The Economy of Kyrgyzstan in 1991 - 2005
The post-Soviet period in the Kyrgyz Republic was marked by dynamic changes. Gaining independence, Kyrgyzstan, at the end of 1991 and the beginning of 1992, like all other CIS countries, began the transition to a democratic system of governance and the implementation of radical economic reforms. They had to start and carry out these reforms under conditions of an unprecedented depth of economic crisis. The collapse of the Soviet Union meant a rupture of cooperative ties between economic entities. The activities of many enterprises were completely or partially paralyzed. The loss of markets in the former USSR, as well as changes in the structure of domestic demand, led to a significant decline in gross domestic product (GDP). The GDP fell most sharply in 1993 — it decreased by more than 25%.
To overcome the systemic crisis, decisive actions were taken to establish the foundations of a market economy, which allowed for the formation of a private sector, primary market infrastructure, the introduction of a national currency ahead of other CIS countries, and the implementation of an independent monetary policy, halting hyperinflation. As a result, economic growth resumed in 1996.
When analyzing the socio-economic development of the republic, several stages are clearly discernible.
First Stage — from 1991 to 1995. The sharp reduction in production and income coincided with a sharp increase in the number of people reaching the poverty line (over 50% of the population), inequality, hyperinflation, followed by initial macroeconomic stabilization. The slowdown of inflation became the basis for the first stage of macroeconomic stabilization (1992-1995). The macroeconomic and structural reforms of that period laid the foundations for market regulation of the economy.
Second Stage — from 1996 to 1999. Economic stabilization was observed, with growth occurring in limited sectors (agriculture, gold mining, and energy). However, a high budget and coverage of the budget deficit made the economy extremely vulnerable. The crisis that occurred in 1998-1999 was primarily due to the collapse of the Russian ruble.
Third Stage — from 2000 to March 2005. Economic growth continued, inflation slowed, the budget deficit decreased, and the exchange rate stabilized. However, the problem of external debt became more acute. The reforms of this period were grouped around deregulation issues. Deregulation is understood as a significant change in the role of the state, a reduction in its interference in the activities of the private sector, the elimination of administrative barriers for entrepreneurship, and a reduction in the number of controlling and permitting state bodies. Since 2000, active work has been carried out on the privatization of strategic sectors of the country — energy and telecommunications.
Current Stage — from March 2005.
Read also:

World Economic Forum 2014-2015: Kyrgyzstan Improved Its Position by 3 Places in the GDP Ranking
Kyrgyzstan ranked 128th in terms of gross domestic product among 144 countries with $7.2 billion...

The International Business Council has developed a vision for the development of Kyrgyzstan's economy.
The International Business Council has developed a vision for the development of the Kyrgyz...

Bishkek Humanities University named after K. Karasaev
BHU Bishkek Humanities University was established on the basis of the Pedagogical Institute of the...
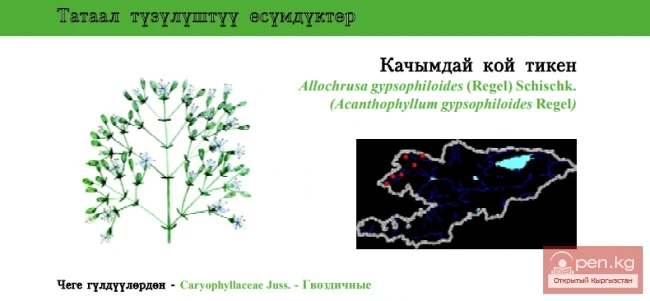
Spiny-leaved Allochrusa / Kachymday Koy Tiken / Gypsophila-like Allochrusa
Kolyuchelistnik kachimovidny Status: VU. A species with a rapidly reducing range. The roots of...
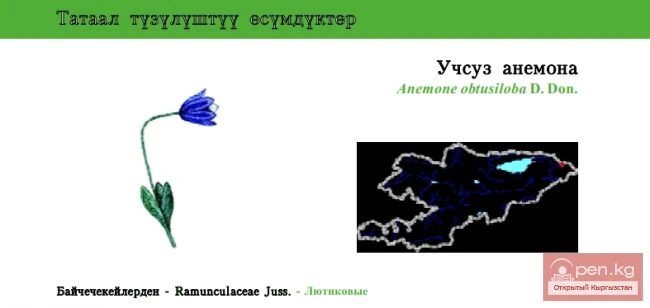
Obtusilobous Windflower / Uchsuz Anemone / Anemone obtusiloba
Obtusilobous Windflower Status: VU. The westernmost boundary of its range in Kyrgyzstan is located...
Kyrgyz Republic - This is Our Land
The Kyrgyz Republic is a country of Heavenly Mountains, stunning nature, and hospitable,...
Tulip Aspiring Upward / Chatkal Yellow Tulip
Chatkal Yellow Tulip Status: VU. An endemic species of the Chatkal Ridge with a decreasing...

Vladimir Ivanovich Nifadyov
Nifadyov Vladimir Ivanovich (1947), Doctor of Technical Sciences (1993), Professor (1995),...

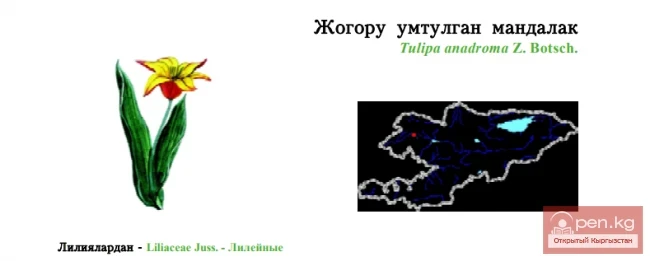
Pink Tulip / Little Red Mandala / Pink Tulip
Pink Tulip Status: EN. A narrowly endemic species of the foothills of the Turkestan Range, sharply...

Karataev Madaminzhan Musaevich
Karataev Madaminzhan Musaevich (1962), Doctor of Medical Sciences (2000), Professor (2002) Kyrgyz....
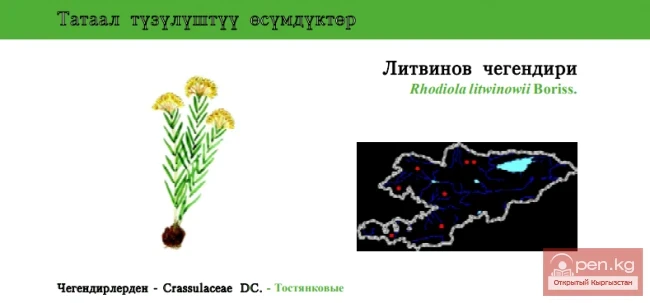
Litvinov's Rhodiola / Litvinov's Legend / Litvinov’s Rosewort
Rhodiola litwinowii Status: LC. A mosaic-distributed species, intensively used in agriculture....

Strange (Paradoxical) Honeysuckle / Укмуштуу шилби / Paradoxical Honeysuckle
Paradoxical Honeysuckle Status: Category CR B2ab(iii). A relict endemic species with a disjunctive...
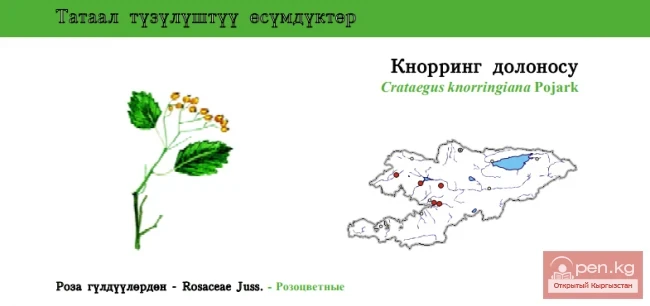
Knorring's Hawthorn / Knorring's Dolenos / Knorring’s Haw-tree
Knorring’s Haw-tree Status: VU. A narrowly endemic species....
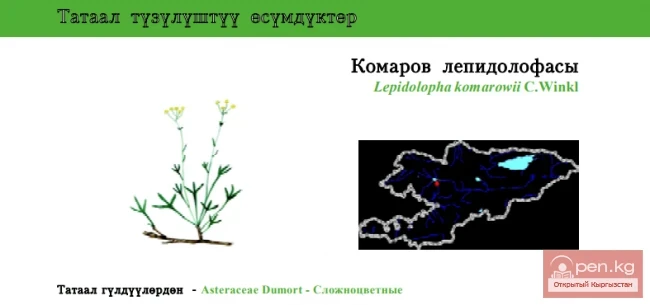
Lepidolopha Komarov / Komarov's Lepidolopha
Lepidolopha Komarovii Status: EN. An endemic species of mountainous Central Asia, representative...

Tamara Mikhailovna Sabitova
Sabitova Tamara Mikhailovna (1934), Doctor of Physical and Mathematical Sciences (1996),...

Niedzvetzki’s Apple-tree \ Red-leaved Apple
Niedzvetzki’s Apple-tree Status: VU. Very rare, endemic, endangered species with a small...
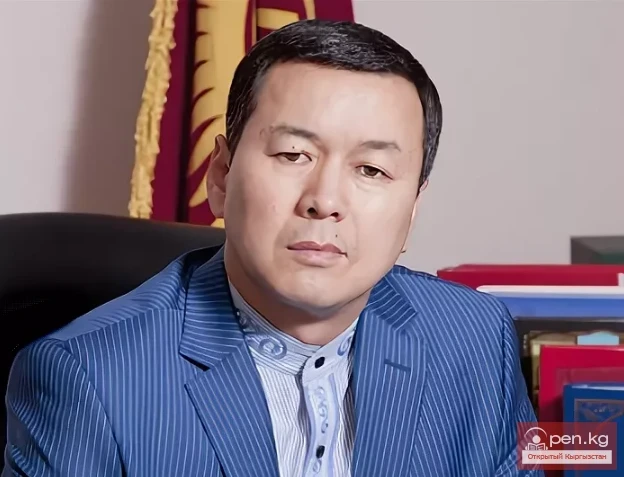

Hero of the Kyrgyz Republic Aliaskulov Aliyasbek Tolbashievich
Aliaskulov Aliyasbek Tolbashievich Born on May 5, 1971, in the village of Ken-Aral, Talas region....

Gray Monitor / Boz Echkemer, Boz Zemzem / Transcaspian Desert Monitor
Gray Monitor Status: Category CR A4bc; E. In Kyrgyzstan - fragmented populations of the declining...

Torobekova Chynara Kerimkulovna
Torobekova Chynara Kerimkulovna Painter. Born on August 18, 1950, in the village of Bystrovka,...

Mamitov Abakir
Mamyotov Abakir (1954), Doctor of Pedagogical Sciences (1999), Professor (1993) Kyrgyz. Born in...
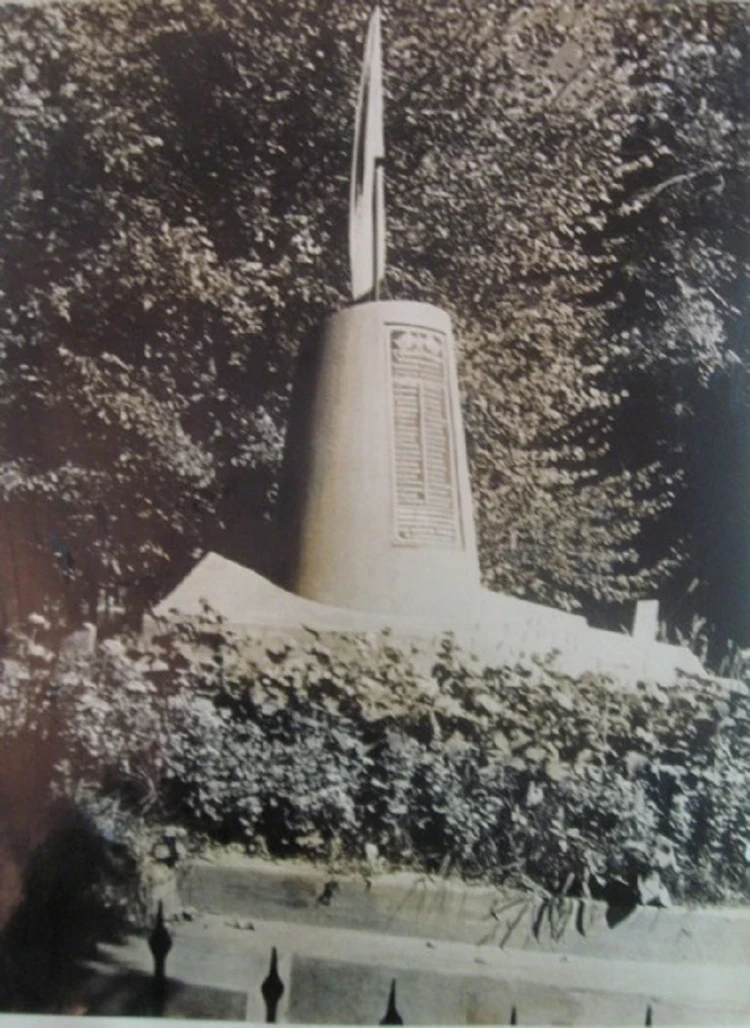

Consideration of the monument project at the Brotherly Grave in Dubovy Sad. Document No. 203 (June 1957).
Frunze, June 17, 1957 Having reviewed the model of the monument developed by the team consisting...

Nadtochiy Maria Alekseevna
Nadtochiy Maria Alekseevna Applied artist. Born on May 8, 1970, in the city of Frunze, Kyrgyz SSR....

Kononets Irina Evgenyevna
Kononets Irina Evgenievna (1950), Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor (2002) Russian. Born in...
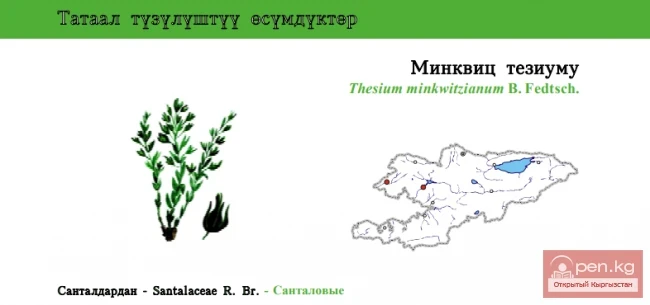
Minkwitz's Bastard Toad-Flax
Minkwitz’s Bastard Toad-Flax Status: CR. Subendemic. An extremely rare relict plant that is...
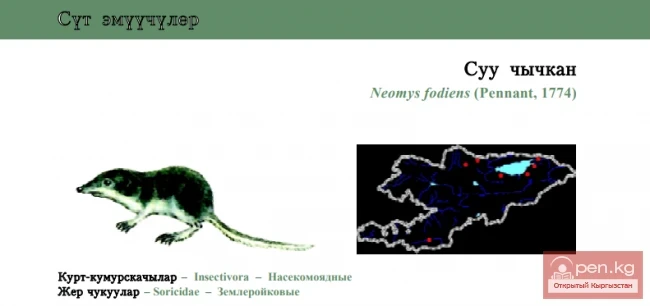
Common Water Shrew / Eurasian Water Shrew
Common Water Shrew Status: Category VI, Near Threatened, NT: R. A rare species for Kyrgyzstan,...

Korolkov's Sage / Korolkov Sage, Korolkov Kyok Bashy
Korolkov’s Sage Status: VU. A rare narrow endemic species. A highly decorative plant....

The History of Kyrgyz Printing
Printing in Kyrgyzstan On November 7, 1924, the first issue of the newspaper "Erkin-Too"...

Abdyldaev Baltabay Bapyshievich
Abdyldaev Baltabay Bapyshievich Painter. Born on May 13, 1962, in the Talas region....
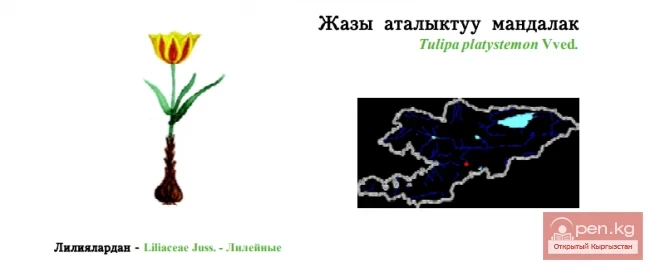
Broad-stamened Tulip / Tulip with Wide Stamens / Жазы аталыктуу мандалак
Broad-stamened Tulip Status: VU. A narrow endemic of the Alai Ridge....
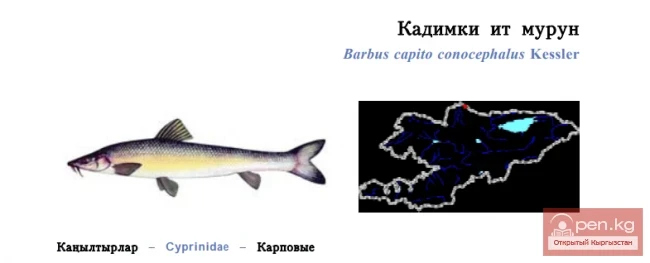
Turkestan Barbel / Kadimki It Murun / Turkestan Barbel
Turkestan Barbel Status: 2 [VU: D]. A subspecies that is endangered in Kyrgyzstan. One of...

Kashgarian Barberry
Kashgarian Barberry Status: VU. Rare species....

Talaibek Jumashievich Koichumanov
Koychumanov Talaybek Jumashovich (1956), Doctor of Economic Sciences (2000) Kyrgyz. Born in the...

Valentina Markovna Nikulina
Nikulinа Valentina Markovna Applied artist. Born on October 16, 1938, in Kyiv. In 1962, she...

Uzun-Akhmat Grape \ Uzunakmat Grape
Uzun-Akhmat Grape Status: VU. Endemic species of Western Tien Shan....

Tenyizbaeva Begaiym Sadikovna
Tenizbaeva Begayim Sadikovna Applied artist. Born on September 18, 1954, in the city of Frunze. In...

Kashgarian Bean Caper
Kashgarian Bean Caper Status: VU. Rare, little-studied endemic species....
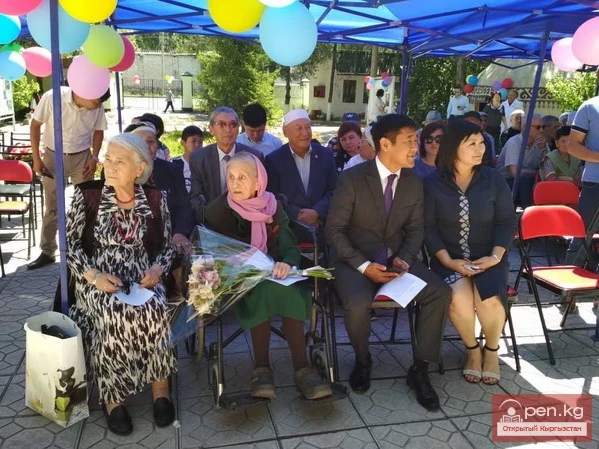

The teacher of Chinghiz Aitmatov turns 100 years old.
Anna Semyonovna Kramaryova has turned 100 years old — the teacher of Chingiz Aitmatov. Anna...
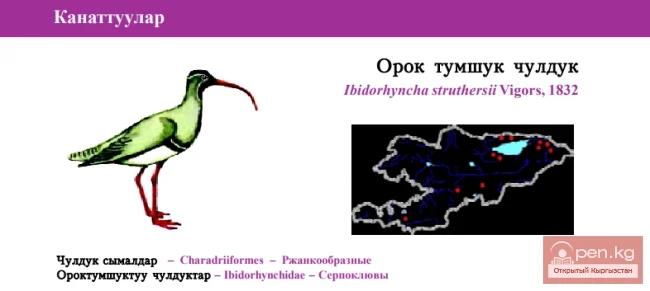
Curlew Sandpiper / Orok Tumshuk Chuldak / Ibisbill
Ibisbill Status: V category, Vulnerable, VU: R, D1. A small number of stenobiont species, at risk...

Hero of the Kyrgyz Republic Abasamat Masalievich Masaliev
Abasamat Masalievich Masaliev — Soviet and Kyrgyz party and state figure. Born on April 10, 1933,...

Kailbuldayeva Saltanat Asanovna
Kailbuldayeva Saltanat Asanovna Graphic artist. Born on March 7, 1959, in the village of...

Tekенов Zhapар
Tekenev Zhapар (1933), Doctor of Technical Sciences (1991), Professor (1994), Corresponding Member...

Brimkulov Ulan Nurgazievich (1948)
Brimkulov Ulan Nurgazievich (1948), Doctor of Technical Sciences (1992), Professor (1995),...

Zoya's Yellow Desert Candle
Eremurus zoae Status: VU. A narrowly endemic species of the Kyrgyz Range....
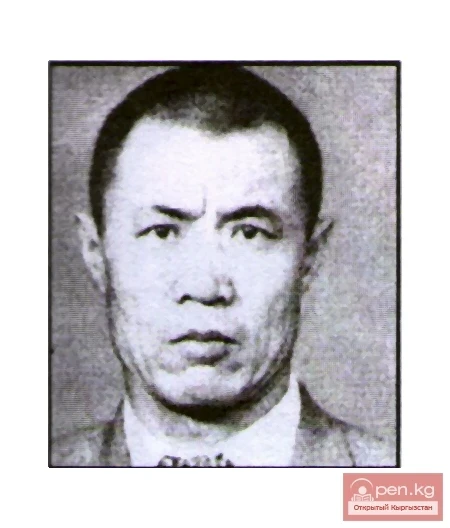

Keldibay Alymkulov (1943)
Alymkulov Keldibay (1943), Doctor of Physical and Mathematical Sciences (1991), Professor (1998)...

Population of Kyrgyzstan as of January 1, 2013
Population of Kyrgyzstan Thanks to the fundamental changes that occurred in Kyrgyzstan after the...
