Experts from the Republican Center for Health and Mass Communication shared recommendations on what physical activity is necessary for people to maintain health and activity throughout their lives.
According to their data, physical activity includes any body movements performed using muscular strength that lead to energy expenditure (measured in kilocalories). This includes both labor and everyday physical activities.
Physical loads can be classified into three levels:
Low physical activity – corresponds to a state of rest, for example, during sleep or reading while lying down.
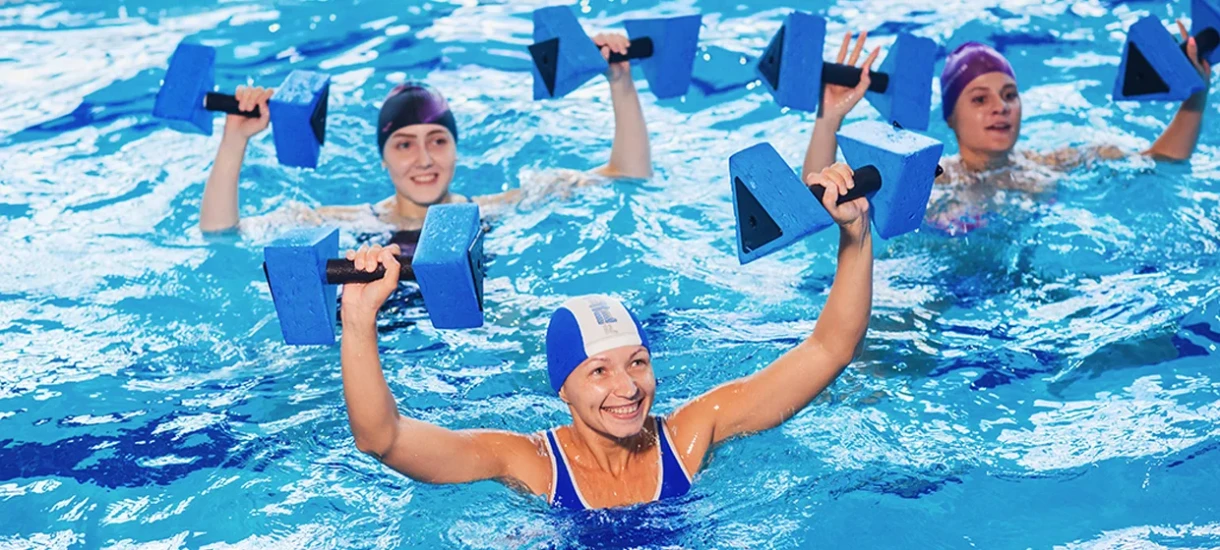
Moderate physical activity – a level at which the heart rate slightly increases, and light shortness of breath appears, for example, during morning exercises, brisk walking, swimming, cycling on flat terrain, or dancing.
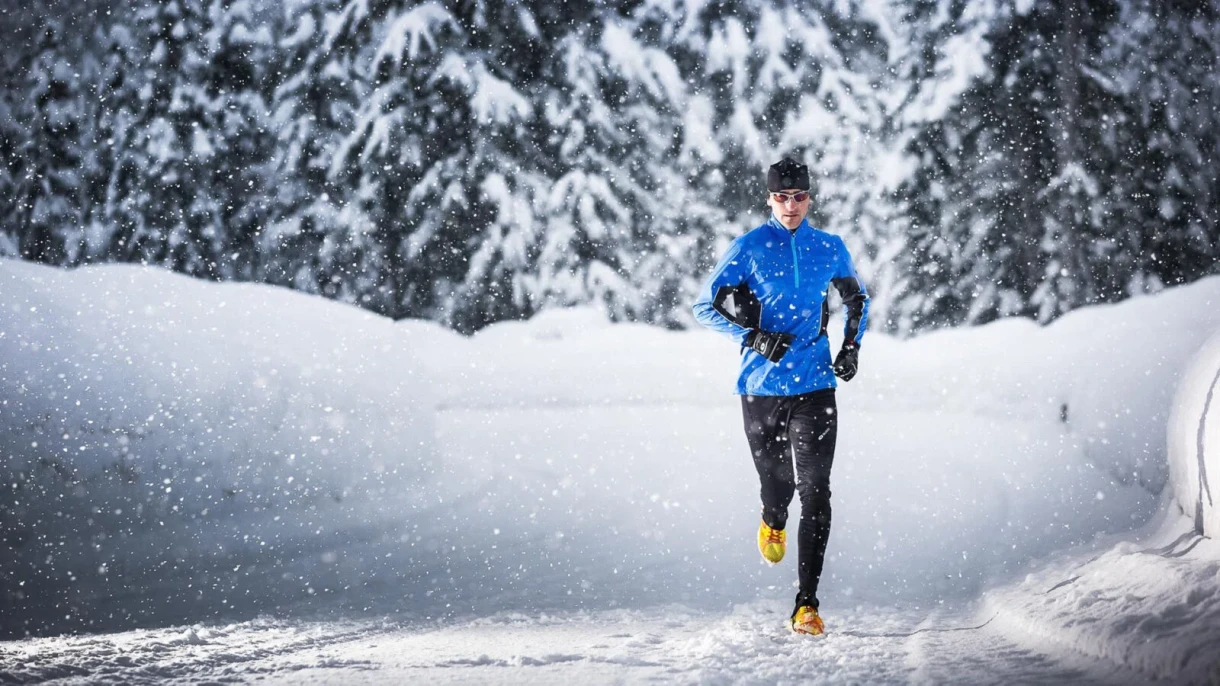
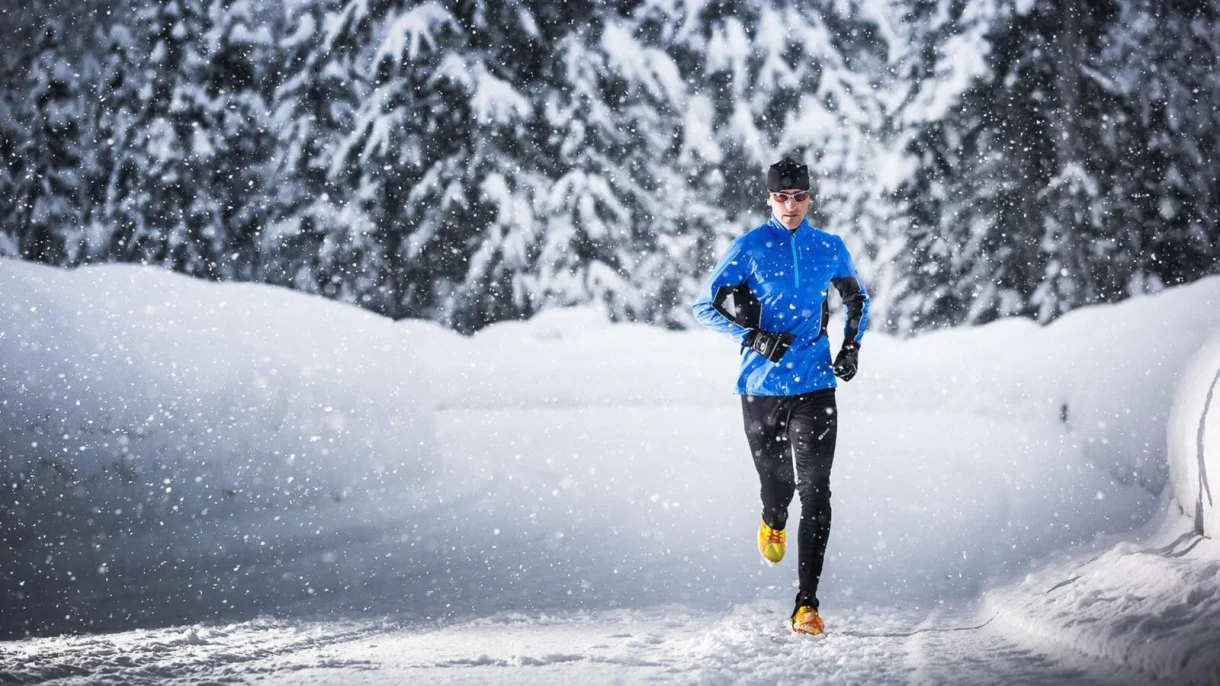
Intense physical activity – this is a load during which the heart rate significantly increases, and sweating and difficulty breathing occur. Examples include running, aerobics, long-distance swimming, fast cycling, and climbing uphill.

Aerobic loads are long-duration low-intensity exercises that should be performed 3-5 times a week with an interval of 1-2 days.
Types of aerobic loads:
- Walking
- Running
- Water aerobics
- Dancing
- Cycling.
Types of anaerobic loads:
- Weightlifting
- Jumping rope
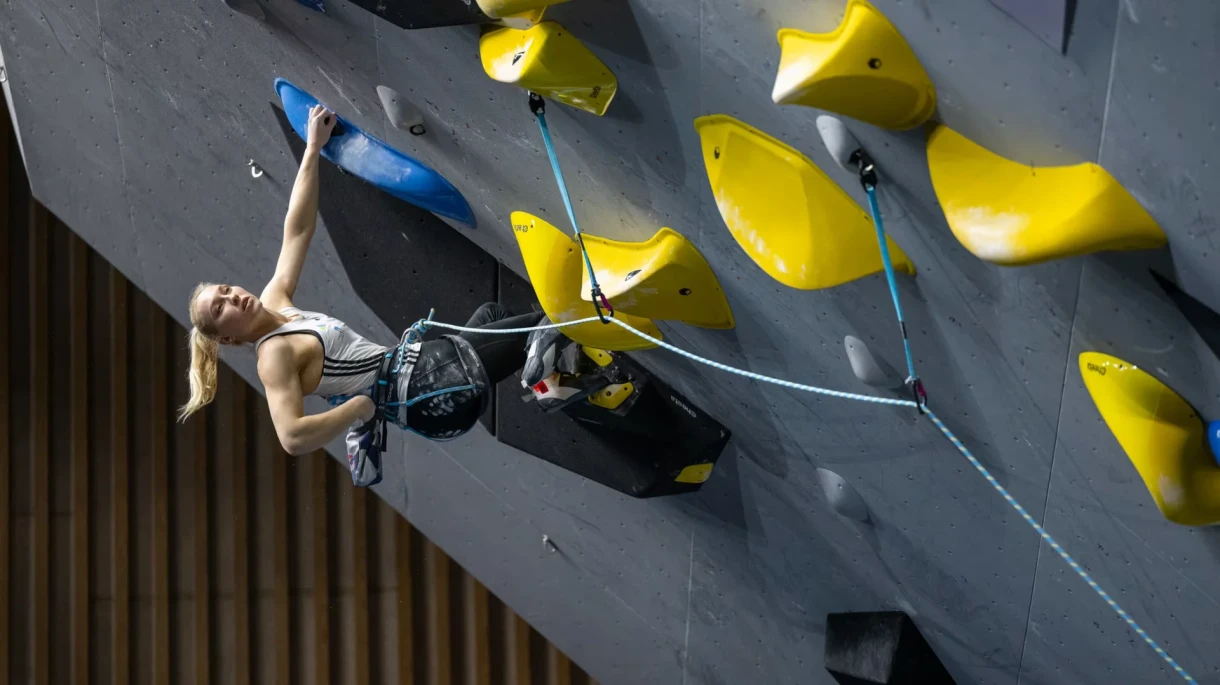
- Rock climbing
- Stair climbing, etc.
The minimum required level of physical activity to maintain cardiovascular fitness is 30 minutes a day (the time of activities can be summed throughout the day, but one session should last at least 10 minutes) or 150 minutes a week. This allows burning about 150 kcal per day.

- 45 minutes of playing volleyball
- 30 minutes of cycling (8 km)
- 30 minutes of dancing (active dancing)
- 30 minutes of walking (3 km)
- 20 minutes of swimming
- 20 minutes of playing basketball
- 15 minutes of running (1.5-2 km)
- 15 minutes of stair climbing.
Physical activity of 150 minutes per week (2.5 hours) reduces the likelihood of:
- premature death;
- development of ischemic heart disease and stroke;
- hypertension;
- type II diabetes;
- depression;
- osteoporosis.
- colon cancer;
- breast cancer;
- overweight.
the energy consumed from food should correspond to the energy expended on metabolism and physical activity.

Children and youth aged 5-17 years should engage in moderate to vigorous physical activity for at least 60 minutes a day.
Adults aged 18-64 years should perform moderate-intensity physical activity for at least 150 minutes a week or engage in vigorous-intensity aerobic exercises for 75 minutes a week.
People aged 65 and older should also engage in moderate-intensity physical activity for at least 150 minutes a week or perform vigorous-intensity aerobic exercises for 75 minutes a week.