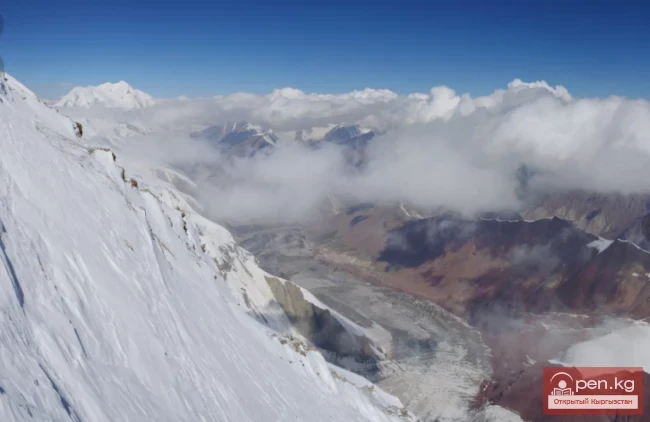
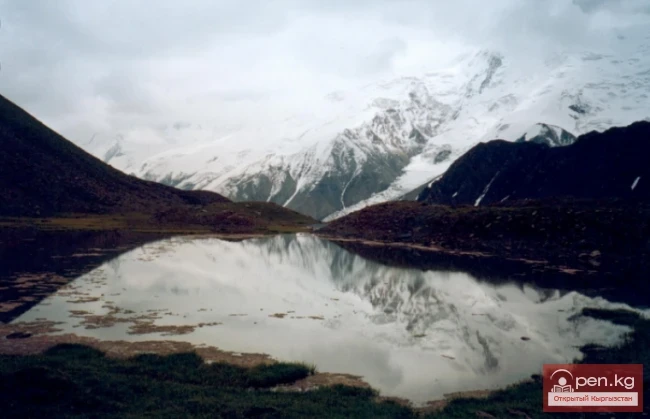
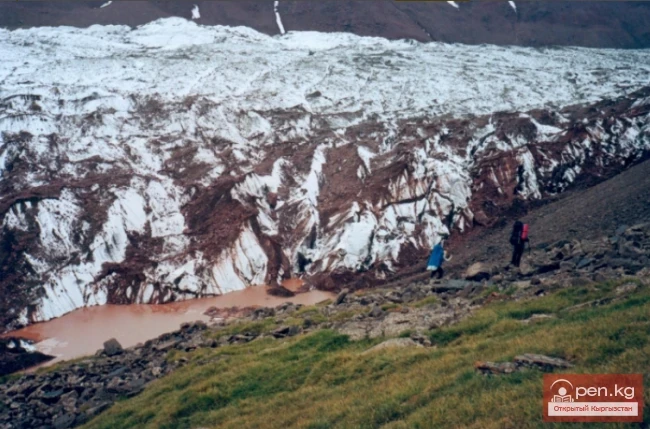
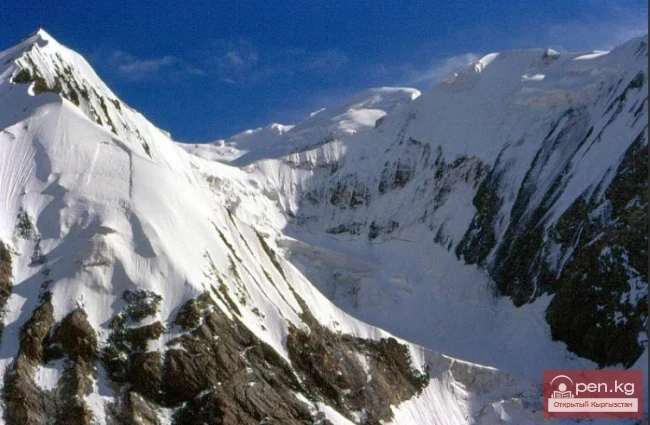
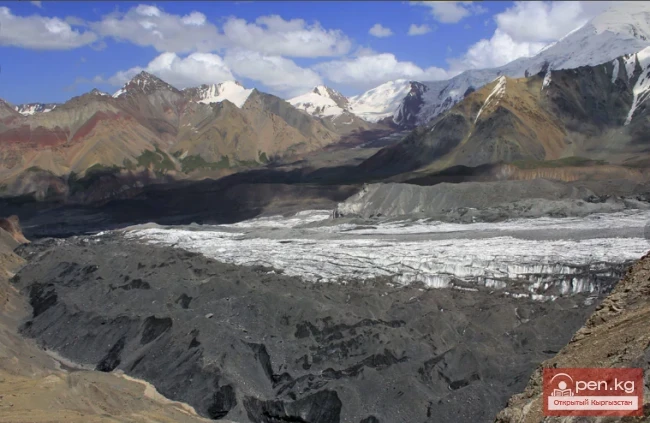
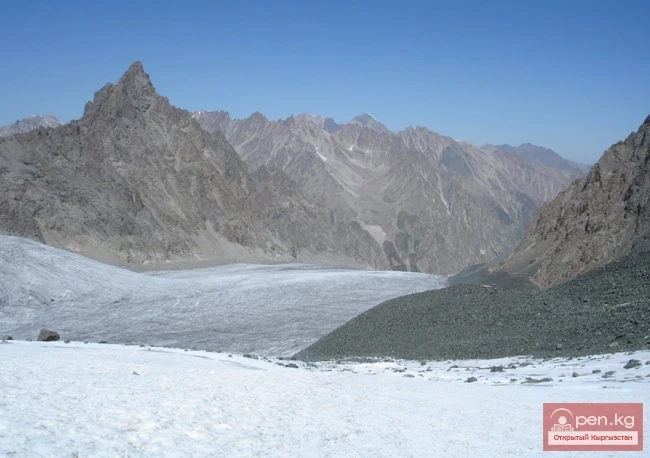
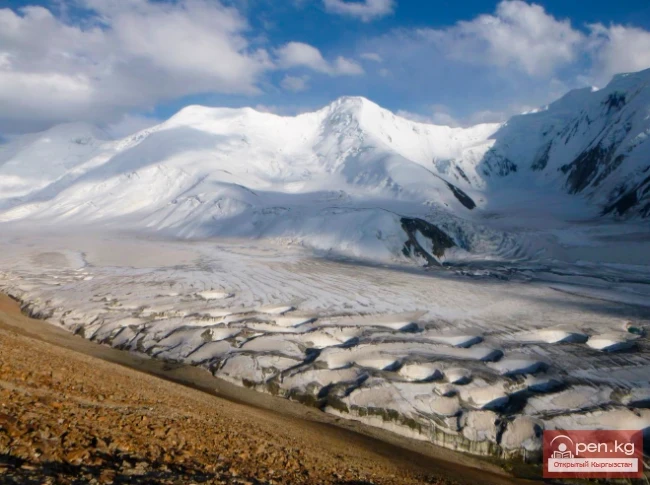
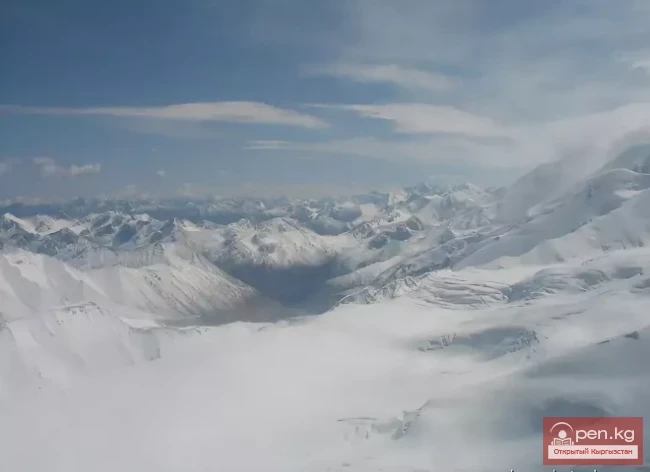
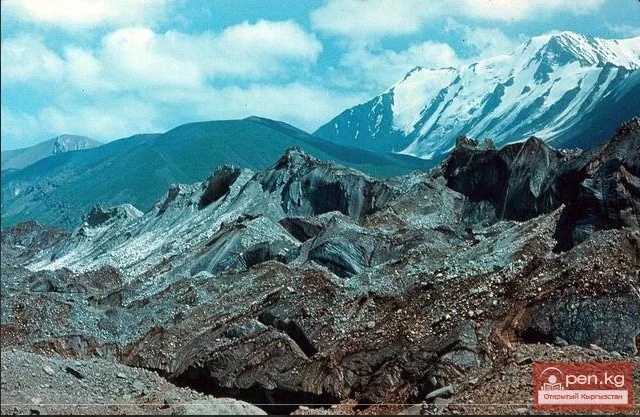
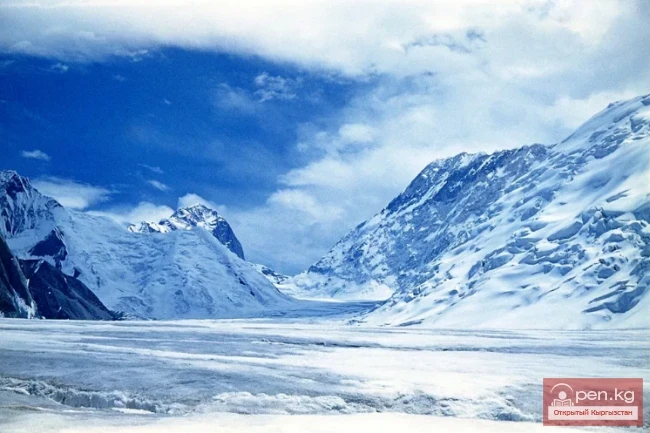
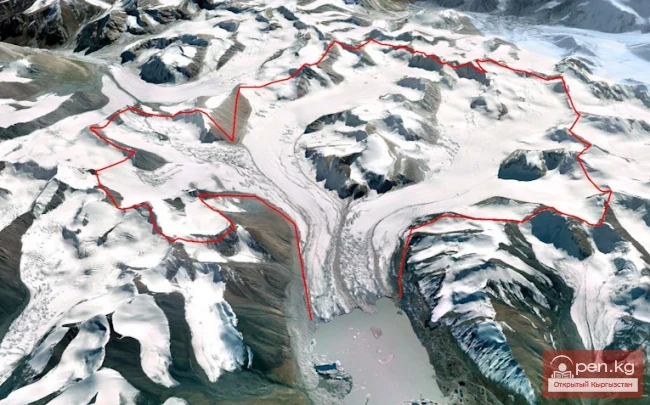
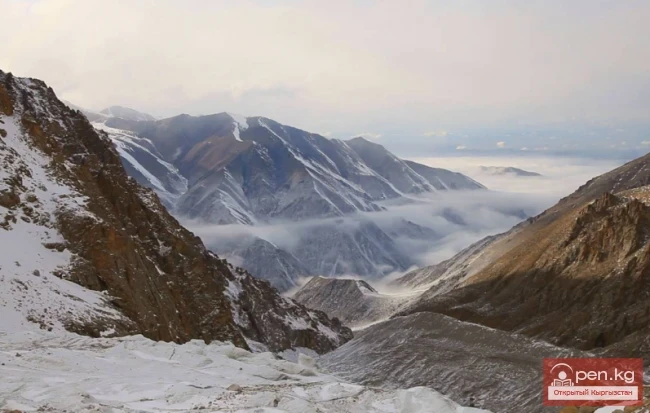
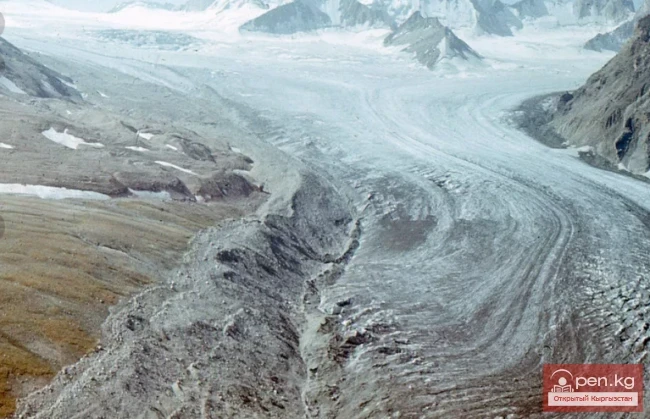
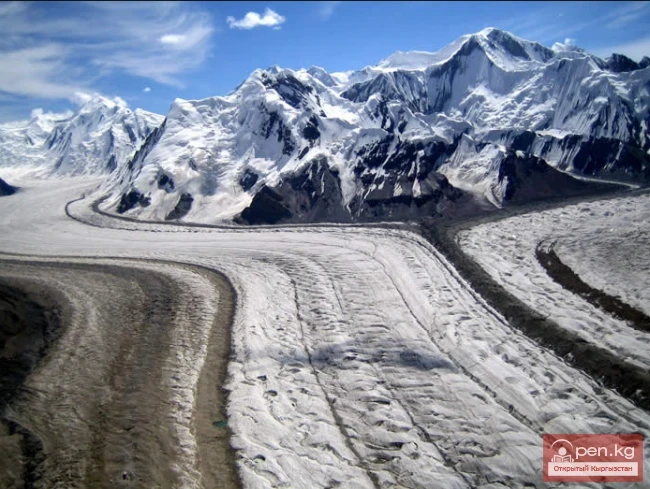
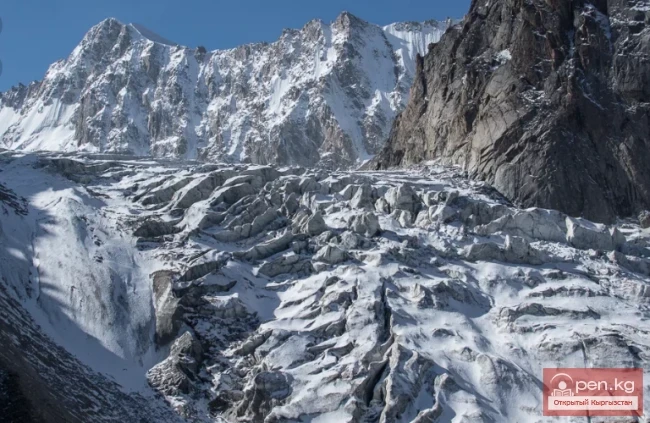
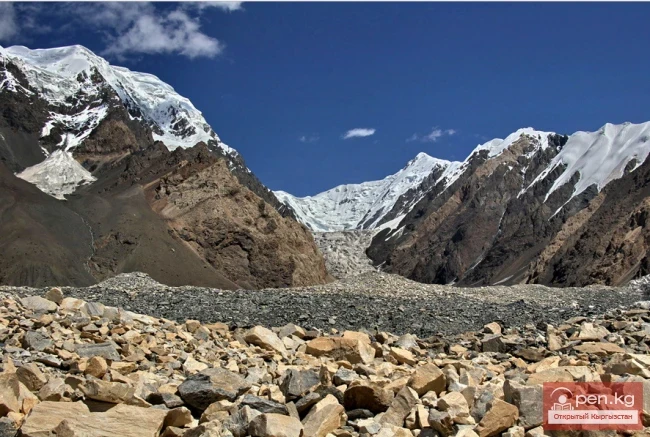
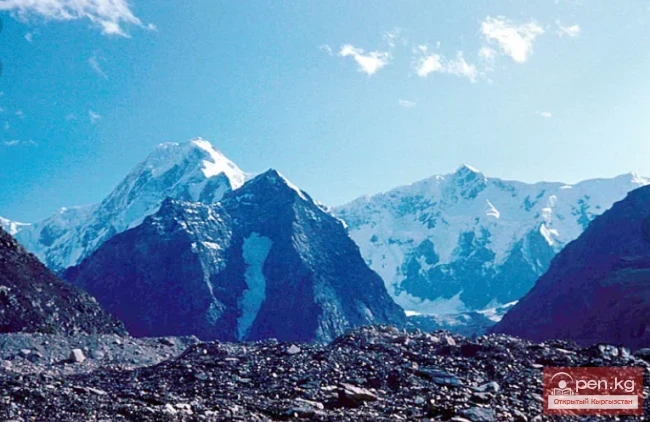
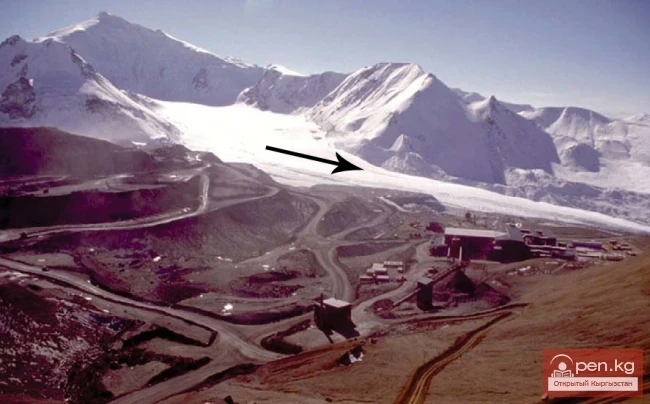
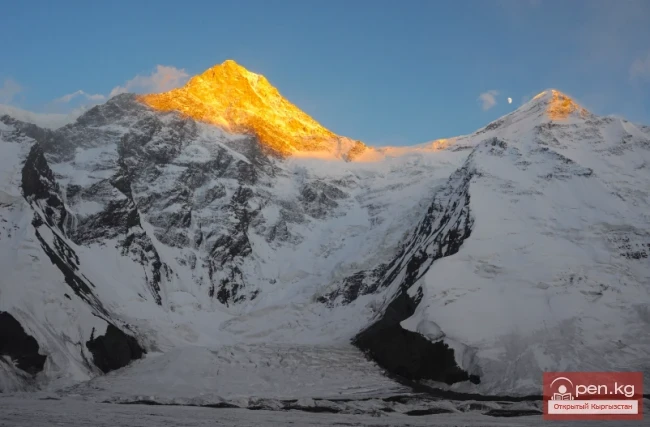
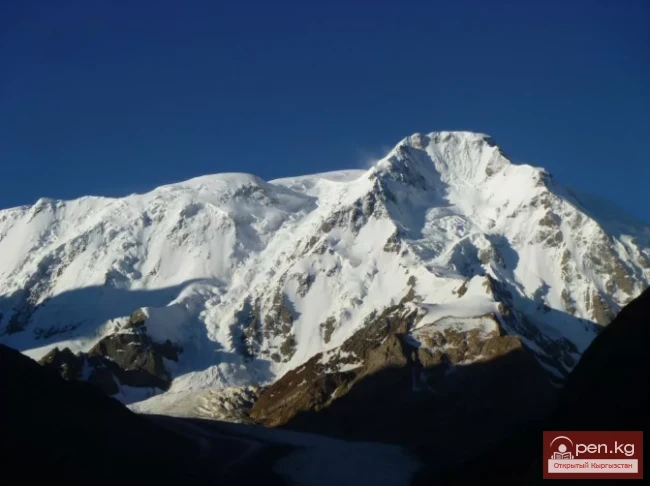
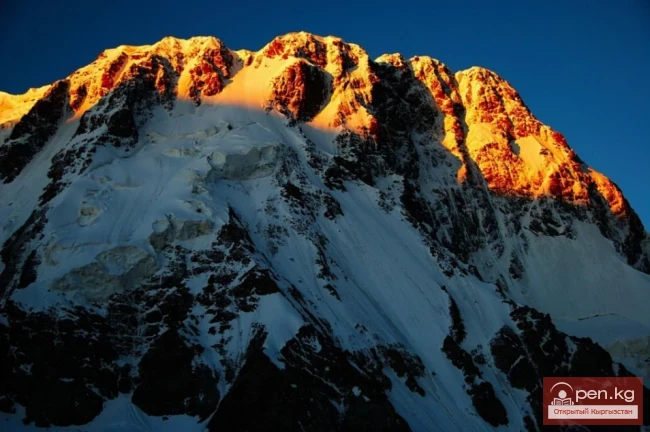
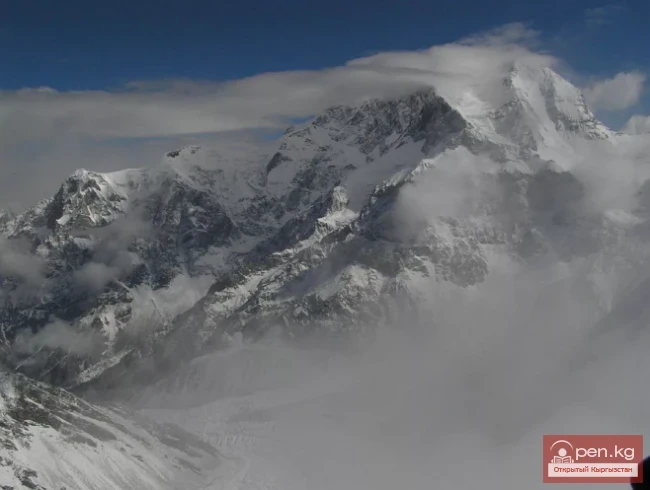
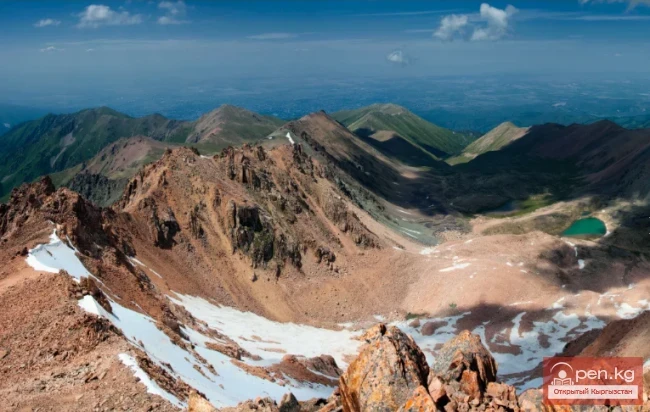
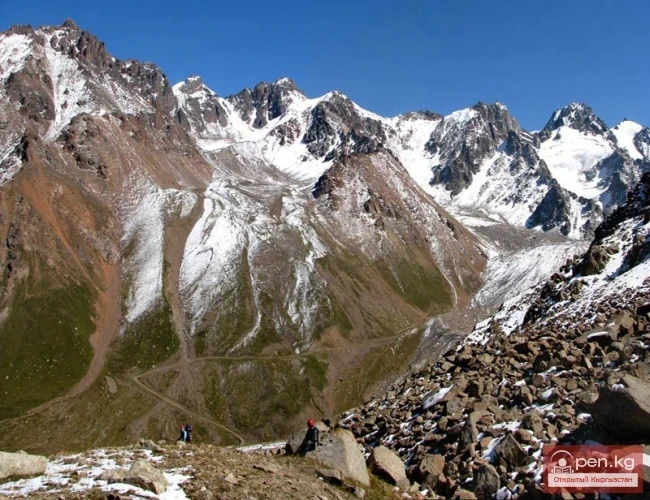
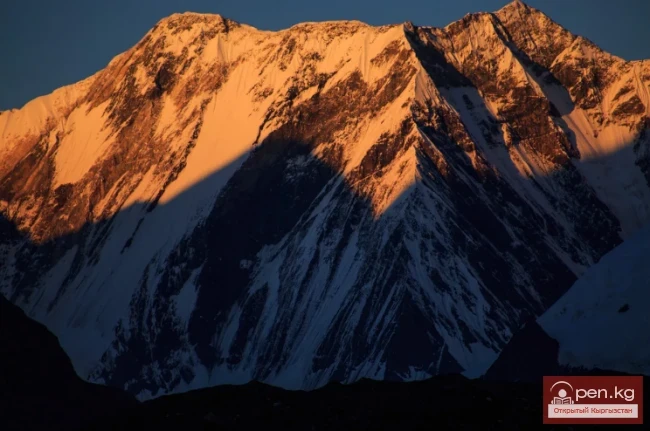
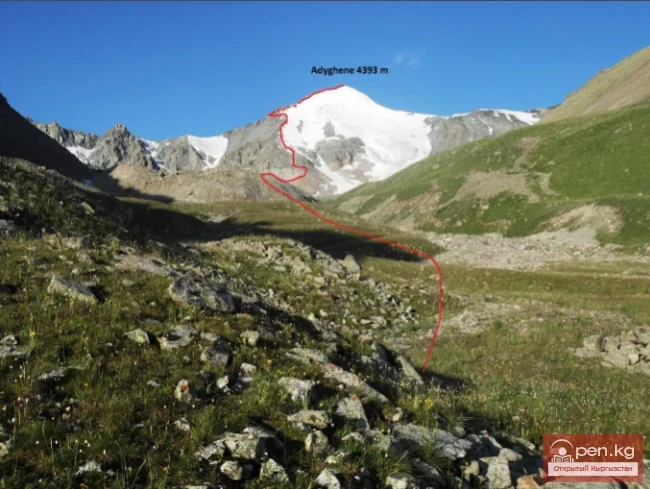
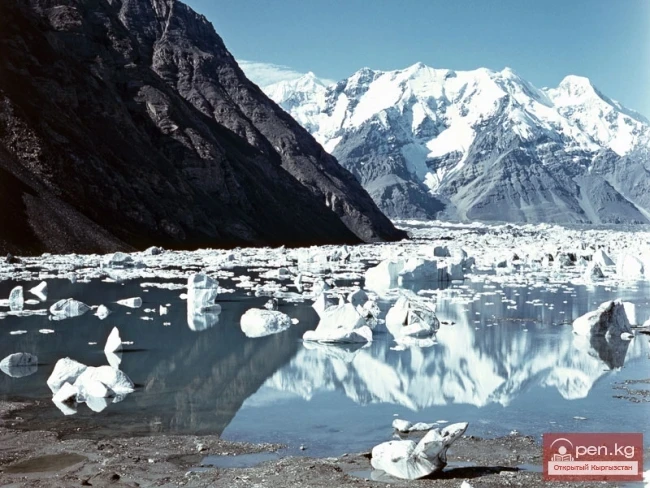
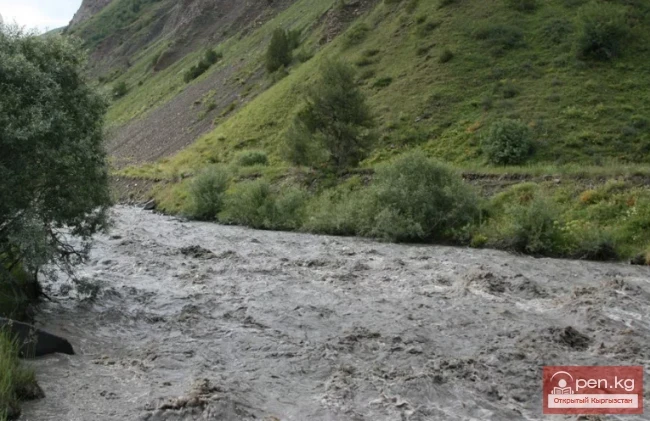
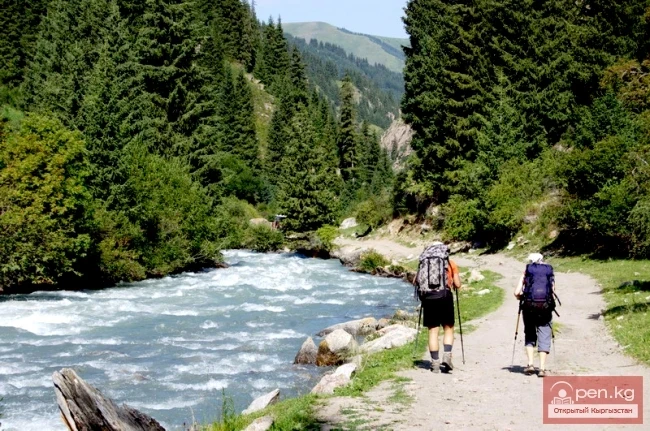
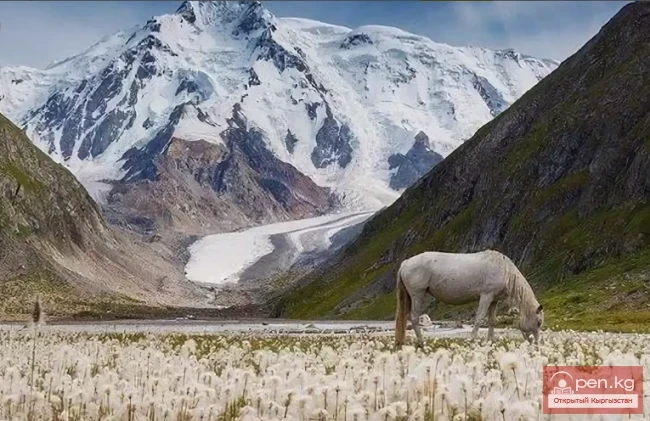
The Nura Glacier is located in the basin of the Eastern Kyzylsu River
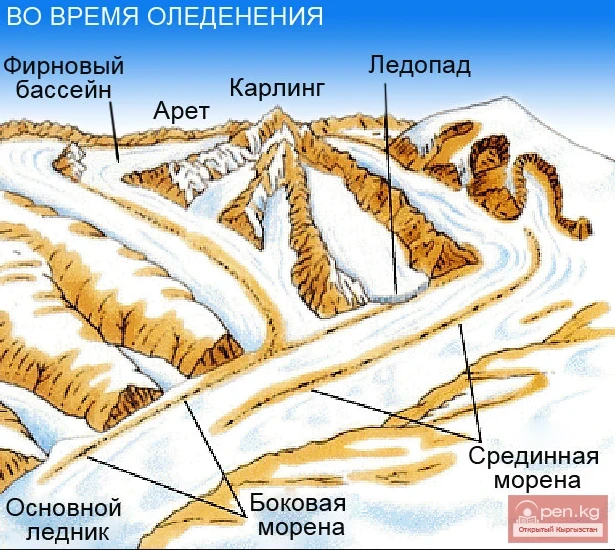
A large complex valley glacier formed from small and medium glaciers flowing from different sides into the main trunk, glacier 85,86. The glacier is gentle, closed, and has crevasses. The overall short and passive tongue is covered by a thick layer of moraine, containing buried and dead ice. The end of the tongue transitions into dissected loose deposits of significant thickness with deep incisions from modern flows. The boundaries of the tongue are camouflaged. Between 1978 and 1980, some activity was noted in the main trunk of glacier 85,86 in its upper part, reflected in the increase of the area of clean ice among the moraines, which completely cover it up to an altitude of 4300 — 4400 m. The tongues of glaciers 89 and 90 swelled, cleared from moraines, and advanced within the main trunk. The boundaries of past movements of glaciers 88 and 91 can be traced in the main trunk. The tongue of glacier 92 is dammed by glacier 91. All changes occurred within the contour of the main trunk and did not affect the configuration of the tongue's end.
In the basin of the Nura River, there are 44 glaciers, covering an area of 73.5 km². Among them, 8 glaciers are smaller than 0.1 km² each, with a total area of 0.5 km². According to the catalog of glaciers of the USSR (Volume 14, Issue 3, Part 19), there were 23 glaciers in this basin with an area of 98.6 km².