In the context of growing global instability caused by geo-economic conflicts and supply chain issues, the strength of bilateral economic relations increasingly depends on their historical foundation. Partnerships based on centuries-old ties in trade and culture demonstrate greater resilience to external crises. In this context, the relationship between India and Nepal serves as an exemplary model of economic symbiosis. More about this can be found in an article from the publication Nepal Aaja.
The economic cooperation between the two countries has developed over centuries and is based not only on official agreements but also on a shared cultural context, close social ties, and geographical proximity, creating a solid foundation for interaction even in the face of global crises.
Geographical and Strategic Aspects of Interdependence
The geographical position of Nepal and India defines their economic interdependence. Nepal serves as a natural buffer for India, while India provides Nepal with access to maritime routes. However, the modern partnership between the countries encompasses a much broader range of interconnections in the fields of economy and infrastructure.Considering changes in the regional economy, this cooperation is becoming increasingly multilateral, including areas such as energy, logistics, digital finance, and joint investments.
Main Areas of Economic Synergy
Tourism, hydropower, organic agriculture, and transport connectivity are the most actively developing spheres of joint cooperation.Tourism continues to be an important driver of growth for both countries. The cultural heritage and natural wealth of India and Nepal contribute to an increase in the number of tourists and attract the attention of the international community. Authorities in both countries are working on developing tourism infrastructure, including new, lesser-known destinations.
In agriculture, India views Nepal as a potential market for organic products. These initiatives combine sustainable development goals with employment challenges and Nepal's integration into regional food chains, with special attention given to workforce training under the Indian Skill India program.
Improving Transport Infrastructure and Trade
The renewal of the Transit Agreement in November 2025 was an important step forward. The amendments are expected to facilitate railway freight transportation between the Indian Jogbani and the Nepali Biratnagar for bulk and large cargo. The liberalization of transit corridors will strengthen multimodal transport links and expand Nepal's trade with both India and third countries.These measures contribute to Nepal's integration into regional and global trade networks and enhance India's role as a key transit partner.
Financial Integration and Digital Stability
Financial integration is an important area of cooperation. The compatibility of India's UPI payment system and Nepal's FonePay QR has become a practical step towards the digital connection of the economies, simplifying transactions for businesses, tourists, and citizens of both countries.Even during the COVID-19 pandemic, trade routes between the countries continued to operate, confirming the resilience and flexibility of bilateral economic mechanisms.
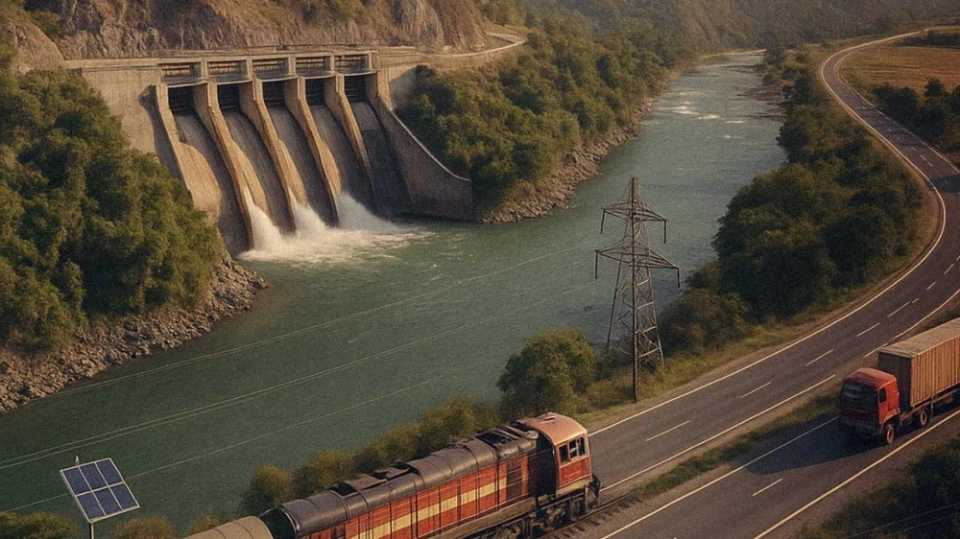
Energy Cooperation: From Hydropower to Clean Technologies
Energy remains one of the cornerstones of economic cooperation. India and Nepal are actively developing a partnership in sustainable energy transition, including the export of liquefied natural gas to Nepal from Indian Oil Corporation Ltd. This project has been implemented using cryogenic storage and regasification facilities in Simara, opening new horizons for industrial and energy development in Nepal.A key project is the Arun-3 hydropower plant with a capacity of 900 MW, being implemented by the Indian company SJVN Limited. It utilizes a significant hydropower potential of Nepal while simultaneously providing India with additional energy resources, contributing to the socio-economic development of the host regions.
Regional Integration and the Future of the Economy
The expansion of cooperation in trade, infrastructure, and energy creates a basis for long-term regional integration. India gains access to reliable energy and labor resources, while Nepal ensures a stable market for sales, investments, and infrastructure development.Shared historical and cultural roots strengthen trust and reduce transaction costs, creating a unique model of economic interdependence. On this basis, bilateral relations are gradually transitioning from traditional partnerships to the formation of a common economic space.