American Urologist: Breast Enlargement Occurs in 30-50% of Men, Milk Production Possible in Rare Cases
Men who come to me for consultation sometimes humorously, and sometimes awkwardly, talk about "man boobs." For some, it's just a layer of fat, while for others, it's gynecomastia—a medical term for the enlargement of breast tissue. In most cases, there is a combination of both factors.
Gynecomastia occurs much more frequently than many think. Studies show that asymptomatic breast enlargement—without pain or discomfort—occurs in 30-50% of healthy men. This indicates that nearly one in two men may experience breast enlargement at some point in their lives, even if they do not notice it.
Structure and Function of Breast Tissue
In both men and women, breast tissue is located above the pectoral muscles and consists of fatty and glandular tissues.
Fatty tissue determines the shape and size of the breast, changing with weight loss or gain. Glandular tissue, made up of milk ducts and supporting structures, responds to hormones. In women, estrogen promotes tissue growth, especially during puberty and pregnancy. In men, testosterone keeps the tissue in an undeveloped state, but the structure remains unchanged: ducts, glands, and nipples.
This is why men can also suffer from breast diseases, such as gynecomastia or, in rare cases, cancer. Understanding the combination of fatty and glandular tissue explains why "man boobs" can mean different things depending on what exactly is enlarging.
The formation of breast tissue in the fetus occurs according to a "female pattern." Nipples develop before the Y chromosome activates male traits. By the time testosterone begins to act, the nipples are already formed—this is a harmless evolutionary artifact indicating the similarity of breast structures in men and women, although in men they are predominantly inactive.
While it may seem like a myth, under certain conditions, men can indeed produce milk. The structure of breast tissue in men is similar to that in women, including milk ducts and cells capable of producing milk. However, testosterone usually suppresses these cells and regulates the overall hormonal balance. Men do not experience the hormonal surges of prolactin that occur in women.
Some medications that increase prolactin levels, as well as pituitary diseases, chronic liver diseases, or hormone therapy for prostate cancer, can sometimes activate these cells. This can lead to galactorrhea, or unintentional milk discharge. This condition is rare and usually not dangerous; however, if the discharge becomes persistent or contains blood, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Pseudogynecomastia: “Man Boobs” Related to Fat Tissue
Fat is the primary reason men notice breast enlargement. When gaining weight, fat can accumulate in the breast area, just as it does in other parts of the body. This condition, known as pseudogynecomastia, is very common, especially considering that two out of five men in the U.S. suffer from obesity.
This type of breast enlargement feels soft and evenly distributed, rather than hard or painful. It poses no medical threat and usually resolves with weight loss, exercise, and a shift to a healthier lifestyle.
Gynecomastia: True Growth of Glandular Tissue
Gynecomastia is the enlargement of glandular tissue in the breast under the nipple and areola (the darker area around the nipple) and is not related to fat tissue. This tissue can become denser and sometimes painful, located directly under the nipple.
The growth of tissue occurs with changes in the ratio of testosterone to estrogen. During puberty, up to 66% of boys may experience varying degrees of gynecomastia. This condition is usually temporary and does not require treatment, as it often resolves on its own as hormonal levels stabilize. Reassurance and patience are often the best strategies in this case.
However, gynecomastia affects not only adolescents. In older men, hormonal changes can also manifest. With age, as testosterone levels naturally decline, gynecomastia becomes more common, often in conjunction with weight gain or the use of medications that affect hormone levels.
Other Factors Influencing Glandular Tissue Enlargement
Changes in breast tissue in men can be caused by more than just hormones. Medications, substances, and diseases can also play a significant role.
Finasteride, used for hair loss or benign prostatic hyperplasia, as well as bicalutamide, used for prostate cancer treatment, can alter the action of testosterone and contribute to breast tissue enlargement. I have seen patients return for treatment months after starting these medications, concerned about unexpected changes in their breasts. In some situations, stopping the medication can reverse the changes. However, if the tissue has been in the body long enough, it may not fully regress.
Frequent or heavy use of alcohol and marijuana can also disrupt hormonal balance. Anabolic steroids, common among bodybuilders, are also a contributing factor to breast changes.
Diseases of the thyroid, liver, or kidneys can also affect hormonal levels, leading to breast tissue enlargement. In such cases, changes in the breast may signal more serious health issues.
Psychological Impact
Gynecomastia can negatively affect self-esteem, posture, and even social interactions for many men. Some avoid the gym or beach, prefer to wear baggy clothing, or experience anxiety in intimate relationships. I remind patients that this is a common condition, and discussing it is not a sign of vanity, but rather a helpful step.
For adolescents, the best approach is to act with confidence and patience, as pubertal gynecomastia most often resolves naturally. Adults should focus on identifying the causes, addressing them, and seeking optimal medical, surgical, and wellness strategies.
When to Seek Medical Help
About 1% of all breast cancer cases occur in men. Therefore, any new lumps or changes in the breast require medical attention. However, most men noticing changes have nothing to do with cancer.
Generally, breast enlargement in men is safe; however, some concerning symptoms should never be ignored. Hard lumps, unilateral breast growth, nipple discharge, or rapid enlargement are factors that require examination by a doctor to rule out breast cancer. Persistent or painful gynecomastia, as well as changes causing significant discomfort, also require specialist attention.
Treatment Methods
The choice of treatment depends on the cause. If the problem is caused by a new medication, changing the drug may be sufficient. Reducing alcohol, marijuana, or steroid consumption can help, although tissue damaged over a long time may not fully regress.
For overweight men, weight loss can be very beneficial. Pseudogynecomastia often decreases with fat loss. Even if true breast tissue is involved, reducing fat mass can lower estrogen levels, which may exacerbate the problem. Strength training aimed at building pectoral muscles can also help improve the shape of this area and boost confidence.
Some men believe they can "get rid" of gynecomastia through push-ups or bench presses. While building muscle helps burn fat and improve breast contours, it does not reduce the volume of glandular tissue. If the issue is true gynecomastia, no amount of exercise will completely eliminate it—in such cases, it is advisable to consult a doctor for a more detailed analysis.
If glandular tissue does not disappear, surgical intervention may be considered. Breast reduction is one of the most common cosmetic surgeries among men, allowing for the removal of glandular tissue and contouring the breast to give it a more masculine appearance. However, not all men want or need surgery. Compression or corrective garments can make the breast appear flatter and enhance self-confidence.
For men with confirmed low testosterone levels, hormone replacement therapy can sometimes help restore balance and reduce breast tenderness. However, this is not a one-size-fits-all approach. In men with normal testosterone levels, additional hormone therapy may exacerbate the problem by converting the hormone to estrogen, which promotes breast tissue growth. Therefore, replacement therapy should only be prescribed under a doctor's supervision after necessary examinations, and not as a standalone solution.
Full translation of the CNN article "Not just fat: The truth about ‘man boobs’."
Read also:
Study: The Number of Cancer Cases Related to Obesity is Rising
A recent global study indicates an increase in cancer cases among youth worldwide, with obesity...
Trees were planted in Botaliyev Park in support of women facing oncology.
On October 25, an event called "Alley of Life" was organized in Bishkek at A. Botaliev...

The CEC summarized the results of candidate nominations: the 27th district became the most competitive
On October 30 at 18:00, the period for submitting applications for candidate nominations for the...

Vladimir Georgievich Yakovlev
Yakovlev Vladimir Georgievich (1915-1994), Doctor of Biological Sciences (1963), Professor (1967),...
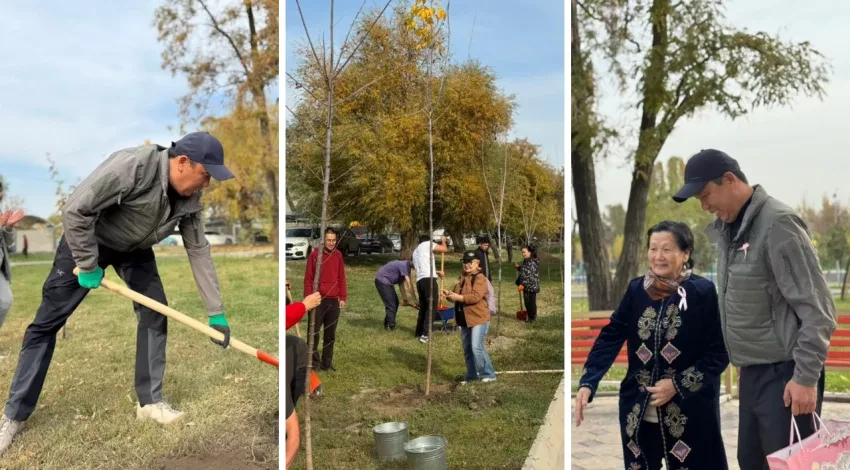

In Bishkek, the "Alley of Life" was planted: over 100 trees as a symbol of victory over cancer
As part of the event, more than 100 young trees were planted, forming a picturesque "Alley of...

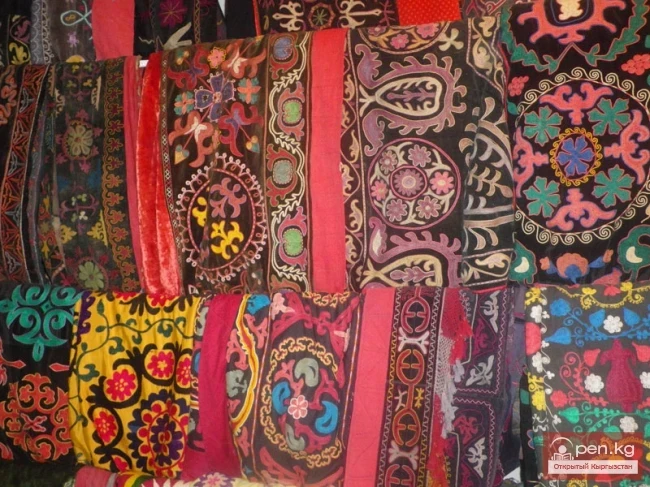
The title translates to "Fabric 'Besh Keshte'."
Sample of patterned fabric 'besh keshté'. Nookat District. The most vibrant and colorful...
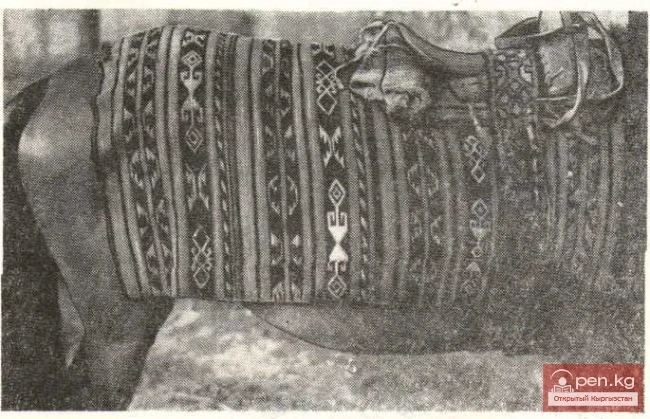

The title translates to "Khadzhary Fabric."
A saddle blanket made from strips of "kadjary" fabric Fabrics made using the...

Men need to exercise twice as much as women to have a healthy heart
A study conducted by a group of scientists from China has shown that women engage in physical...

Reported by the National Statistical Committee
National Statistical Committee: Female Population Predominates in Cities of Kyrgyzstan, While Male...
The Mufti of Kyrgyzstan called on men to respect and protect women
The Mufti of Kyrgyzstan, Abdulahiz Zakirov, spoke out about the importance of respecting and...
Fabric production increased by 47% over the year — to 19.8 million sq. m
- The production volumes of textiles and clothing in Kyrgyzstan have shown growth in most...

Creating Patterned Fabric
Typically, two women work on the navoi. One unwinds the threads onto the warp (erish) of the...
Scientists have found a molecule that helps the heart recover after a heart attack
A group of scientists from the Temple University School of Medicine (USA) has identified a new...
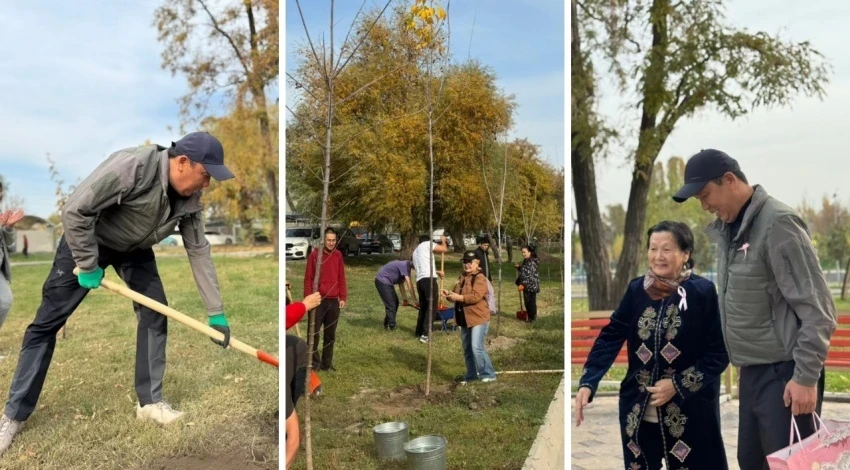

More than 100 trees planted on the "Alley of Life" as a symbol of victory over cancer
In the capital, at Botaliyev Park, an event was held to support women who have faced cancer. Among...

WHO: Alcohol is one of the main causes of cancer in Europe, costing the EU billions of euros
In the European Union, where alcohol consumption levels are among the highest in the world,...
Non-communicable diseases cost the economy of the Kyrgyz Republic nearly 30 billion soms
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) inflict an economic loss of 29.8 billion soms on the economy of...
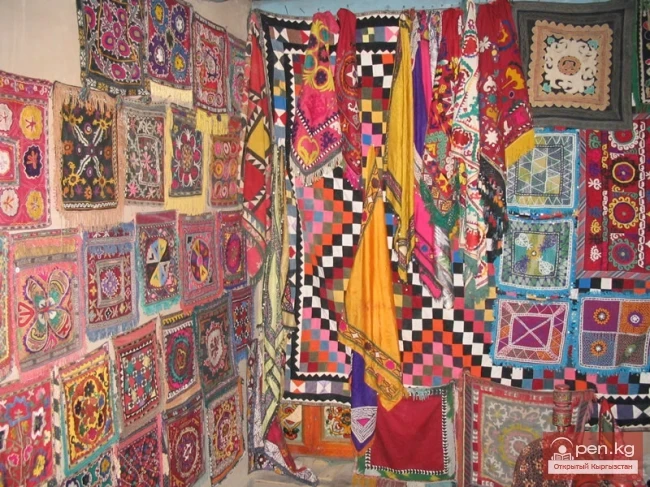

Fabrics of Kyrgyz Production
Fabrics of Kyrgyz production are characterized by plain weave, which is considered the simplest...
The Story of Kyrgyzstani Sardarbek Su laymanov in Denmark: Even Using the Toilet Doesn't Save You from Fare Evasion
Sardarbek, born on August 24, 2003, in the Nookat district of the Osh region, currently lives in...
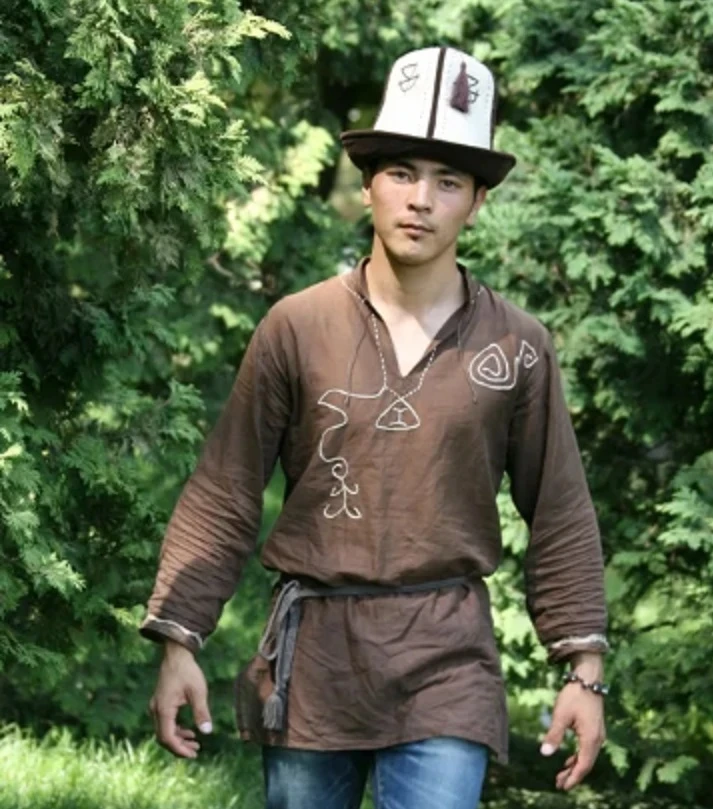

Men's Clothing of the Kyrgyz. Open-front Shirt
The main items of men's undergarments in the 19th century among the Kyrgyz were the open...
Hidden fat, not excess weight — the real cause of cardiovascular diseases
According to the findings of the study, visceral fat located in the abdominal area and surrounding...

In Bishkek, a tree planting event took place as a symbol of victory over cancer
Photo from the archive of Almagul Ibraeva In the capital of Kyrgyzstan, in Botaliyev Park, a...
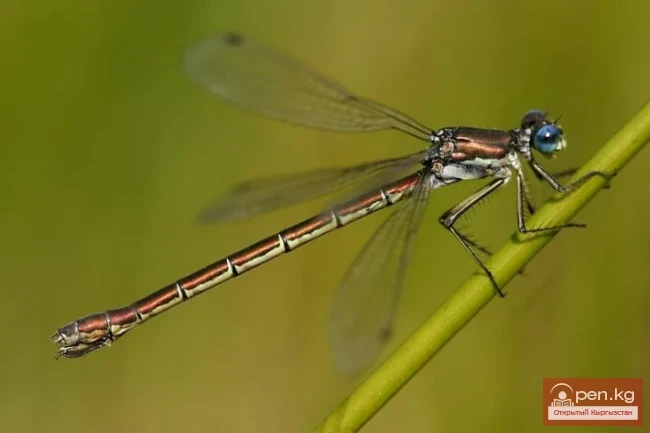

Dull Bitterling - Gray Bitterling
Dusky Darner - Sympycna fusca V. d. Lind. The body of this dragonfly is mainly brown-bronze in...
The doctor explained whether there are side effects of the flu vaccine.
On the air of "Birinchi Radio," family doctor Elmira Agalieva shared information about...
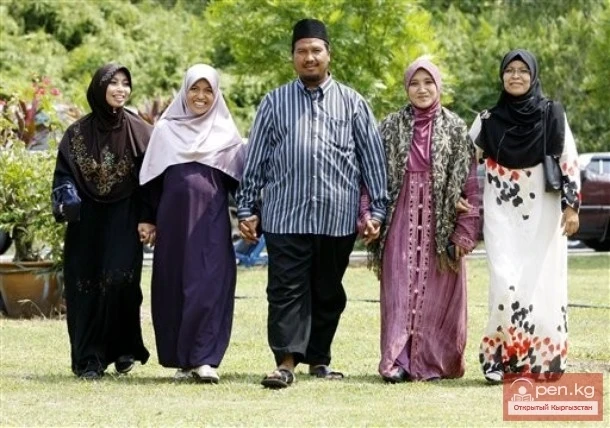

Polygamy
One of the major surahs of the Quran (the 4th surah, consisting of 175 verses) is called...
Salaries in Education Are Growing Slower Than in Other Sectors
According to the latest data from the National Statistics Committee, the average nominal salary in...

Patterned Weaving
Alongside the production of simple solid-colored or striped fabrics used for making clothing and...
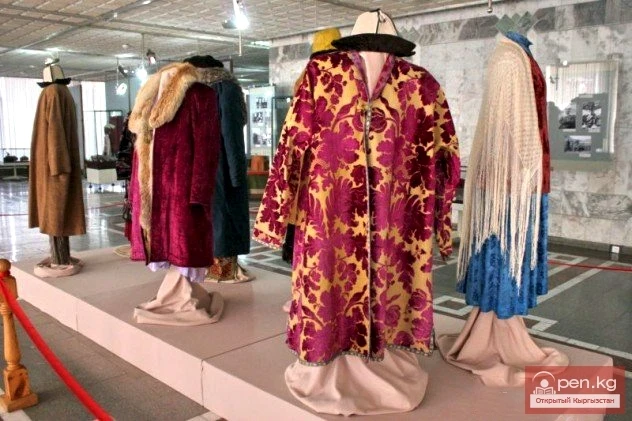

Clothing of the Kyrgyz
Researchers note the traditional nature of the clothing of the peoples of Central Asia, which has...

Fabric "terme"
The fabric "terme" is known to all Kyrgyz people. It is widely used among the...
In Kyrgyzstan, the production of mandarins, oranges, and lemons has increased
In Kyrgyzstan, there is an increase in the production of citrus fruits such as mandarins, oranges,...
Nobel Laureate in Economics Identifies Main Reasons for Declining Birth Rates Worldwide
Claudia Goldin, a Nobel Prize-winning economist, published a study analyzing the key reasons for...

Tynaliev Medin Tynalievich
Tynaliev Medin Tynalievich Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Corresponding Member of the...

What is the most important thing for a Kyrgyz?
Men and Women An elder was asked: "Who are more numerous - men or women?" - Of course,...
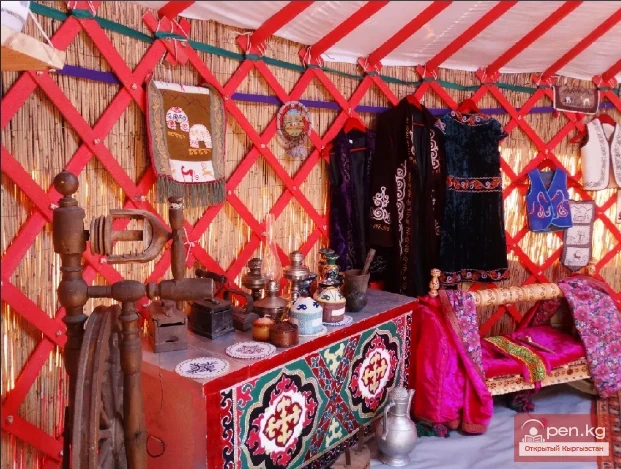

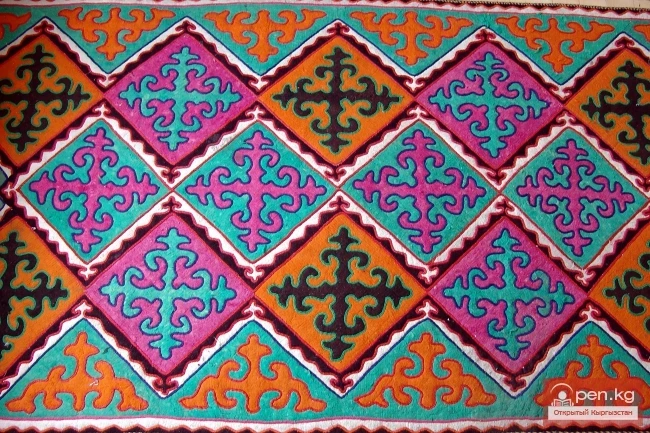
Traditions of the Folk Craftsmanship of the Kyrgyz
Traditions of Folk Craftsmanship. The uniqueness of the lifestyle of the Kyrgyz herders determined...
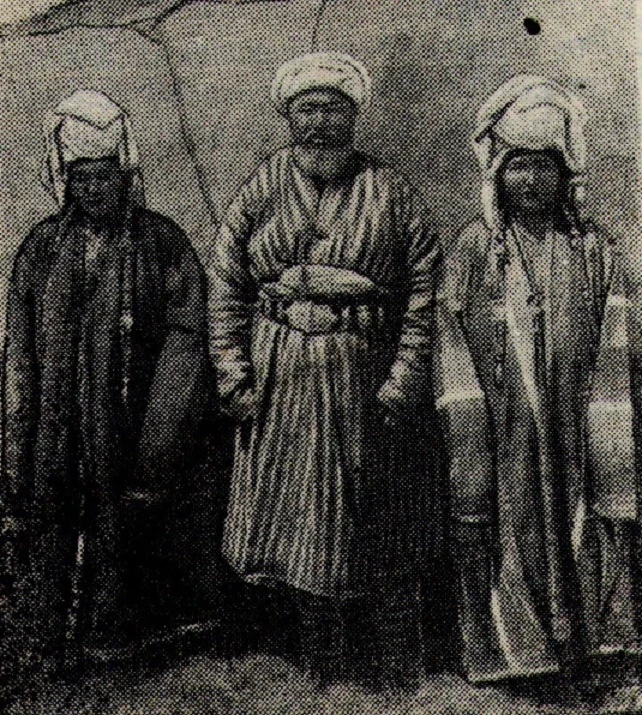

Clothing of the Southern Kyrgyz. Part - 1
The clothing of the southern Kyrgyz has not received special attention in literature. There are...

Kyrgyz Weaving Loom
The southern Kyrgyz are also known for a manual device for cleaning raw cotton from seeds — the...
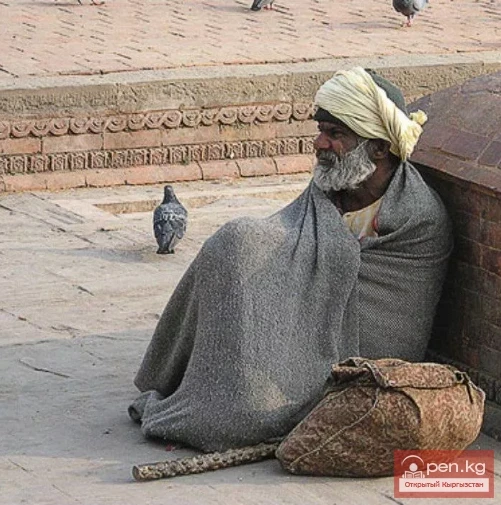

"See with the Heart"
"Spring will come, but I will not see it" Once, while traveling in distant lands, a...
The production of non-metallic products increased by 31.8% over 9 months
According to statistical data, from January to September 2025, there is a significant increase in...
Flu and ARVI Season. FOMS Reminds What Medical Services Are Provided for Free
The Mandatory Health Insurance Fund (MHIF) reminds that with the onset of autumn and winter, there...
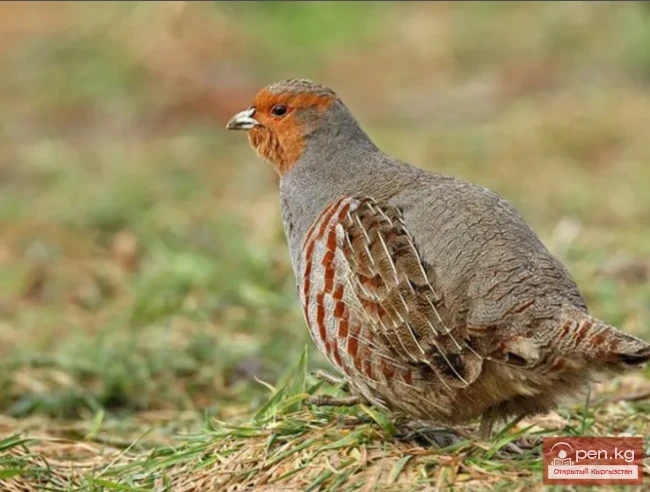

The title translates to "Partridge - Kekilikti."
Partridge (gray, bearded) — widely distributed species. Description of the bearded partridge: Very...

In Suzak, two men were detained for deceiving a local resident out of 1 million soms
Two men suspected of fraudulent activities have been detained in the Suzak district, reports the...
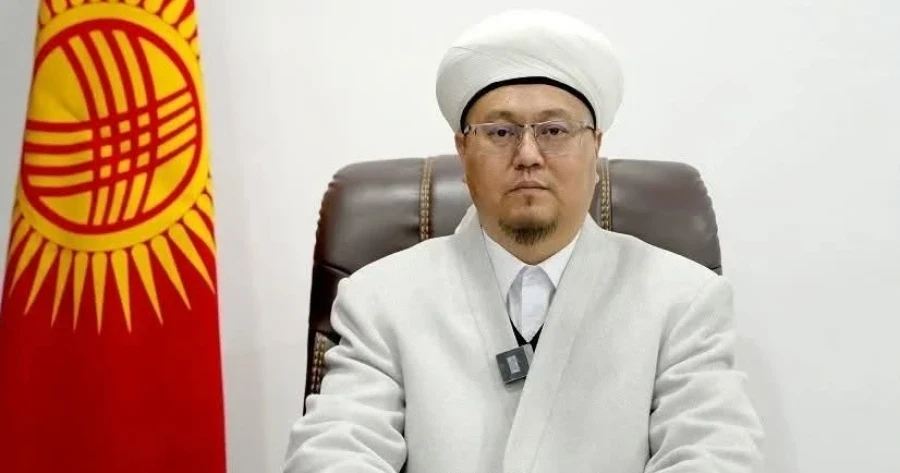

Abdulaziz Zakirov: Respect for Women is a Sign of Faith
“And cruelty towards her is spiritual darkness” In his address to the people of Kyrgyzstan, titled...

In Kyrgyzstan, 130 shipments of goods and animals were not allowed in over nine months
Out of the 130 returned batches: • 39 return acts were sent to the Republic of Kazakhstan...

Weaving
Among other domestic crafts, weaving held one of the primary places among the Kyrgyz in the past....

Babich Valentina Vasilievna
Babich Valentina Vasilievna Candidate of Technical Sciences, laureate of the State Prize of the...
The Nature of Kyrgyzstan
The incredible beauty of Kyrgyzstan's nature...