In Kyrgyzstan, among metalworking enterprises, a repair and mechanical plant was commissioned in Bishkek in 1931. In the 1930s, the metalworking industry developed at an accelerated pace. From 1928 to 1940, the gross output of the industry increased by 10.4 times, while that of metalworking increased by 26.1 times. During this period, the foundation of domestic machine engineering was formed. Machine engineering developed particularly rapidly during the Great Patriotic War based on evacuated enterprises. Between 1956 and 1960, new branches of machine engineering emerged, such as instrument engineering, automotive engineering, electrical engineering, and pump manufacturing. From 1941 to 1960, the gross output of the machine engineering and metalworking industry in Kyrgyzstan grew by 27.2 times. The output of the electrical engineering industry increased by 30.9 times from 1961 to 1970, and specialized plants were put into operation: the Kayyndy cable plant, "Kyrgyzelektrodvigatel," "Tyazhelektromash," the Issyk-Kul association of electrical engineering plants, and the Mailuu-Suu electric lamp factory. In the automotive industry, two plants were built: "Kyrgyzavtomash" and the Bishkek automobile assembly plant. Highly specialized plants were also commissioned: the Osh pump plant and "Kyrgyzcable."
Machine engineering and metalworking in Kyrgyzstan were once subjects of the all-union specialization of the republic in inter-republican division of labor, and the overwhelming majority of their products were used to meet the needs of the entire USSR. Their normal functioning was based on the supply of components from other republics and on the supply of products from the ferrous metallurgy sector. Currently, machine engineering has a small share in the gross industrial output of the republic. The types of products are few, and the volume of production is not large. The machine engineering enterprises of Kyrgyzstan produce simple items and consumer goods.
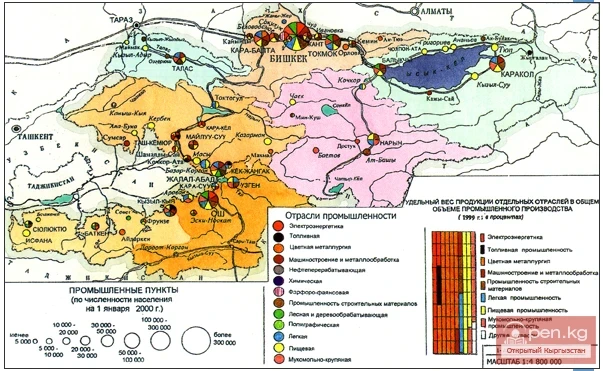
Machine engineering and metalworking include the following sub-sectors: electrical engineering, chemical and oil machine engineering, machine tool and instrument engineering, instrument engineering, automotive industry, tractor and agricultural machine engineering, metalworking, and others. Currently, there are 494 enterprises operating in this sector in the republic. Among them, there are 12 enterprises in electrical engineering, 2 large plants in chemical and oil machine engineering, 3 in machine tool and instrument engineering, 9 in instrument engineering, 3 in the automotive industry, 3 in tractor and agricultural machine engineering, 64 in metalworking, and 16 in other branches of machine engineering. The largest share in machine engineering and metalworking is held by electrical engineering (56%) and instrument engineering (19.0%); chemical and oil machine engineering — 1.0%, machine tool and instrument industry — 3.3%, automotive industry — 6.2%, tractor and agricultural machine engineering — 0.9%, metalworking — 19.2%, and other branches of machine engineering — 14.9%.
Electrical engineering plays an important role in the economy of Kyrgyzstan. The electrical engineering complex of the republic, producing large and small electric motors, transformers, lighting and semiconductor devices, cables and wires, household electrical goods, and devices for measuring, controlling, and regulating energy carrier consumption, consists of 9 plants. These include: the joint-stock company "OREMI" (formerly a heavy machine engineering plant), which produces large electric machines, transformers, and complete transformer substations (in 2000, products worth 36 million soms were produced); the corporation of the joint-stock company "KEMZ," which produces low-power electric motors for industrial and household use, and consumer goods. The Kemin electrical engineering plant produces electric welding machines and control panels. The electromechanical plant (in Karakol) produces electric regulators and electric stoves; the corporation of the joint-stock company "Kazhysay Electric Engineering Plant" produces semiconductor equipment and consumer goods. The joint-stock company "Electrotechnics" produces electric lamps, non-standard equipment, and consumer goods. The open joint-stock company "Mailuu-Suu Electric Lamp Plant" produces electric lamps and consumer goods (in 2000, products worth 643.6 million soms were produced); the joint-stock company "Kayindy Cable" produces cables and enamel wires (37.2 million soms); the plant "Kyrgyzelectroizolit" produces electrical insulation tubes and consumer goods. Additionally, electrical engineering products (starters, switches, etc.) are produced by other machine engineering enterprises in the republic. More than 40 types of electrical engineering consumer goods are produced in the republic: electric meters, electric boilers, electric water heaters, electric stoves, feed grinders, oilseed processing devices, water-lifting pumps, electric meat grinders, electric mixers, electric irons, washing machines, woodworking machines, and others.
Currently, one of the main tasks is to provide the population of the republic with food products. Therefore, it would be most reasonable and economically justified to produce those groups of electrical engineering devices that help solve the set tasks. A range of electrical engineering products and installations with high energy and economic performance indicators is produced: electric mills of various capacities for processing grain into flour; presses for extracting vegetable oil from oilseeds; installations for producing pasta; high-capacity electric meat grinders for producing minced meat and sausages; electric juicers for processing fruits and vegetables into juices; feed grinders for processing grain; corn cobs, and various grasses and hay for animal feed.
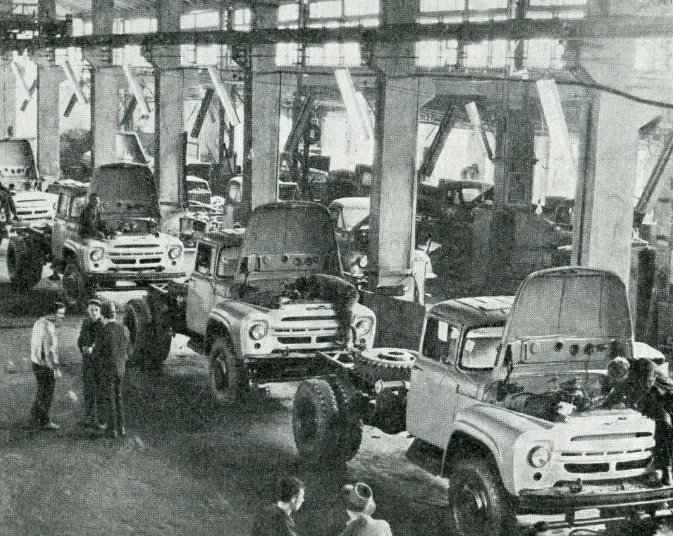
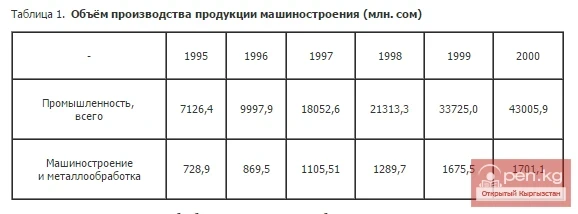
A major enterprise in chemical and oil machine engineering is the limited liability company "Osh Pump Plant" (the volume of production in 2000 amounted to 10.5 million soms); in machine tool and instrument engineering — the joint-stock company "Bishkek Machine Engineering Plant" (produced products worth 67.2 million soms); in instrument engineering — the joint-stock company "Transnational Corporation Dastan" (171.8 million soms); in the automotive industry — the joint-stock company "Kyrgyzavtomash" (66.5 million soms); in tractor and agricultural machine engineering — the joint-stock company "Bishkekselmash" (9.0 million soms); from other branches of machine engineering — the experimental plant in the Jayil district (45.5 million soms), the joint-stock company "Kyrgyz Radio Plant" (40.2 million soms). The volume of manufactured goods amounted to 869.5 million soms in 1996, 1675.5 million soms in 1999, and 1701.1 million soms in 2000.
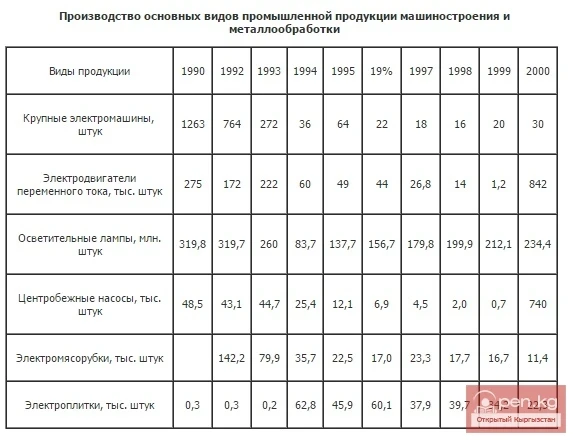
From 1991 to 2000, the share of machine engineering decreased by half. Currently, the disruption of economic ties with former partners, instability of market relations, and the non-competitiveness of manufactured goods, among other factors, hinder the development of machine engineering. However, in recent years, compared to previous ones, there has been growth in production sectors. In 2000, the physical volume index for the production of machines and equipment was 102%. Compared to 1999, more industrial boilers (2.9 times), technological equipment for trade and public catering enterprises (27.5%), radiators (20.2%), and centrifugal pumps (13%) were produced. The conclusion of contracts with foreign firms for the production of medical equipment allowed the joint-stock company "Transnational Corporation Dastan" to increase its output by 4.8 times; laboratory centrifuges by 3.9 times. Despite the reduction in industrial production, the number of employees in this sector is 26,946 (1999).
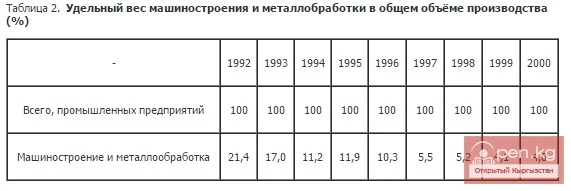
In 2000, machine engineering accounted for only 4.0% of the structure of industries. Compared to 1990, the share of machine engineering and metalworking in the sectoral structure decreased from 24.5% to 4.0%. The products produced by domestic manufacturers are non-competitive. Currently, there is demand only for certain household items — such as incandescent lamps and low-power electric motors.