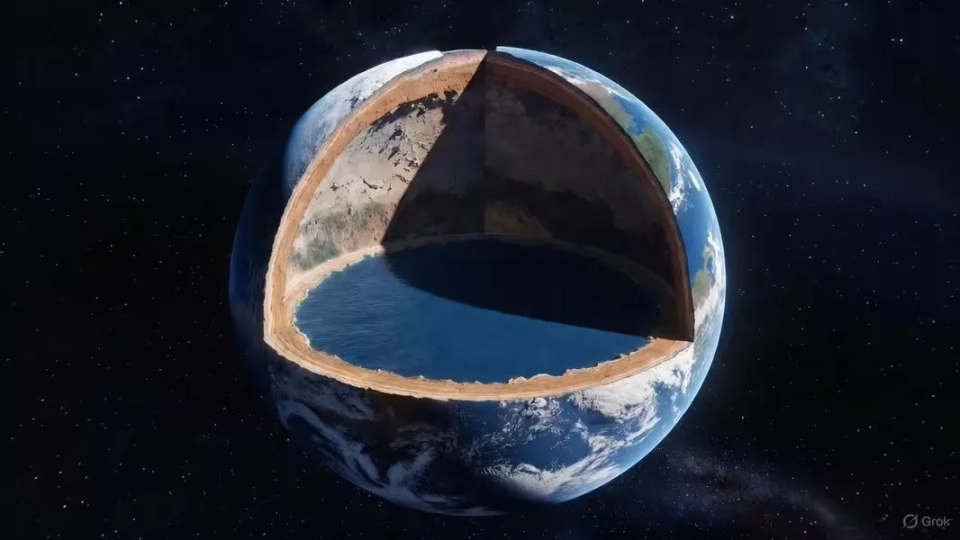
"Deep within the Earth, a 'superocean' may exist: this is indicated by the results of a new experiment"
A team of researchers has developed an innovative technological platform that was able to simulate the conditions existing 660 kilometers underground, where the pressure reaches 23-32 GPa and the temperature ranges from 1273 to 2100 K.
According to scientific data, the Earth 4.6 billion years ago was not like it is today. As a result of frequent collisions with other celestial bodies, its surface and interior were filled with molten oceans of magma, which prevented water from existing in a liquid state and made the emergence of life impossible. As the magma ocean cooled, it crystallized into solid minerals, forming the mantle.
Bridgmanite, the mineral that forms first in the mantle, makes up more than half of its composition. It acts as a "container for storing water," and its ability to retain moisture determines how much water can be transferred from magma to the solid part of the Earth.
Recent studies show that minerals can hold significantly more water at elevated temperatures. This discovery suggests that during the peak temperatures of the "magma ocean," bridgmanite could have captured and retained much more water than previously thought.
The crystallization model created based on experimental data demonstrates that after the solidification of the magma ocean, the lower mantle became the largest reservoir of water in the solid mantle, with a storage potential that could exceed previous estimates by 5 to 100 times.
Read also:

Continents are "peeling off" from the bottom and feeding oceanic volcanoes, - geologists
British researchers have made a revolutionary discovery, uncovering the mechanism by which...
Satellites of "rogue planets" can remain habitable after a star explosion
A team of international researchers from Hungary conducted simulations covering over 4,000...

Global warming may unexpectedly trigger a new ice age
Research conducted by scientists from the MARUM Center for Marine Environmental Sciences at the...

Scientists believe that human activity has caused the tilt of the Earth.
The research is based on the principle of conservation of angular momentum, which states that...
What will the weather be like in Bishkek on November 2?
Bishkek November 2, Sunday At night, the temperature will be from +1 to +3 °C, with overcast...

Several Interesting Facts About Planet Earth
Unique Planet Earth Planet Earth is just one of eight (according to the latest data) planets in...
In Kyrgyzstan, the volume of pension financing amounted to 96.1 billion soms
According to preliminary data, from January to November 2023, pension funding in Kyrgyzstan...
In Tehran, warnings issued about possible nighttime water outages due to severe drought
According to Euronews, the water level in the reservoirs supplying Tehran has reached a...
No precipitation, daytime temperatures will rise to +20 — weather forecast for November 27
Weather overview in Kyrgyzstan for November 27. According to information from Kyrgyzhydromet, no...
Scientists have created a neuroimplant that restores vision even in complete blindness
A team of international researchers has developed a neuroimplant measuring just 2×2 mm, which is...

Express Facts about Earth
Air pollution in China is so severe that it can be seen from space. A cubic meter of the...

Diving at Toktogul Reservoir
Geographical Reference: Toktogul Reservoir is formed by the dam of the Toktogul Hydroelectric...
In the city of Osh, drinking water will be turned off for a day on the right bank of Ak-Buura.
In the city of Osh, a temporary shutdown of drinking water will affect the right bank area. This...
In Kyrgyzstan, there are 44 deposits of underground fresh and mineral waters
According to statistical data, the Kyrgyz Republic has 44 deposits of underground fresh and mineral...

Uranus and Neptune May Turn Out to Be Rocky Worlds Instead of Icy Ones
The solar system is traditionally divided into groups based on composition: four rocky planets...

TMK approaches commercial gas production indicators in Mongolia
The TMK Energy company's project for the development of the Gurvantes XXXV coal seam in...

Astronomers have discovered a previously unknown quasi-moon near Earth
Illustrative photo Recent studies by astronomers have revealed an interesting cosmic object that...
Master Plan 2050. Bishkek Plans to Introduce a Limit on Drinking Water Consumption
In order to prevent a shortage of drinking water in Bishkek, the authors of the general plan...

Carbonated Water in the Chayek Well
Carbonated water in the Chaek well. For now, this is the only well of its kind in the republic...
A 7.6 Magnitude Earthquake Occurred in Japan, Tsunami Threat Declared
Today, at 23:15 local time (20:15 Bishkek time), a strong earthquake occurred off the eastern coast...

The population of Tehran may be evacuated due to a water shortage
Critical situation with water supply in Tehran: reservoirs are depleting Due to a lack of water,...
The annual damage from the use of the Toktogul Reservoir in irrigation mode amounts to $155 million, - Institute of Water Problems
According to information provided by Rysbek Satylkanov, the annual damage from the operation of the...

Diving at Lake Merzbacher
Geographical Reference: In the eastern part of Kyrgyzstan, where the northern and southern arcs of...
Part of Bishkek is left without drinking water
In Bishkek, the temporary suspension of drinking water supply has affected several microdistricts....
New Vaccine Prevents the Development of Aggressive Cancer in 88% of Cases
The developed vaccine has shown impressive results in experimental mice: according to previous...
Central Asian countries agreed on water limits for 2025-2026
The State Commission for the Coordination of Water Management in Central Asia has approved limits...
Call Center: Residents of Lomonosov Street Oppose the Construction of a Five-Story Building
Local residents of the Lenin District have appealed to the President of Kyrgyzstan with a request...

Interesting Facts About the Earth's Population
The Earth's Population This is the total number of people living on our planet. As of today,...

Tortkul Reservoir
Tortkul Reservoir is a unique structure. It is located in the Batken region on the Isfara River....
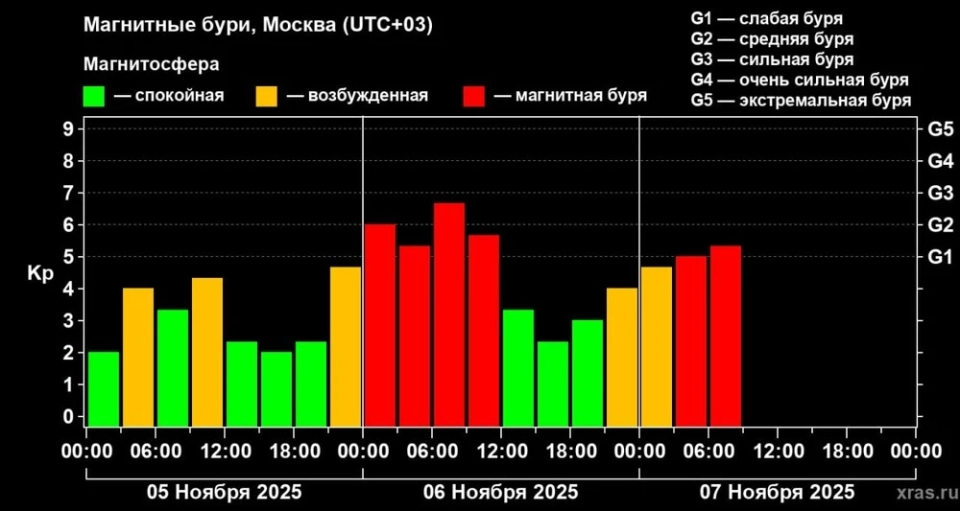
The largest geomagnetic storm of this year has begun on Earth
On this day, the Earth is facing the influence of a large coronal hole and two streams of plasma...
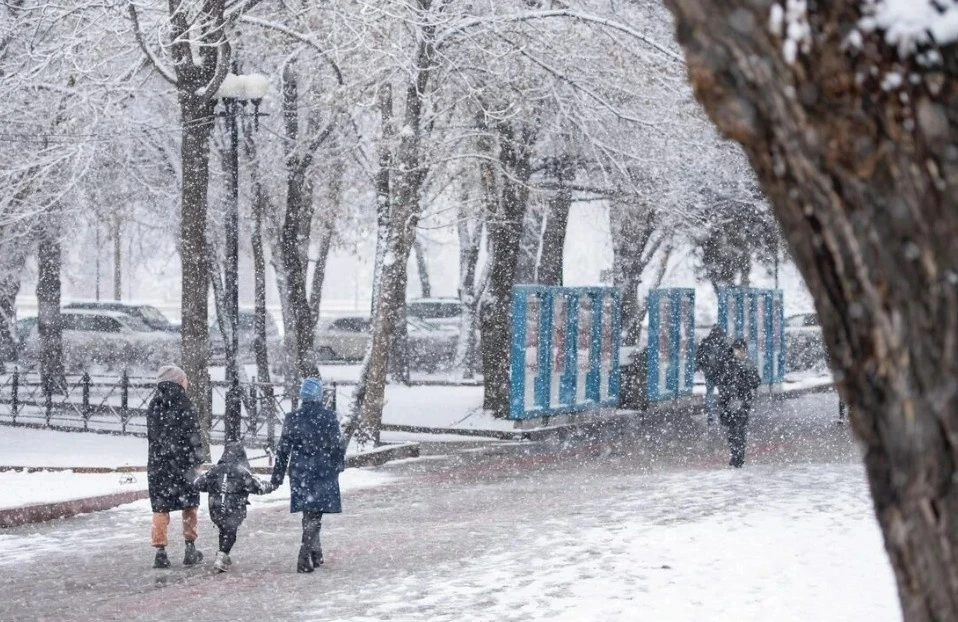

A sharp drop in temperature to -33° is expected in Kyrgyzstan
According to meteorologists, from December 8 to 10, Kyrgyzstan is expected to experience sharp...
In Bishkek, no precipitation, warm during the day up to +16 — weather forecast for November 28
Weather conditions in Kyrgyzstan on November 28. According to the Kyrgyz Hydrometeorological...

What are mineral waters, and what types are available in Kyrgyzstan?
The components and indicators that provide grounds for assessing water as mineral can include the...
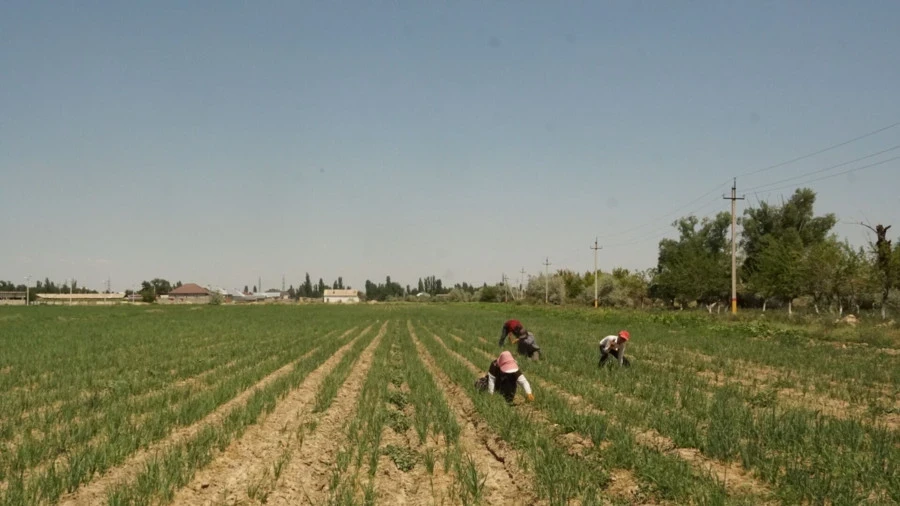

In southern Kazakhstan, a shortage of irrigation water is forecasted in 2026.
At a government meeting held on Tuesday, Deputy Prime Minister Kanat Bozumbaev voiced a concerning...
Astronomer Expresses Concerns About the Possible Extraterrestrial Nature of the Interstellar Object 3I/ATLAS
Object 3I/ATLAS, which was discovered in July of this year and has a mass comparable to Manhattan,...
Floods and landslides in Vietnam claimed the lives of 41 people
Local media report that more than 60,000 people have been forced to leave their homes, while around...
Kyrgyzstan is among those economies that can make a "structural leap" through processing in industrial sectors, - EDB
- Analysts of the EDB presented an assessment of the industrial potential of the Kyrgyz Republic...
Accident on the water main of Bishkek's 5th microdistrict has been resolved. Water supply has resumed.
In Bishkek, on November 14, the work to restore the water supply system after the accident on the...
Scientists have created the largest map of Ancient Rome's roads in history
Researchers from nearly 40 countries, including regions from North Africa to the United Kingdom,...
In the Talas District, work is underway to lay concrete pavement on the "Big Canal"
- In the Talas region, where work is underway to lay a concrete surface on the "Big...
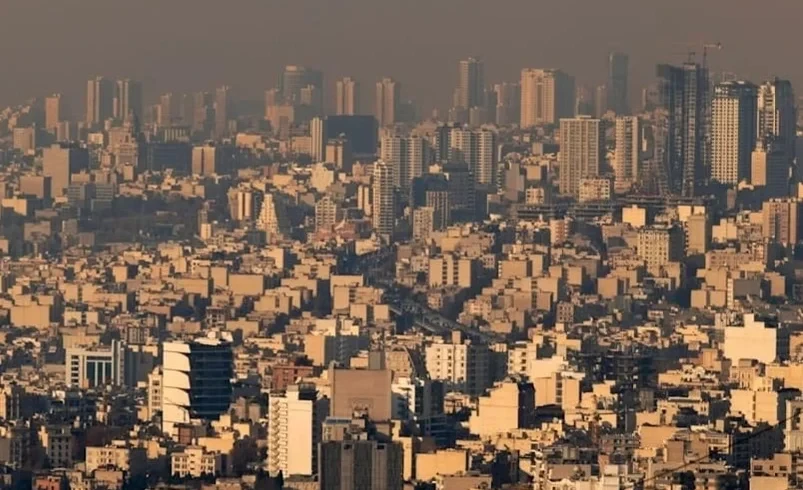

Tehran May Run Out of Water: Evacuation Plan Being Prepared
Tehran is facing a critical situation with water supply, and local authorities are considering the...
In the southern part of Bishkek, there is no water due to damage to the water pipeline.
On the night of November 14, the press service of the Bishkek mayor's office announced the...

Land Resources. Their Role in Nature and Human Life.
Land resources refer to lands that are systematically used or suitable for use for economic...

The title translates to: "The 'Night at the Museum-2014' event took place in Bishkek."
Last weekend, the State Historical Museum opened its doors with a special program - a night event....
