 AQI (smog map)
Based on IQAir data, as of November 10, 2025, at 11:00, the air quality level in Bishkek is 86 AQI....
Unhealthy. The air quality in Bishkek at 17:00 is 198 AQI (smog map)
According to information from IQAir, as of 5:00 PM on December 27, 2025, the air quality index in...
Harmful to vulnerable groups. The air quality in Bishkek at 16:00 is 125 AQI (smog map)
As of November 15, 2025, at 16:00, the air quality index in Bishkek is 125 AQI. This value...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 16:00 is 91 AQI (smog map)
As of November 9, 2025, at 16:00, according to IQAir, the air quality index in Bishkek is 91 AQI....
Harmful for Vulnerable Groups. Air Quality in Bishkek at 11:00 is 148 AQI (smog map)
As of 11:00 on November 15, 2025, the air quality level in Bishkek, according to IQAir, is 148 AQI....
Very Unhealthy. The air quality in Bishkek at 5:00 PM is 250 AQI (smog map)
According to information from IQAir, as of January 14, 2026, at 5:00 PM, the air quality index in...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 10:00 is 82 AQI (smog map)
As of the morning of October 29, 2025, the air quality level in Bishkek is reported by IQAir to be...
Very Unhealthy. The air quality in Bishkek at 5:00 PM is 248 AQI (smog map)
According to IQAir data, on January 15, 2026, at 5:00 PM, the air quality index in Bishkek is 248...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 10:00 is 79 AQI (smog map)
Based on IQAir data, as of 10:00 on October 26, 2025, the air quality index in Bishkek is recorded...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 17:00 is 52 AQI (smog map)
As of October 25, 2025, at 17:00, the air quality index in Bishkek is 52 AQI. This figure indicates...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 17:00 is 63 AQI (smog map)
According to IQAir, as of 5:00 PM on October 29, 2025, the air quality level in Bishkek is 63 AQI....
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 17:00 is 60 AQI (smog map)
According to IQAir data, as of 5:00 PM on November 27, 2025, the air quality index in Bishkek is 60...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 17:00 is 66 AQI (smog map)
As reported by IQAir, on November 1, 2025, at 5:00 PM, the air pollution level in Bishkek was...
Unhealthy. The air quality in Bishkek at 10:00 is 178 AQI (smog map)
Based on IQAir data, in Bishkek, on November 8, 2025, at 10:00, the air quality index was 178 AQI....
Harmful for Vulnerable Groups. Air Quality in Bishkek at 11:00 is 137 AQI (smog map)
According to information provided by IQAir, on January 8, 2026, at 11:00, the air quality index in...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 17:00 is 82 AQI (smog map)
According to IQAir data, on November 2, 2025, at 5:00 PM, the air pollution level in Bishkek is 82...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 11:00 is 64 AQI (smog map)
According to IQAir data, at 11:00 on January 13, 2026, the air quality in Bishkek is 64 AQI. This...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 17:00 is 96 AQI (smog map)
As of 5:00 PM on November 18, 2025, the air quality index in Bishkek, according to IQAir, is 96...
Satisfactory. The air quality in Bishkek at 11:00 is 76 AQI (Bishkek smog map)
According to IQAir data, as of December 27, 2025, at 11:00, the air quality index in Bishkek is 76...
Harmful to vulnerable groups. The air quality in Bishkek at 17:00 is 139 AQI (smog map)
Based on IQAir data, the air quality in Bishkek at 17:00 on November 17, 2025, is 139 AQI. This...