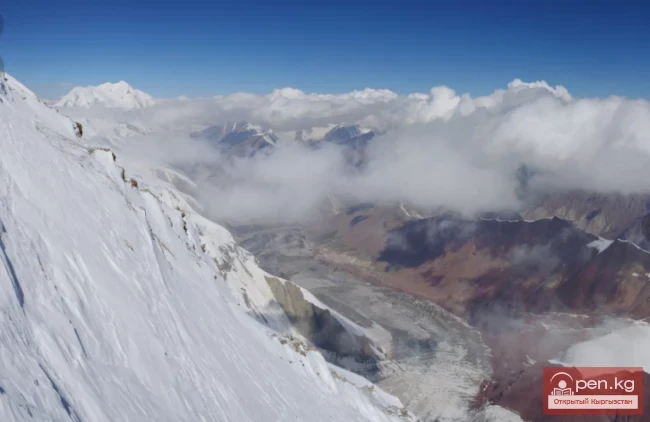
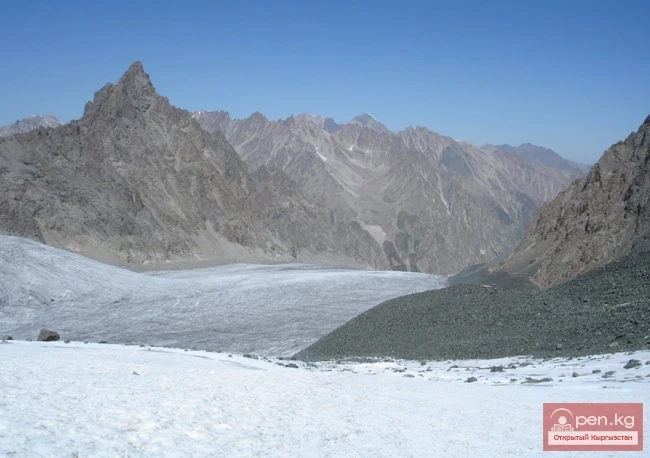
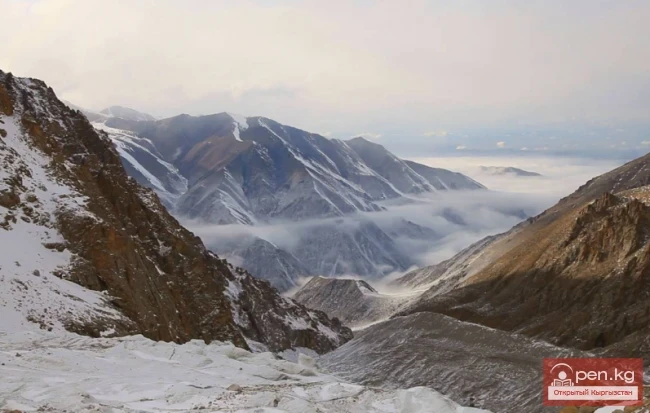
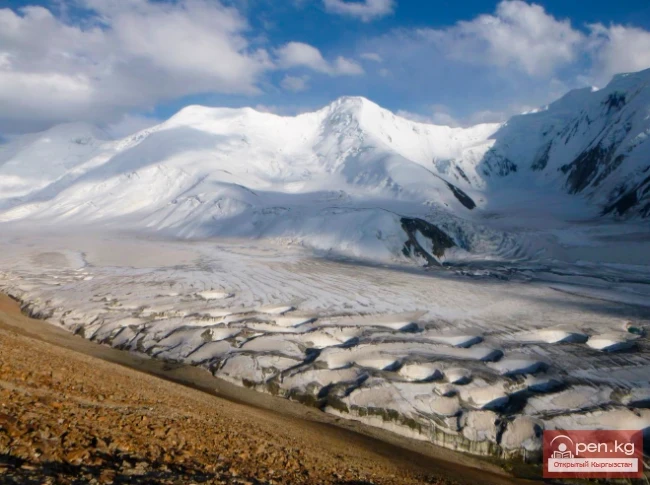
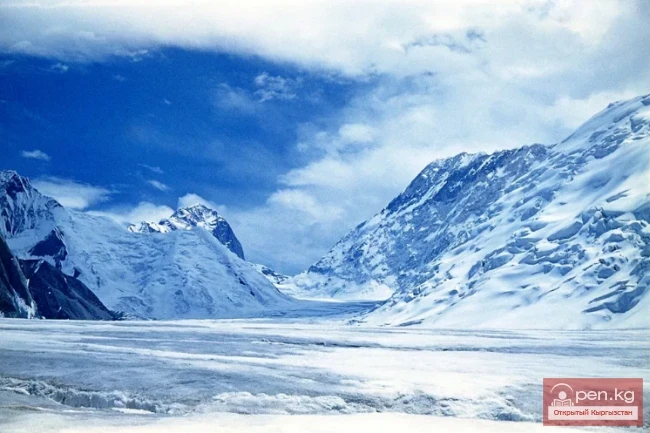
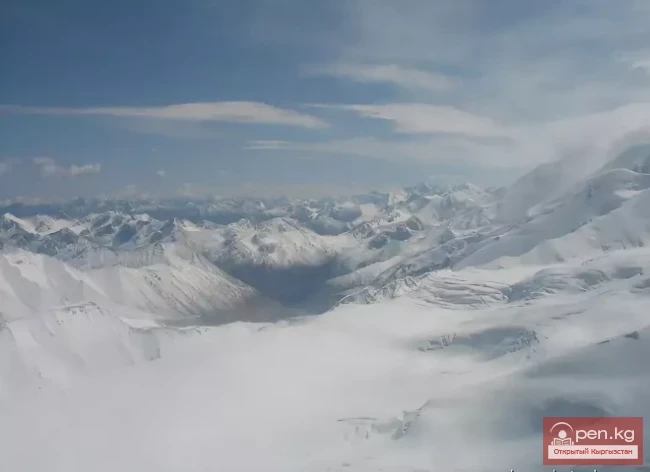
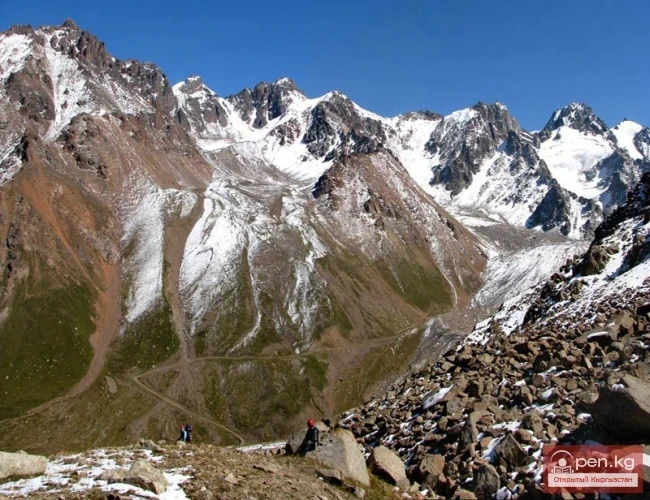
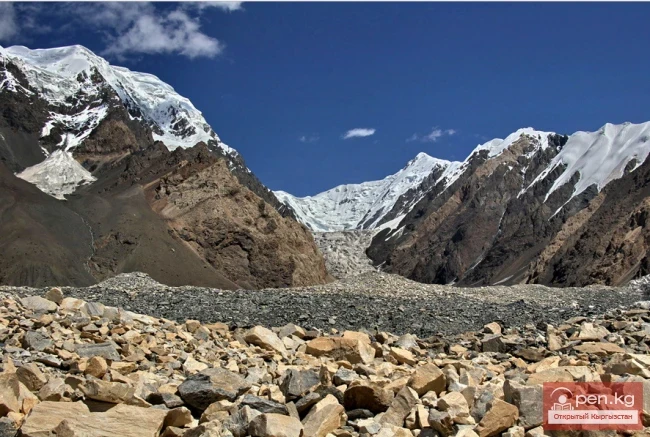
The expedition was organized as part of a government initiative aimed at studying and protecting glaciers, as well as in accordance with a government decision regarding the UN international glacier protection program.
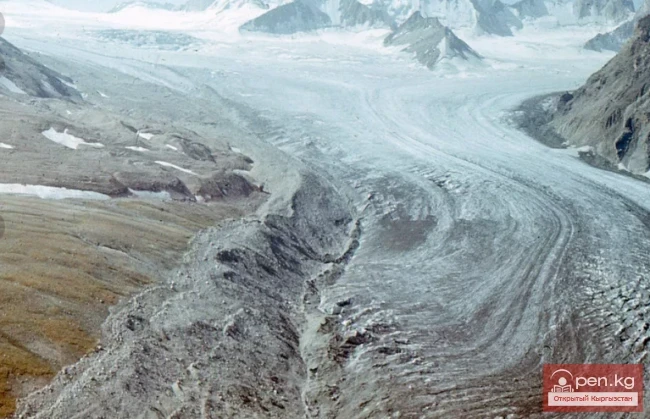
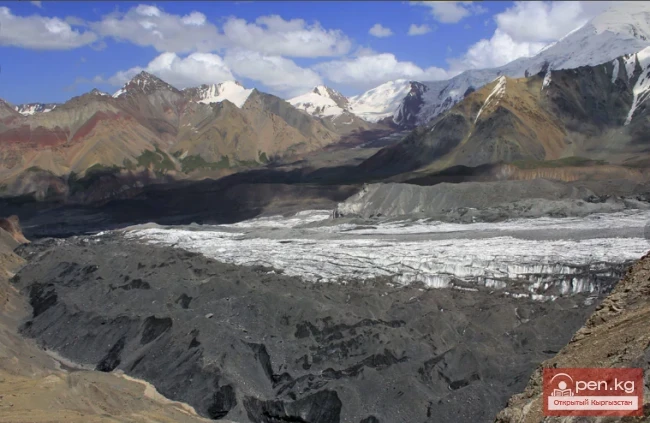
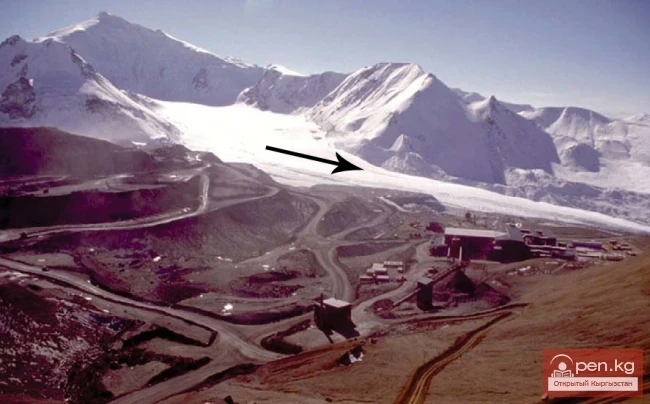
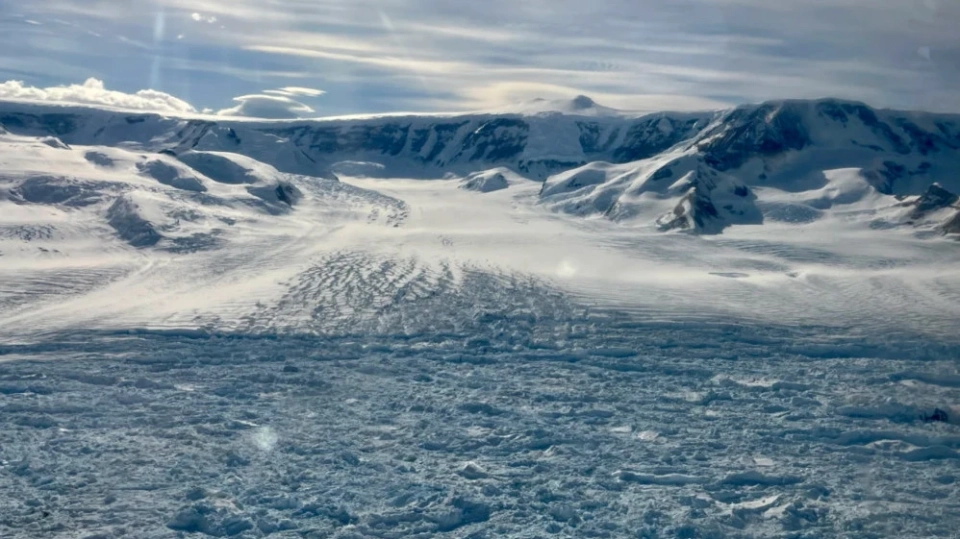
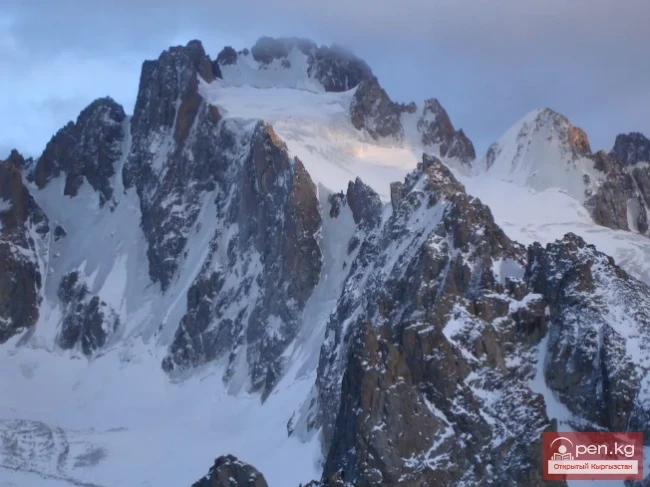
The glacier, which began to move on October 25, advanced 520 meters in November, which is about 20 meters per day.
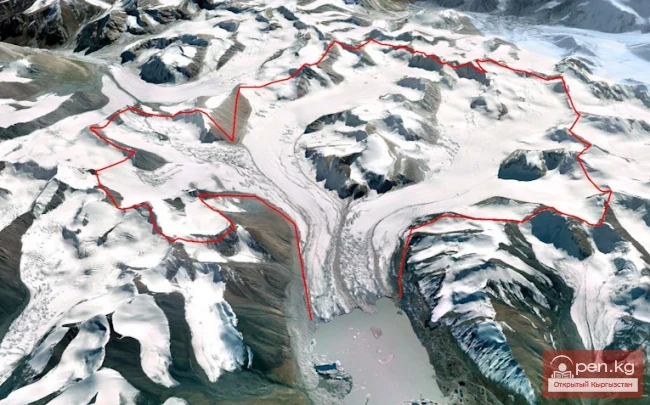
Experts note that the height of the front of the glacier ranges from 25 to 30 meters, while its width varies from 80 to 120 meters. These changes indicate serious natural processes occurring within the glacier.
The Dehdal Glacier is under constant observation by scientists who record its movement speed and changes in size. This allows for an assessment of the impact of glacier melting on the surrounding nature and human life.
This observation is particularly significant as glaciers serve as the main source of fresh water for Tajikistan. Climate change is leading to accelerated glacier melting, which, in turn, can negatively affect water levels in rivers, agriculture, and the energy sector.
A decrease in glacier volume or sudden movement can trigger natural risks, such as sudden increases in water levels or the formation of glacial lakes.
Thus, timely research is crucial for preventing potential ecological threats.
Previously, experts linked the movement of the Dehdal Glacier to hot weather and prolonged lack of precipitation. On October 25, a large mass of ice measuring up to 1500 meters in length and about 50 meters in height was recorded as separating from the glacier, which became noticeable to residents of nearby villages. According to the Emergency Situations Committee, there were no casualties or damage reported as a result of this event.
During a press conference on October 31 at the Hydrometeorology Agency, representatives of the agency explained the reasons for the glacier's movement.
According to them, the glacier shifted more than 5 kilometers in just 15 minutes. "The rise in air temperature and the lack of precipitation over a long period have become the main factors contributing to the intense melting of the glacier and changes in the hydrological balance," the specialists noted.
Agency representatives emphasized that the current movement of the glacier is a consequence of climate change, which exacerbates the processes of glacier degradation in the mountainous regions of the country.
Scientists continue their observations and are preparing a detailed report on the state of the glacier.