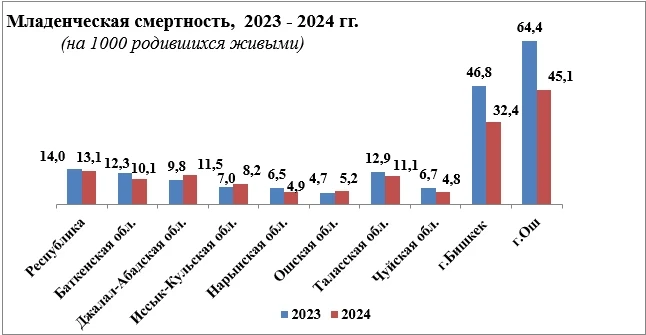
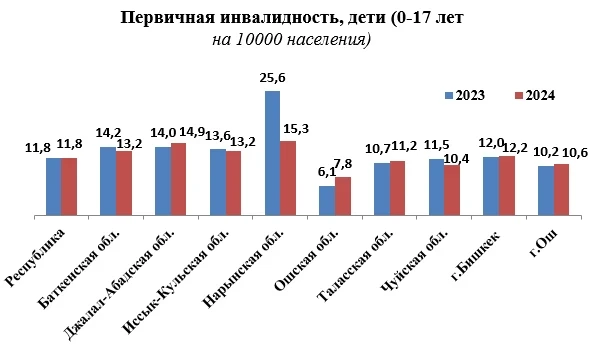
A team of specialists from Sun Yat-sen University analyzed data from over 226,000 adult participants in the UK Biobank, whose observations lasted an average of nearly 14 years. During this period, 2,893 individuals were diagnosed with kidney stones.
Study participants provided information about themselves, including personal details, type of employment, and lifestyle.
It was found that people working during evening hours, at night, or on a shift schedule are 15% more likely to develop kidney stones compared to those working a standard schedule from 9:00 AM to 5:00 PM.
The risk is even higher for two specific groups:
- Night shift workers — 22% higher likelihood of disease
- Those frequently changing work shifts — 19% higher likelihood
The most pronounced negative effect is observed in individuals under 50 years old and those who do not engage in physical labor.
Researchers concluded that the reasons for the connection between shift work and the formation of kidney stones lie in a higher level of harmful habits among people with non-standard schedules:
- Smoking
- Disrupted sleep patterns
- Excess weight
- Low physical activity
- Insufficient fluid intake
Scientists emphasize that shift work is a significant risk factor for the development of kidney stones. To minimize negative consequences, employers are recommended to:
- Implement employee wellness programs
- Promote a healthy lifestyle
- Assist workers in overcoming harmful habits
Note: Kidney stones are a common urological condition affecting 1% to 13% of the population in different countries. Contributing factors to stone formation include genetic predispositions, metabolic disorders, and lifestyle characteristics.