What to Expect from Kyrgyzstan's Economy in 2026? About Risks and Forecasts in the EFSR Report
Fund analysts provided a detailed assessment of key macroeconomic indicators, suggesting that the country's economy will transition from a recovery phase to sustainable growth.
1
GDP Growth and Investments
Inflation is catching up with the economic growth of Kyrgyzstan: results for the 11 months of 2025
After reaching a peak of around 10% in 2025, GDP growth is expected to stabilize at 6.4% in 2026, and then be between 5.5-6% in 2027-2028.
Experts believe that the main driving force behind growth will be investment demand. Significant capital investments in energy, such as the Kambarata HPP-1 project, as well as in transport infrastructure, will create a multiplicative effect for the industrial sector. However, consumer activity may slow down due to strict monetary policy conditions.
2
Inflation and Monetary Policy
It is expected that the inflation rate in Kyrgyzstan will begin to decline, reaching 6.4% in 2026 and a target of 5.8% by 2028.
The National Bank of the Kyrgyz Republic raised the discount rate to 11 percent
The EFSD report emphasizes that the National Bank of the Kyrgyz Republic's policy played a significant role in controlling prices, as it increased the discount rate from 9% to 11%. This was a necessary step to minimize the impact of rising electricity and heating tariffs.
Nevertheless, analysts note that pro-inflationary pressure remains in the future, associated with annual increases in electricity tariffs, high food prices, and fuel and lubricants. A decrease in the inflation rate is only possible with reduced volatility in international markets and tightening monetary conditions.
3
Currency Market and Reserves
The exchange rate of the US dollar to the som is projected to be 96 in 2026, 97.5 in 2027, and 98.5 in 2028.
The state of external assets is assessed as "comfortable." The active strategy of the National Bank of the Kyrgyz Republic to accumulate gold and foreign exchange reserves has allowed it to reach a level that covers 5.9 months of imports, creating a reliable buffer against sharp fluctuations in the exchange rate.
4
Budget Policy and Government Expenditures
The state budget sector is characterized by a high share of government funding. In 2025, expenditures to support the public sector amounted to 11% of GDP.
The budget surplus of the Kyrgyz Republic in 2025 will exceed 10 billion soms — government
Previously, the main recipients of budget assistance were loss-making energy companies (such as the National Electric Network of Kyrgyzstan and Electric Stations OJSC), but in 2025, the number of recipients significantly increased. More than half of the budget support is now directed to the banking sector (for example, Eldik Bank OJSC, Aiyl Bank OJSC, Capital Bank OJSC, the State Development Bank of the Kyrgyz Republic), the construction industry (for example, the State Mortgage Company OJSC), and transport (for example, the National Company "Kyrgyz Temir Zholu"). According to the draft budget for 2026-2028, further expansion of the list of enterprises is planned, primarily due to companies in the financial sector.
The fund also points out the "expansionary nature" of fiscal policy. Although non-tax revenues remain at a high level, the budget deficit, considering quasi-fiscal operations (such as recapitalization of state banks and companies), is projected to be around 3.6% of GDP. Experts advise gradually transitioning to budget consolidation to ensure long-term sustainability.
5
Foreign Trade and Remittances
The trade balance deficit is expected to remain significant (imports will exceed exports), which will be partially offset by remittances. However, the fund warns of risks associated with dependence on the economic situation in partner countries. The stability of gold exports and the garment industry will be critical for the balance of payments.
6
Main Risks
In the EFSD report, three development scenarios are highlighted, among which the main negative factors include the potential deficit of irrigation water for agriculture and critically low water levels in the Toktogul Reservoir, which may limit export potential and lead to an increase in electricity imports.
Read also:
The forecast for the economic growth of the Kyrgyz Republic has improved, according to the Eurasian Fund for Stabilization and Development.
According to the latest data from the Eurasian Fund for Stabilization and Development (EFSD), the...
The EDB has once again improved the forecast for Kyrgyzstan's economic growth in 2025.
According to the EFSR forecasts, by the end of 2025, the gross domestic product of Kyrgyzstan will...
Analysts voiced the risks of economic growth in Kyrgyzstan
In a recent report from the Eurasian Fund for Stabilization and Development, experts highlighted...
What Will Lead to the Budget Deficit of the Kyrgyz Republic in 2028, Forecasted by EFSD Analysts
The Eurasian Fund for Stabilization and Development (EFSD) has presented a medium-term analysis...
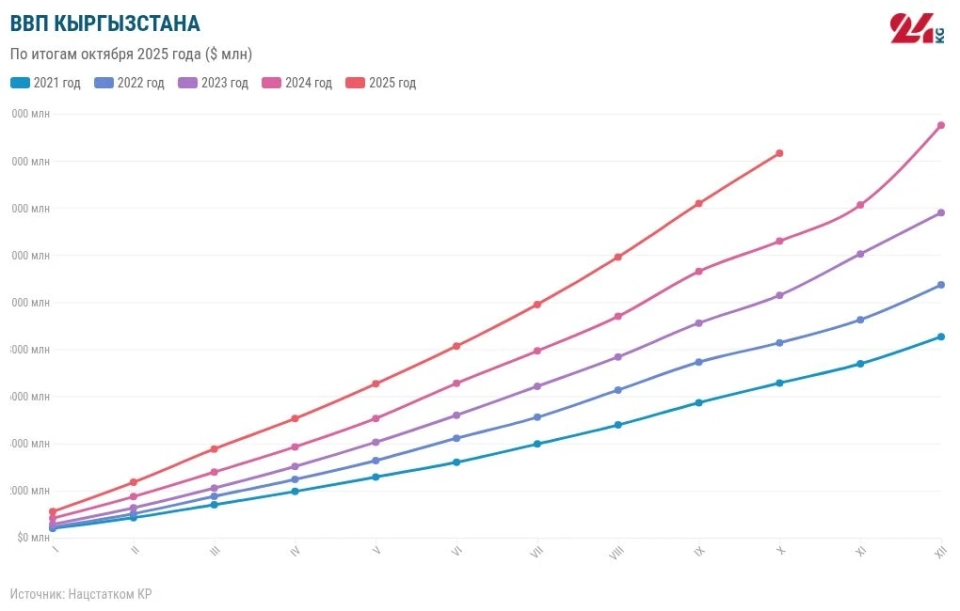
GDP is Growing, Inflation is Accelerating: Economic Results of 10 Months and Forecasts
According to preliminary data, the gross domestic product of Kyrgyzstan for the period from...
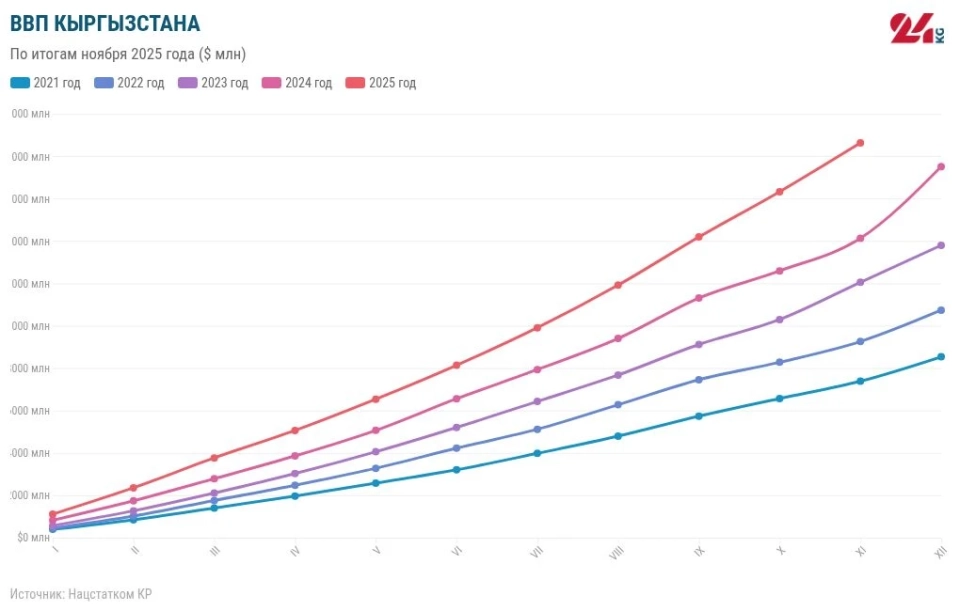
Inflation Catches Up with Economic Growth in Kyrgyzstan: Results of 11 Months of 2025
According to preliminary data, the gross domestic product of Kyrgyzstan from January to November...

The National Bank of Kyrgyzstan has raised the discount rate to 11%
On November 24, 2025, the Board of the National Bank of Kyrgyzstan decided to raise the key...
The Ministry of Finance forecasts growth of Kyrgyzstan's agriculture to 3.1% by 2027
- According to the data presented in the explanatory note by the Ministry of Finance, growth in...
The Cabinet has determined the minimum wage for 2026 — 3,280 soms
The government of Kyrgyzstan has approved the minimum wage level for 2026, which will amount to...
The National Bank of Kyrgyzstan has raised the discount rate to 11%. Why did this happen?
The Board of the National Bank of the Kyrgyz Republic has decided to increase the key policy rate...
Increase in electricity tariffs by 23.8% in May boosted inflation in Kyrgyzstan, - EFSR
- The analysis of the reasons for the inflation increase in Kyrgyzstan for June 2025 was presented...
The EFSR reported on how the Ministry of Finance of the Kyrgyz Republic allocated funds from the placement of Eurobonds.
In May 2025, the Kyrgyz Republic issued eurobonds worth $700 million, which led to an increase in...
In Kyrgyzstan, the excise tax on alcohol is being increased
The Ministry of Economy and Commerce of the Kyrgyz Republic is proposing a draft resolution to...
The Eurasian Development Bank Forecasts Record Economic Growth for Kyrgyzstan
According to forecasts from the Eurasian Development Bank, Kyrgyzstan's economy is expected to...
The Economy of Kyrgyzstan Will Grow Faster than All Central Asian Countries, but the Risks Are Too High
The IMF has presented its growth forecast for economies around the world, including the Middle East...
The National Bank of Kyrgyzstan has raised the discount rate
The decision to raise the key interest rate by 75 basis points to 10% was made by the Board of the...

The National Bank of Kyrgyzstan has raised the discount rate to 10%
On October 27, 2025, the Board of the National Bank of Kyrgyzstan decided to increase the key...
The National Bank raised the discount rate to 10%
- On October 27, 2025, the Board of the National Bank decided to increase the discount rate (key...

Head of the Cabinet: The consolidated budget for 2025 will exceed 1.1 trillion soms
During the meeting, the head of the government drew attention to the draft republican budget for...
The National Bank of the Kyrgyz Republic has raised the discount rate to 11 percent
On November 24, the Board of the National Bank of the Kyrgyz Republic made a decision to raise the...

The National Bank of Kyrgyzstan has raised the discount rate to 10 percent
As of October 28, the decision comes into effect...

EADB: Kyrgyzstan's Economic Growth Will Reach 10.3% in 2025
In the latest macro overview from the Eurasian Development Bank, it is reported that by the end of...

Analysts assessed the prospects of global oil demand
According to the forecast by the International Energy Agency (IEA), published in Reuters, global...
How Excise Taxes Will Increase from 2026: Beer, Wine, and Vodka Will Become More Expensive
The Ministry of Economy and Commerce of the Kyrgyz Republic has presented for public discussion a...
In Kyrgyzstan, alcohol excise taxes are increasing
The Ministry of Economy and Commerce of the Kyrgyz Republic has proposed a draft resolution that...

EBRD forecasts record economic growth for Kyrgyzstan
Investment in fixed assets in the republic increased by 18.9 percent...

The Ministry of Economic Development spoke about the increase in alcohol excise tax
The goal of the new initiatives is to reduce the consumption of harmful products The Cabinet of...

The Ministry of Economy of Kyrgyzstan Initiates Gradual Increase in Excise Tax Rates on Alcohol
As part of this project, an increase in the excise tax on certain alcoholic products is planned....

"In Kyrgyzstan, we have seen record economic growth over the past three years"
In the capital of Kyrgyzstan, Bishkek, a business forum dedicated to Central Asian Regional...
The project activities of the Turkic Investment Fund will begin in 2026.
The second meeting of the Board of Governors of the Turkic Investment Fund took place in Bishkek,...

The IEC announced how much the excise tax on alcohol will increase each year
The Ministry of Economy and Commerce of the Kyrgyz Republic has initiated a draft resolution of...

The National Bank raised the discount rate to 10 percent: what is behind this decision
Photo 24.kg The press conference held in the new building of the National Bank of Kyrgyzstan...

Gold and Platinum Price Forecasts Raised
The Fitch Ratings agency has updated its forecasts regarding the prices of several precious...
A competition has been announced in Kyrgyzstan for the 2026-2028 World University Games
The Ministry of Science, Higher Education and Innovations of the Kyrgyz Republic has initiated a...
The National Bank of the Kyrgyz Republic has raised the discount rate to 10 percent
On October 27, 2025, the National Bank of the Kyrgyz Republic announced an increase in the key...
The development program for the state language until 2028 has been prepared in Kyrgyzstan.
The draft program concerning the development of the state language in Kyrgyzstan for 2026-2028 has...
"Resource Dependency". Analysts Explain Why Abundant Natural Resources Do Not Guarantee Prosperity
Analysts conducted a study regarding the impact of commodity trade on the slowdown of economic...
Central Asia Among Leaders in Warehouse Infrastructure Growth Rates - EDB
According to the Eurasian Development Bank, Central Asia and the South Caucasus are leading in the...
During the implementation period of the Drinking Water Supply Systems and Settlements Development Program of the Kyrgyz Republic until 2026, $594 million in investments have been attracted from donors.
In the course of implementing the Program for the Development of Drinking Water Supply and...
Kyrgyzstan is among those economies that can make a "structural leap" through processing in industrial sectors, - EDB
- Analysts of the EDB presented an assessment of the industrial potential of the Kyrgyz Republic...
Analysts named 4 industries in Kyrgyzstan with high growth potential
- Specialists from the Eurasian Development Bank (EADB) have assessed the industrial potential of...

Oil prices predicted to plummet
According to Reuters, by the end of 2026, the average price of Brent crude oil could drop to $56...

Urban Forum in Bishkek
When: June 6 and 7...