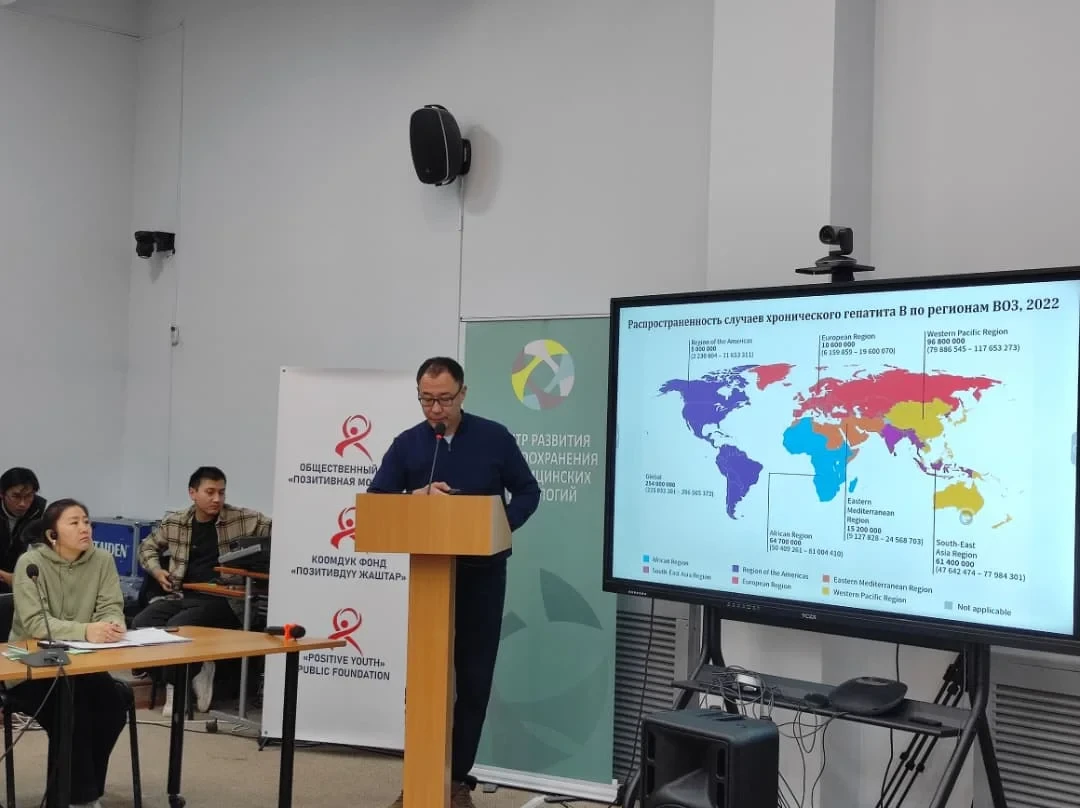
Key factors in this area include infrastructure, funding, modern organization of research institutes (RIs) and national centers (NCs), as well as their integration at the international level. The importance of medical science for the development of scientific intelligence is highlighted by Professor and former Minister of Health Talantbek Batyraliev in his interview.
In his opinion, it is important to move forward without dwelling on past achievements.
In this regard, I recalled the article “How to Reorganize Rabkrin”, written by the leader of the October Revolution V.I. Lenin. In it, he proposed establishing close ties between party and state regulatory bodies to combat bureaucratism and prevent a split in the party.
This work from the Soviet era reminds us of the importance of reforms necessary for modern sciences, especially in Kyrgyzstan. To begin with, a clear and realistic concept of scientific reform is required. Comparing oneself to countries like the USA or Germany is impractical, as they operate on a completely different scale. However, countries like Japan, South Korea, and Singapore, despite their small territory, have managed to develop their concepts for advancement in high technology and science, securing respectable positions on the world stage.
Japan is considered one of the leaders in science. The Basic Law on Science and Technology, adopted in 1995, introduced five-year plans for scientific and technological development. In 2021, a new law was passed that expanded previous provisions. The country holds high positions in areas such as high technology, automotive engineering, energy conservation, robotics, medicine, and space research. For Kyrgyzstan, high technology, energy conservation, robotics, and medicine are particularly important.
South Korea (Republic of Korea) is also known for its achievements in science and technology, actively investing in research aimed at creating future technologies. dzen.ruissras.ru
Some aspects of South Korea's state policy in science and technology include:
Investment in large research infrastructures. The government has developed two roadmaps aimed at strengthening the country's position in science and technology. issras.ru
Support for strategic technologies. Experts have identified 120 technologies of strategic importance for Korea, including semiconductors and autonomous vehicles. issek.hse.ru
Attracting foreign scientific centers. In 2004, the Korean Foundation for International Cooperation in Science and Technology (KICOS) was established to turn the country into a scientific center of Northeast Asia. eup.sgu.ru
Participation in international scientific infrastructures, such as CERN and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory. issras.ru
Singapore also plays a key role in global science through the development of education, research, and funding for scientific activities. The country aims to become a center for scientific achievements, actively collaborating with other states. funduma.ruinternationalwealth.infodzen.ruOnlinePatent.ru
In the field of education, key aspects include:
Attention to STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics). The state is forming a talent pool for high technology through programs like the TechSkills Accelerator (TeSA), aimed at upskilling workers. rsbu.sg
Application of the Singapore method — focusing on deeper teaching of mathematics and other subjects, which is actively implemented in schools and beyond. dzen.ru
Orientation towards international experience — the Ministry of Education studies best practices from other countries and applies their standards. externat.foxford.ru
Regarding scientific research, important directions include:
Development of biomedical sciences. For example, the establishment of the Institute of Bioengineering and Nanotechnology (IBN) has led to the development of gene engineering methods for cancer treatment. vk.com
Creation of IT-oriented ecosystems, such as Punggol Digital District and Singapore Science Park, which unite startups and research institutes to stimulate innovation. rsbu.sg
In terms of infrastructure, Singapore is developing:
Research institutes focused on the country's economic growth.
Research-intensive universities concentrating on fundamental research.
Scientific medical centers and hospitals engaged in clinical research.
Funding for science in Singapore is carried out through:
Government regulation — A*STAR manages grants and scholarships, as well as contracts with enterprises. Priority funding areas are assigned to divisions — Biomedical and Engineering specialties.
Private funding — despite the presence of government programs, private investments in R&D make up a significant portion of funding. In 2021, 7 billion Singapore dollars (about $5 billion) were attracted for engineering fields alone, which is almost seven times more than government funding.
International cooperation — Singapore actively participates in global scientific projects and exchanges experiences with foreign colleagues.
These points are very important for comparison and require careful study.
Turning to personnel issues in science, it is worth noting that they require special attention. An analysis of the state of science in the Kyrgyz Republic shows the presence of serious structural limitations hindering development.
One of the reasons is the low prestige of scientific activity and insufficient levels of remuneration. Salaries for scientists and university faculty do not match market conditions, which reduces motivation for scientific work. A scientific career is perceived as socially and economically unattractive, making it difficult to attract young specialists and exacerbating the personnel shortage.
The existing practice, where the entire administration and accounting of institutions receive funding from open grants while performers receive minimal amounts, deters applications for grants. It is necessary to prohibit in the statutory documents of RIs and universities the funding of individuals not directly involved in projects, as well as to clearly define the roles of all participants to exclude the involvement of outsiders posing as performers.
International grants should be addressed to specific researchers with their nominations indicated. Mechanisms are needed to support researchers working outside government programs, as well as participation in international projects, including startups and more serious initiatives.
The development of a funding system for science should take into account the themes of government projects that will receive sufficient funding, expanding them instead of narrowing.
When considering issues of science management, it should be understood that current structures are weakly capable of self-assessment. For an objective evaluation, international consulting is necessary to eliminate the influence of interested parties.
The National Academy of Sciences of the Kyrgyz Republic (NAS KR) needs to establish strict deadlines for reviewing dissertation works and attestation cases. New academic titles for researchers should be introduced, equated in status to associate professors and professors of universities.
Simplifying the process of submitting documents for academic degrees, creating checklists with minimal requirements, and establishing deadlines for their review are important steps towards improving the situation.
Discussing the personnel potential of science, it is important to recognize the necessity of reforming the NAS KR, as it still has professors with outdated publications that do not meet modern requirements. It is necessary to review the composition of such specialists and attract young scientists with relevant qualifications, providing them with the opportunity to become members of the Academy for high scientific activity.
For the growth of the Academy of Sciences, it is essential to attract outstanding scientists from Kyrgyzstan and abroad, as well as conduct independent audits and international consulting to assess its effectiveness.
It is also important to establish international connections and improve access to global scientific data. Issues of digitalization in scientific activities require the elimination of restrictions on data exchange speeds, which is key for integrating Kyrgyzstan's science into the global scientific community.
Digitalization of science should become a strategic direction within the state program "Digital Kyrgyzstan," focusing on the implementation of technologies in scientific infrastructure.
The basis for this process will be a common digital environment, requiring the creation of new fiber-optic lines and data centers.
Integration into the global scientific space requires the active placement of Kyrgyz scientific journals on international scientific platforms. A transparent scientific environment is necessary for science to develop and gain recognition.