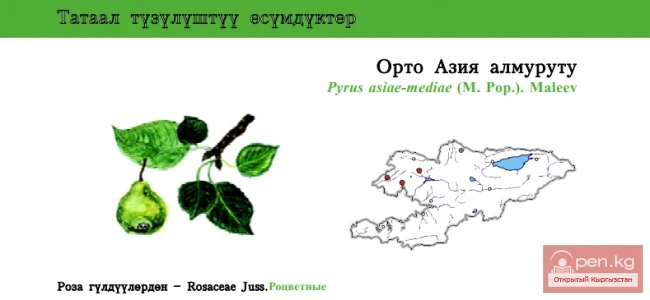
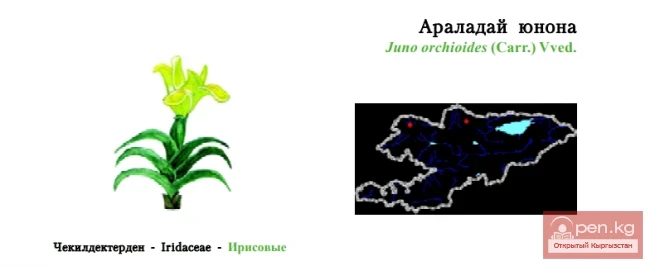
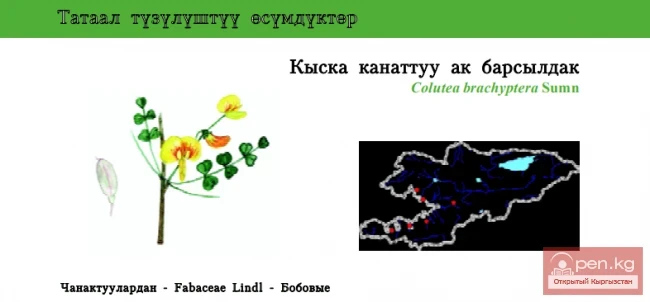
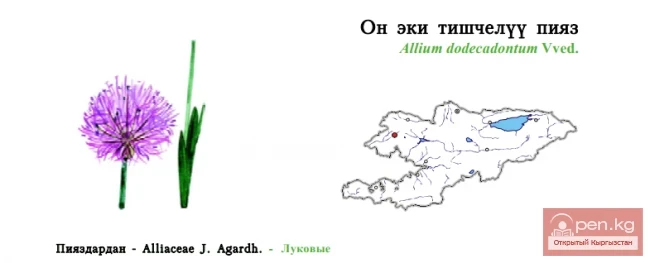
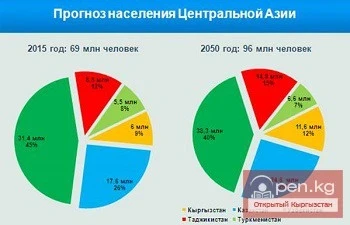
As of the end of 2025, China's population stood at 1.404 billion, which is 3.39 million fewer compared to the figures at the end of 2024, according to the report from the National Bureau of Statistics of China.
In 2025, 7.92 million children were born in the country, significantly lower than the 9.54 million in 2024. The birth rate was 5.63 per thousand residents. At the same time, the number of deaths reached 11.31 million, while in 2024 there were 10.93 million registered deaths. Thus, the mortality rate was 8.04 per thousand. The natural population decline was 2.41 per thousand, with 716.85 million men and 688.04 million women in the country.
The aging population process is becoming increasingly noticeable: the number of people over 60 years old reached 323.38 million, accounting for 23% of the total population. Urbanization also continues to gain momentum — the urban population increased by 10.3 million, reaching 953.8 million (67.9% of the total). At the same time, rural areas saw a decrease of 13.69 million, resulting in a total rural population of 451.09 million.
According to Reuters, China's population has been declining for the fourth consecutive year, with the decrease in 2025 being the most pronounced. The number of newborns has reached the lowest level in decades. These demographic changes pose serious challenges for Beijing, which is striving to boost domestic consumption.