The Department of Disease Prevention and State Sanitary and Epidemiological Surveillance reported the current risk assessment related to the Nipah virus for Kyrgyzstan, which has been deemed low.
General Overview of the Nipah Virus
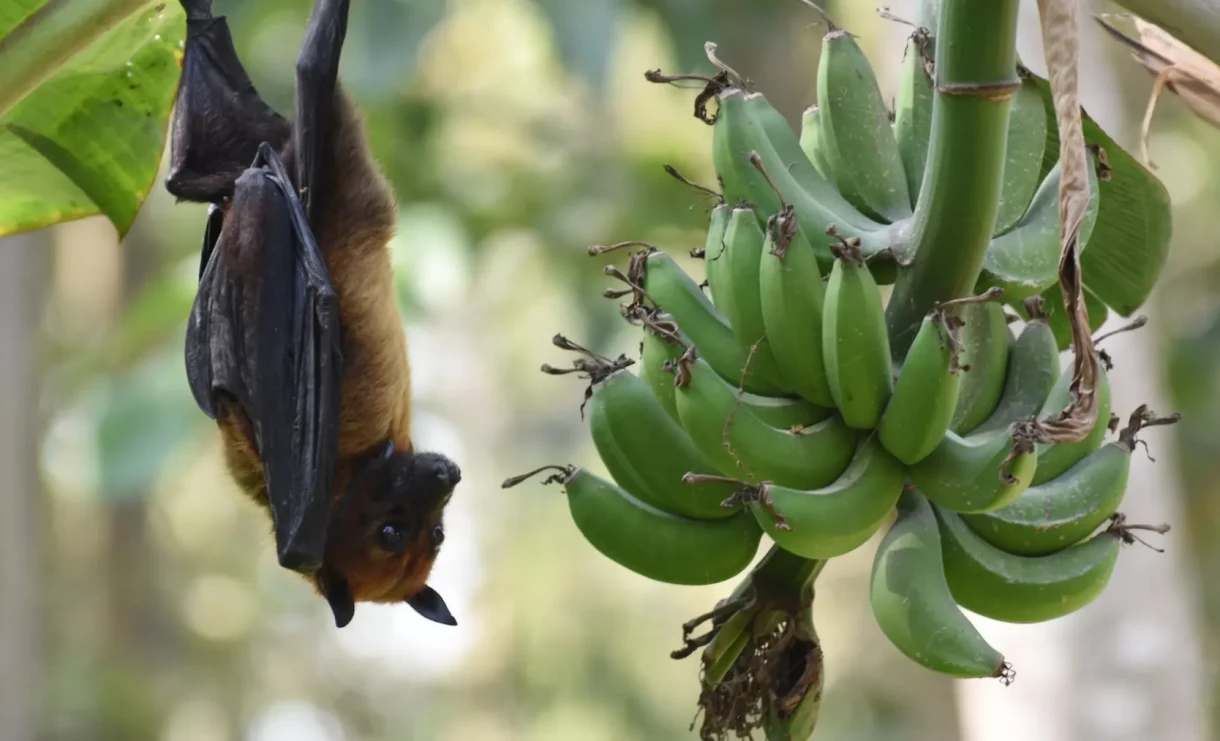
The Nipah virus is a zoonotic pathogen that is transmitted from animals to humans. The primary carriers of this virus are fruit bats, known as flying foxes.
The virus was first identified in 1999 during an outbreak among pig farmers in Malaysia. Since then, 12 outbreaks of the disease have been recorded in South Asia.
Current Events
In January 2026, a new local outbreak was registered in the Indian state of West Bengal, near Kolkata, with five confirmed cases of infection. Experts believe that this outbreak is local and seasonal in nature.
Risks for Kyrgyzstan
According to the information from state sanitary and epidemiological surveillance, the likelihood of the Nipah virus appearing and spreading in Kyrgyzstan is assessed as low for the following reasons:
- there are no natural foci of infection in the republic;
- the virus is spread among specific species of tropical bats;
- human-to-human transmission of the virus is limited, unlike viruses such as influenza and COVID-19;
- the infection is primarily transmitted via the fecal-oral route;
- infection can occur through fruits (especially dates) that have been contaminated with the saliva or urine of infected bats;
- contact with infected domestic animals, primarily pigs, can also lead to infection.
Symptoms of the disease include:
- high fever;
- intense headache;
- vomiting and sore throat;
- possible neurological symptoms: dizziness, drowsiness, confusion.
The state sanitary and epidemiological surveillance recommends that citizens planning trips to India:
- wash hands regularly with soap and use sanitizers;
- wash fruits and vegetables before consumption;
- avoid drinking water from unverified sources;
- avoid contact with sick animals (bats, pigs);
- immediately consult a doctor if symptoms appear (high fever, severe headache, pronounced cough).
The agency continues to monitor the epidemiological situation and urges citizens to adhere to preventive measures.