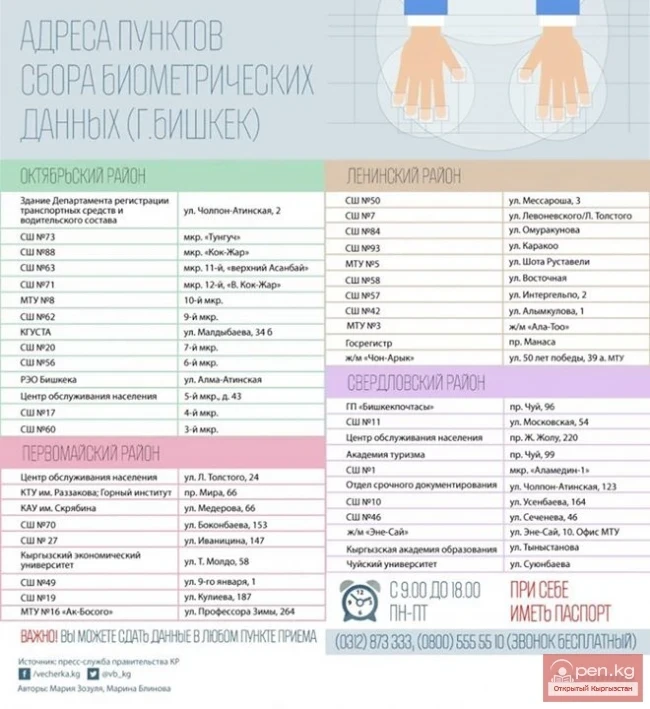
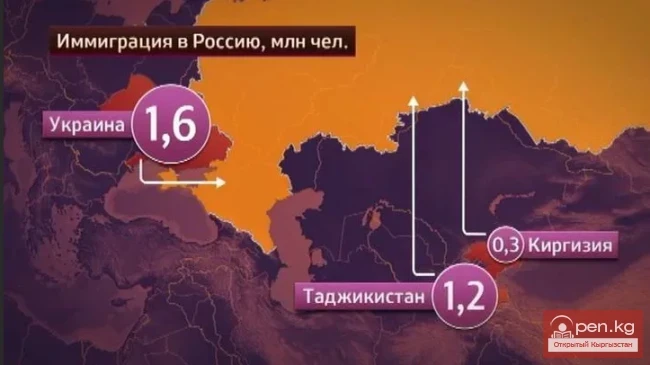
The collection and processing of such data must ensure protection against loss, distortion, and unauthorized access, as well as prevent any unlawful interference with information resources.
Government agencies responsible for registration are required to ensure the confidentiality and protection of data in accordance with current legislation.All actions involving genomic and fingerprint information, including collection, processing, storage, and destruction of data, must be carried out strictly according to established rules.
Authorized bodies carry out the anonymization and de-anonymization of data during processing.
The transfer of genomic and fingerprint information to judicial, law enforcement, and special agencies is carried out in accordance with the laws of the Kyrgyz Republic and registration rules.
Such data may also be transferred to foreign states in accordance with international treaties and the laws of Kyrgyzstan.
The draft law provides for both mandatory and voluntary registration.Mandatory genomic registration includes:
- individuals convicted of serious crimes and crimes against morality (selection is conducted by internal affairs agencies);
- unknown individuals whose biological material was seized during investigations of unsolved crimes;
- unidentified corpses (selection is conducted by forensic specialists).
Consent for the collection of biological material from minor relatives of missing persons must be obtained in the presence of a legal representative.For individuals recognized as incapacitated, consent from a guardian is also required for the collection of biological material.
The collected biological material is used exclusively to obtain genomic information.If an individual has already undergone genomic registration, repeated collection of biological material is not conducted.
The information obtained will be used for:
- preventing and solving crimes;
- searching for missing persons;
- identifying unidentified corpses;
- establishing familial relationships.
- public servants of law enforcement agencies;
- individuals recognized as incapacitated;
- individuals whose identity cannot be established by other means;
- suspects or accused of crimes;
- unidentified corpses;
- foreigners and stateless persons.
- permanently residing in Kyrgyzstan;
- studying in educational institutions;
- working in the country;
- illegally present in the territory of the republic;
- requesting refugee status or replacement of identification;
- subject to expulsion or falling under international readmission agreements.
Children aged 12 to 16 can undergo fingerprint registration on a voluntary basis, while children under 12 are exempt from this procedure.Voluntary registration is carried out based on a written application and in the manner established by internal affairs agencies.
Fingerprint information will be used for:
- identifying citizens and foreigners;
- accounting for their stay in the country;
- searching for missing persons;
- identifying unidentified corpses;
- preventing and solving offenses.
Refusal of genomic registration may also lead to fines.
The photo on the main page is illustrative: istra-adm.ru.