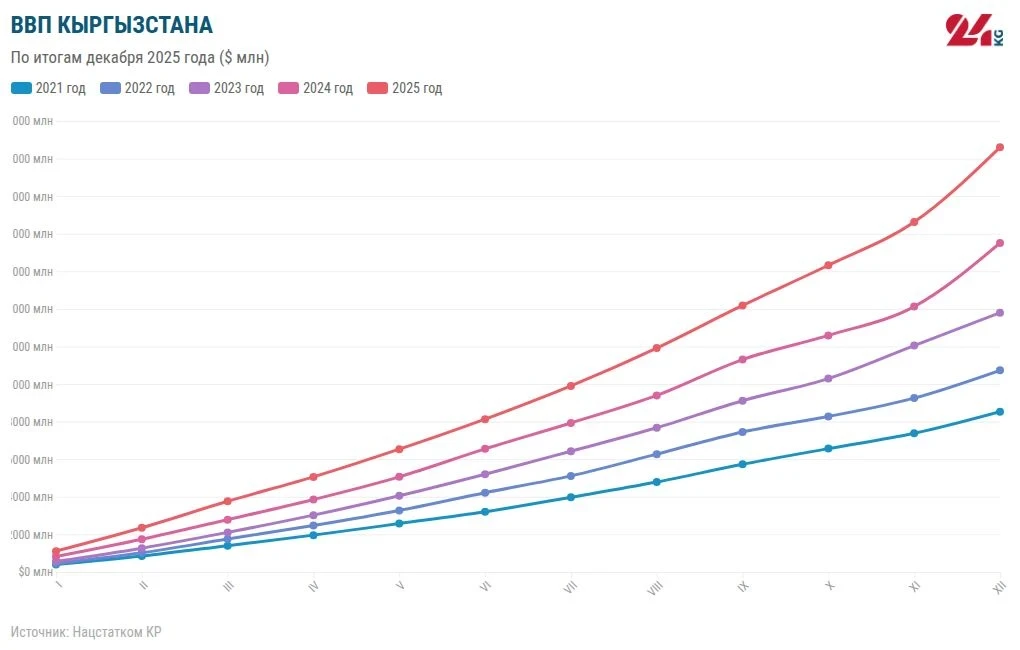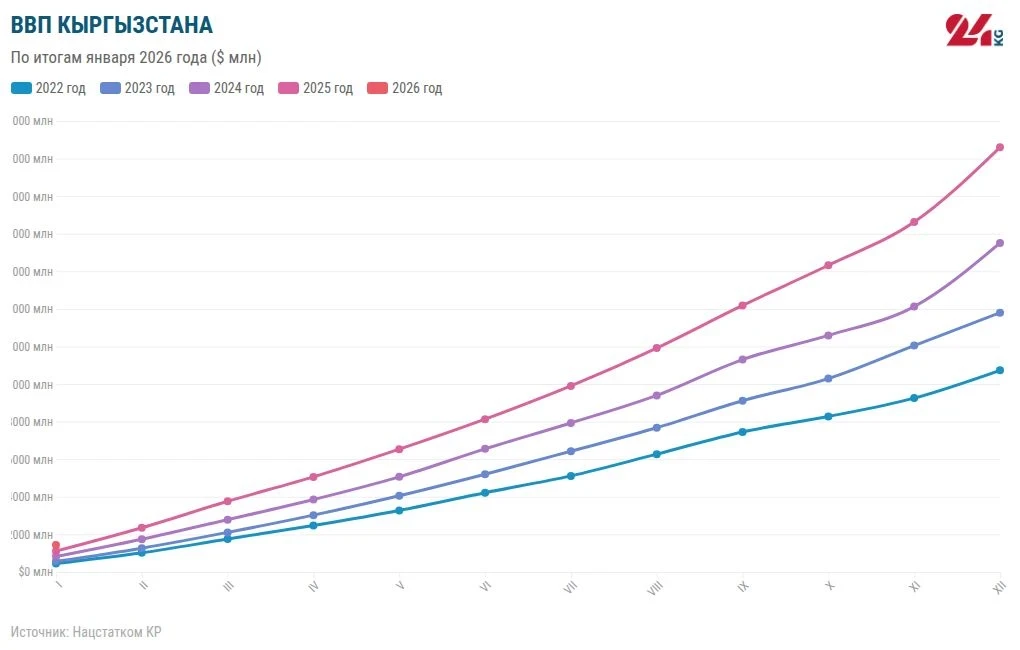
The growth of the economy was driven by activity in commodity production, the service sector, and an increase in net taxes on products.
The main factors contributing to economic development in January were the increase in the production of wooden and paper goods, as well as a growth in printing activities (by 1.8 times), rubber and plastic products, construction materials (by 1.7 times), and chemical products (by 38.9%).
- 24.kg conducts analysis based on data from the National Statistical Committee. However, we cannot guarantee complete compliance of this data with the real economic situation in the republic, as alternative sources of information are absent.
Gross Domestic Product
When calculating GDP and its changes, various factors are taken into account, including prices, production volumes by sectors, as well as government expenditures and budget revenues. Kyrgyzstan, as an import-dependent country, is influenced by these factors, which is especially noticeable when converted into other currencies. In this review, we use official data expressed in soms.
In the structure of GDP, the service sector accounts for 52.3%, commodity production for 30.7%, and net taxes on products make up 17%.
Industrial Sector
In January 2026, the volume of industrial production amounted to 69 billion 831.1 million soms, which is 12.6% more compared to the previous year. The main factors of growth include:
- increase in the production of wooden and paper products, printing products — by 1.8 times;
- growth of rubber and plastic products, construction materials — by 1.7 times;
- increase in the production of chemical products — by 38.9%;
- mineral extraction — by 37.7%;
- transport vehicles — by 36.1%;
- refined petroleum products — by 21.1%;
- food products (including beverages) and tobacco products — by 13.6%;
- pharmaceutical products — by 8.9%;
- basic metals — by 6%.
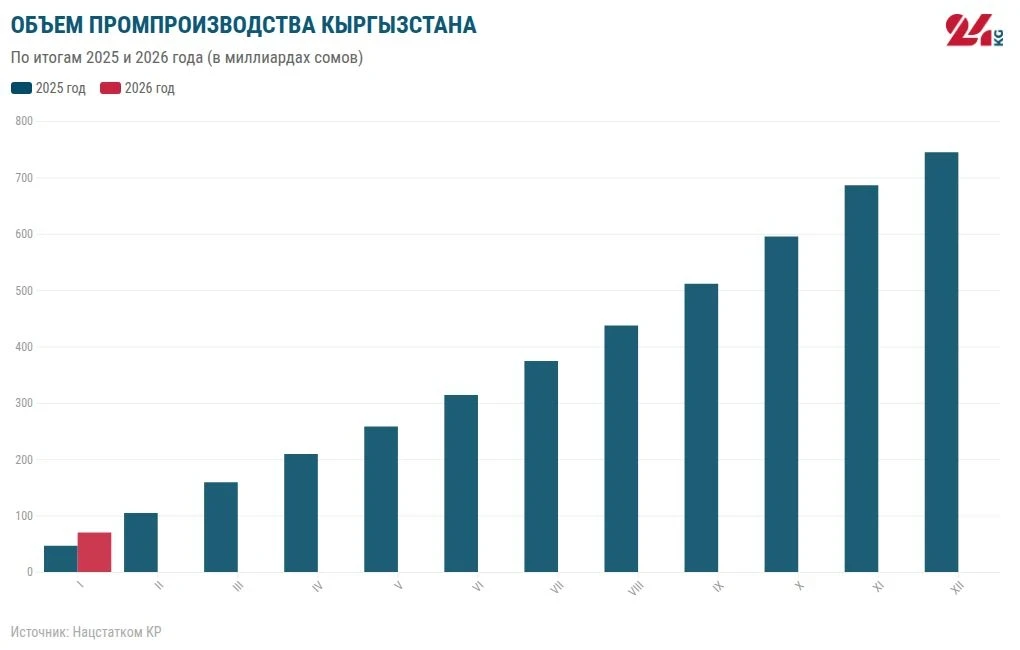
Positive changes are also observed in construction, where production volumes increased by 25.7%, in wholesale and retail trade — by 21.1%, in the hotel and restaurant business — by 10.3%, and in freight transportation — by 9.4%.
At the same time, production volumes in the textile and garment industry decreased by 8.5%.
The energy sector, providing electricity, gas, and steam, showed a growth of 0.7%, which is related to the increase in the distribution of electricity and fuel through gas networks.
In the area of water supply, purification, waste processing, and obtaining secondary raw materials, growth was 13.8% due to improved collection and distribution of water.
Investments in Fixed Capital
Investments in fixed capital increased by 17.9% compared to January 2025, which is related to the growth of internal sources of financing by 14.8%. External investments increased by 1.6 times, reaching a total volume of 6 billion 25.4 million soms.
The bulk of investments in January 2026 (about 90% of the total volume) was directed towards the construction of housing, water supply facilities, waste purification and processing, as well as providing electricity, gas, and air conditioning, the processing industry, education, hotels, and restaurants.
Economic Forecasts
According to forecasts from international financial organizations, the economy of Kyrgyzstan will continue to grow in 2026, although the growth rates will be lower than in previous years.
It is expected that the economy of the republic will grow by:
- 4.5% — according to the International Monetary Fund;
- 6.5% — according to the World Bank;
- 9.3% — according to estimates from the Eurasian Development Bank.
Experts believe that the main growth factors will remain the service sector, construction, and industrial recovery.
The economy of Kyrgyzstan will continue to grow in 2026 due to domestic demand, investments, and government expenditures. This forecast was announced by senior economist of the World Bank Bakyt Dubashov.
Current Topics
The Economy of Kyrgyzstan — 2025: Records of Growth and Price Shocks
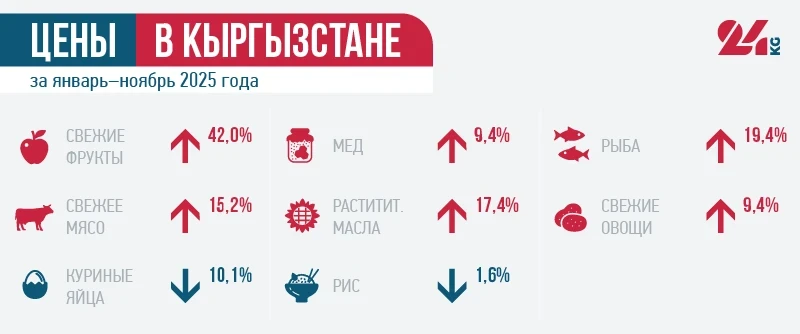
Nevertheless, one of the main problems for the country remains inflation, which amounted to 9.4% at the end of 2025, exceeding the National Bank's target range of 5-7%.
According to experts from the Asian Development Bank, to stabilize prices, it is necessary to adhere to a strict monetary policy and normalize supply chains.
Among the risks, there is also a high dependence on the external economic situation of major trading partners, fluctuations in gold prices, and climate challenges affecting the agricultural sector.