In 2013, the development and implementation of technological, marketing, and organizational innovations in the industry of the republic were carried out by 39 enterprises, or 5.5 percent of the surveyed number.
At 13 industrial enterprises, innovative processes were completed, and industrial products were being produced, while the others experienced process innovations, as well as innovative processes that were in the final stages.
The most active innovative activity was noted in enterprises producing food products, including beverages, tobacco, textile and clothing production, and other non-metallic mineral products (16 enterprises – 41 percent of the total number of innovation-active enterprises).
There was a complete absence of innovative activity in enterprises producing leather, leather goods, and footwear, petroleum products, rubber and plastic products, wood processing and wood products, pulp and paper production, and publishing activities.
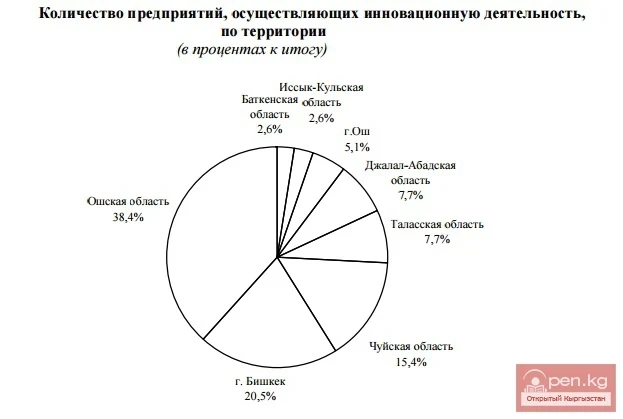
Innovative processes were more actively implemented in the industrially developed zones of Bishkek and the Chui region - at 14 enterprises (35.9 percent of the total number of innovation-active enterprises), in the Osh region – at 15 enterprises (38.4 percent of the total number of innovation-active enterprises). At the same time, no enterprise in the Naryn region implemented innovations in production processes in 2013.
In 2013, the surveyed enterprises shipped innovative products worth 1,243.7 million soms, or 1.2 percent of the total volume of shipped products (in 2012 - 1.6 percent, 2011 - 0.4 percent, 2010 - 1.5 percent, in 2009 – 3.0 percent).
At the same time, the volume of newly introduced or significantly technologically changed products amounted to 1,239.5 million soms (99.7 percent of the total volume of innovative products) and other innovative products – 4.2 million soms (0.3 percent).
The largest volumes of innovative product production were accounted for by enterprises in the Chui region (87.0 percent) and Bishkek (10.2 percent). Moreover, the entire volume of innovative products was produced by enterprises with private ownership.
Innovation-active enterprises developed and released 27 new types of products. Among them are new types of radiators, rotors, centrifuges, paving stones, fabrics, fruit teas, flavored milk cocktails and drinks, non-alcoholic and alcoholic beverages. The production of energy-saving lamps, new types of furniture, and functional underwear (diapers) was also established.
The volume of innovative product exports in 2013 was estimated at 870.7 million soms, or 70.0 percent of the total volume of shipped innovative products (in 2012 - 69.2 percent). It should be noted that 84.2 percent of exported products came from enterprises producing other non-metallic mineral products, and 10.3 percent from enterprises producing vehicles and equipment.
Expenditures on technological innovations in the industry are clearly disproportionate to the real needs of the domestic economy for updating fixed production assets and expanding the production of fundamentally new competitive products.
In 2013, expenditures on technological innovations amounted to 1,437.0 million soms. There is a trend of growth in those types of innovative activities that are directly related to the introduction of innovations and the acquisition of modern technologies. Thus, the acquisition of machinery and equipment in 2013 was carried out by 9 enterprises, with expenditures amounting to 1,186.2 million soms (82.5 percent of total expenditures on technological innovations). New technologies were acquired by 11 enterprises for a total of 20 million soms.
Research and development were conducted by two enterprises, which spent 200.4 million soms for these purposes. Production design was carried out by only two enterprises, which spent 19.5 million soms on preparing production for the release of new types of products.
Marketing research was conducted at only three enterprises, which does not meet the modern requirements for the innovative development of the economy.
In 2013, no expenditures were made for training and preparing personnel related to innovations. In the total expenditures on technological, marketing, and organizational innovations, the enterprises' own funds accounted for only 6.5 percent, foreign investments - 17.8 percent, and other sources of financing - 75.7 percent.
Based on the above, it should be noted that the process of implementing innovations by enterprises in the republic remains extremely low and simultaneously dependent on the import of foreign innovations in the form of equipment and technologies.