CAMEROON. Republic of Cameroon
A country in the northwest part of Central Africa, it has access to the Atlantic Ocean. Area— 475.4 thousand km². Capital - Yaoundé (1.5 million), largest city and economic center - Douala (approx. 2 million). Administratively, it is divided into 10 provinces. Population - 16.2 million (2004); main ethnic groups - Fang, Bamileke, Douala, Basa, Bumun, Bata, Mandara. Official languages - French and English. Religion: 54% of the population are Catholics, 4% are representatives of other Christian denominations, 35% are adherents of Islam, and the rest adhere to local traditional beliefs.
Currency - Central African CFA franc.
It has diplomatic relations with the Russian Federation (established with the USSR on November 20, 1964).
National holiday — May 20 - Day of the Proclamation of the Unitary State (1972).
Cameroon is a republic. According to the new version of the constitution of 1996, executive power belongs to the president (head of state) and the prime minister (the government is accountable only to the president), legislative power - to the parliament - National Assembly. The president is Paul Biya, elected to this position for the 5th time (after 1982) in 2004 (for a term of 7 years). The prime minister is Ephraim Inoni. The current composition of the parliament (180 deputies, elected on the basis of universal direct voting for a term of 5 years) was formed in June 2002 as a result of the regular multiparty elections. The formation of the upper house of parliament (the senate) provided for by the constitution has not yet been realized.
Currently, about 120 parties are registered. According to the results of the parliamentary elections held in June 2002, the following major parties are represented in the highest legislative body of the country: the Democratic Rally of the Cameroonian People (ruling, 149 seats, founded in 1966, chairman - Paul Biya), the Social Democratic Front (22 seats), the Democratic Union of Cameroon (5 seats), the Union of the Peoples of Cameroon (3 seats).
In 1972, a unified trade union center was established - the National Union of Workers of Cameroon, renamed in 1985 to the Trade Union Organization of Workers of Cameroon.
In Northern Cameroon in the 15th-16th centuries, the Mandara Sultanate arose, in the early 19th century - several feudal Muslim principalities, in Central Cameroon - in the 18th century, the state of Bamum was formed, in Southern Cameroon - state formations took shape in the early 20th century. In 1884, Germany began the conquest of Cameroon and by 1914 had seized the entire territory of the country. After World War I, by the decision of the League of Nations, Eastern Cameroon was placed under the mandate of France, and Western Cameroon - under that of Great Britain. In 1946, these territories became trust territories of the UN under the administration of France and Great Britain.
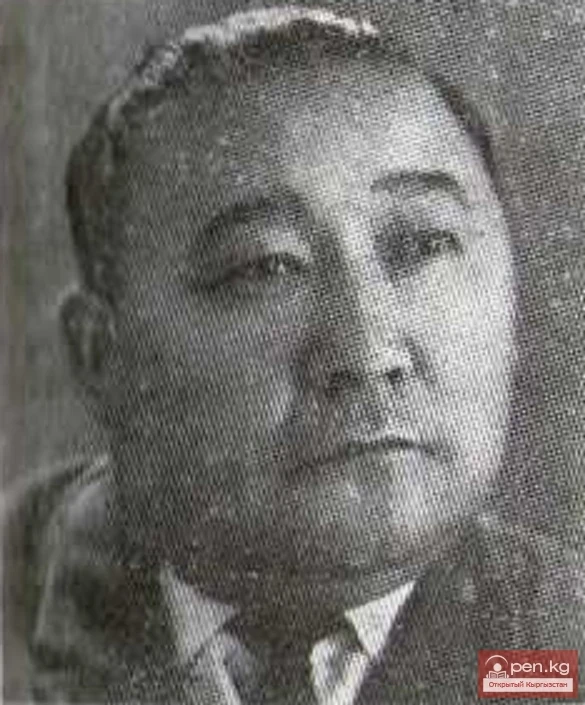
Under pressure from the national liberation movement, in January 1960, France was forced to grant independence to Eastern Cameroon. After a referendum held in 1961 in Western Cameroon, its southern part joined Cameroon, while the northern part joined Nigeria; in October 1961, the Federal Republic of Cameroon was created, consisting of Eastern Cameroon and the southern part of Western Cameroon, which had autonomous governing bodies. The leader of the Cameroon Union party, Ahmadou Ahidjo, became president. In May 1972, a nationwide referendum was held, which approved the formation of the United Republic of Cameroon, the creation of a unified political system, and the abolition of autonomous governing bodies in both parts of the country. In 1984, a new name for the country was adopted - the Republic of Cameroon.
In the sphere of domestic policy, the ruling circles of Cameroon pursue a line to strengthen the unity of the Cameroonian nation, develop national entrepreneurship, and encourage foreign capital activity with the regulatory role of the state. After significant complications in the domestic political situation in the first half of the 1990s, caused by both the exacerbation of the economic crisis (especially the consequences of the devaluation of the African franc in 1994) and the activation of the opposition, the Cameroonian leadership managed to generally keep the situation under control and maintain stability. There began a leveling of the living standards of the population. On the international stage, the government pursues a policy of non-alignment, advocates for the development of relations with all countries, and the resolution of conflicts through political means. Cameroon is a participant in the Pact of Non-Aggression among the member countries of the UN Standing Advisory Committee on Security Questions in Central Africa. The most developed ties are with the countries of Western Europe and the USA.
Cameroon is a member of the UN (since 1960), the African Union - formerly the OAU (since 1963), the Central African Economic and Monetary Community, and an associated member of the EU.
Since November 1, 1995, Cameroon has become a full member of the Commonwealth, headed by Great Britain.
In the Central African region, Cameroon, despite a slight decrease in GDP, consistently occupies leading positions in economic indicators; according to the UN classification, it belongs to the group of countries with a medium income level. Currently, average annual GDP growth rates of about 4-5% have been observed. The annual GDP volume is $10 billion (2004). The share of industry in the GDP structure is 44%, agriculture - about 1/3.
External debt - about $7 billion. The IMF, World Bank, Paris Club, EU, and France provide significant external financing and loans to assist in carrying out economic reforms and restoring economic growth.
It has a variety of natural resources: oil, gas, iron, bauxite, manganese, zinc, lead, tungsten, molybdenum, tin, titanium, gold, precious stones, but the locations are still not sufficiently explored. The country has large forest resources and ranks 6th in the world in the export of valuable timber.
There are enterprises in the oil extraction and refining, aluminum, leather and footwear, textile, and woodworking industries. Annual oil production is 5 million tons, and about 2 million m³ of timber, mainly of valuable species, is harvested annually.
Over the years of independence, the country has achieved food self-sufficiency. For domestic consumption, millet and sorghum, sweet potatoes and potatoes, corn and rice, and vegetable crops are grown.
Exports include: cocoa, coffee, bananas, timber, aluminum, rubber, shoes, and fabrics. Imports include: equipment, cars, petroleum products, household appliances, and food. Main trading partners: France, the Netherlands, the USA, Germany, and Spain.
Trade turnover in 2004 amounted to $3.71 billion.
The total length of railways is 1,175 km, and of roads - 64,500 km. Major seaports - Douala, Kribi, Limbe (95% of all foreign trade). International airports - in Yaoundé, Douala, and Garoua. There is a wide network of telephone communications, including satellite automatic communication.
The country ranks among the leading places in Africa in terms of school enrollment for children - 85%. A major university is located in Yaoundé, and there are also 4 specialized university centers - in Douala, Buea, Ngaoundéré, and Dschang; several inter-African institutes are functioning.
In Cameroon, about 50 newspapers and magazines are published; the largest among them are: "Cameroon Tribune" (75,000 copies), "Gazette," "Cameroon Outlook," "Cameroon Times," "Liberal," "Republican" (several tens of thousands of copies). The government information agency is "Camnews." There is a developed state broadcasting network, and national television was established in 1985.