Architecture of the Village in the Mid-20th Century
The significance of rural architecture in the life of Kyrgyzstan is very great, as more than half of the population of the republic are rural residents. There are about 2000 rural settlements in Kyrgyzstan. Despite a noticeable increase in the rural population over the past four decades, there has been a trend towards a reduction in the network of rural settlements with subsequent concentration and consolidation.
An important role in the further development of rural construction was played by the resolution of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union and the Council of Ministers of the USSR dated September 12, 1968, regarding the regulation of construction in rural areas, and based on it, the resolution of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Kyrgyzstan dated January 10, 1969, which directed state organizations and design institutes to develop and adjust projects for district planning, general plans, and construction projects for rural settlements, as well as to develop standard projects for residential houses and public buildings.
In the republic, the design of rural construction is handled by specialized design organizations — "Kyrgyzgiprozem," "TsNIIP-ovtseprom," "Kyrgyzagropromkolkhozproekt" (B. Barakanov, M. Lovushkina, A. Novoselov, and others).
The social restructuring of the village is one of the most important state and national tasks, which has become part of the country's Food Program. Today, architects are tasked with creating modern comfort and beauty in the environment, where their creations would correspond to national traditions in terms of everyday life and the external appearance of buildings. The basis for the formation of such rural settlements should be general plans that provide for the rational placement of housing, public and production zones, as well as a series of standard projects for residential and public buildings.
In the last decade, several series of standard residential house projects have been created for the construction of villages in the republic, with a set of apartments ranging from 2 to 6 for various climatic zones. The house designs widely take into account local features — verandas, ayvans, summer kitchens, and utility buildings are provided, and there is an opportunity to conduct personal subsidiary farming on the plot in an expanded volume. For the construction of these houses, in addition to bricks, adobe, and clay, small-sized and large blocks, as well as large-panel construction, are used. The most common public buildings in the village — schools, preschool institutions, trade and public catering enterprises, clubs, cinemas, and medical institutions — are mainly built according to standard projects specifically developed for this purpose.
Among the most important tasks of rural architecture at the present stage is the further improvement of the planning and compositional structure of rural settlements by creating group systems of populated areas that fully take into account labor, cultural, domestic, and economic ties with urban settlements. The issues of forming a holistic architectural and spatial environment of the village and its complexity remain unresolved.
The further restructuring of rural architecture in the republic will take place under the conditions of the State Agro-Industrial Complex. With the creation of this organization, the structure of design and construction in villages is changing. Enterprises are gaining greater independence in the construction of rural settlements. In these conditions, it is important not to lower the level of architecture and the quality of construction, as the success of addressing the issues of restructuring rural architecture will largely determine the face of our republic.
Read also:
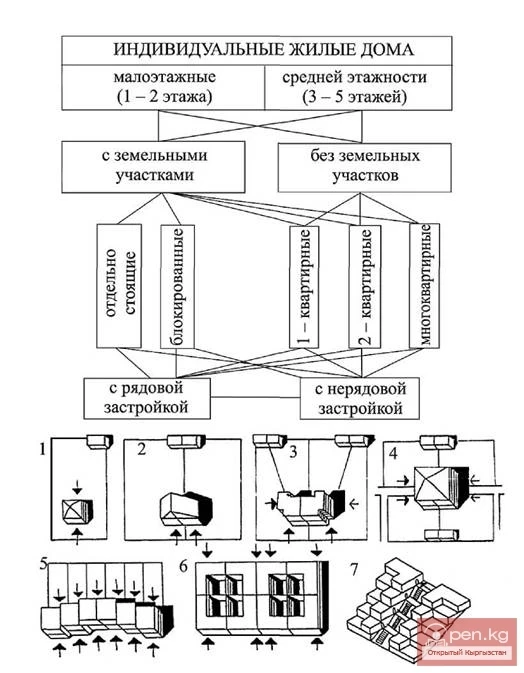
Tasks for the Development of Villages and Rural Settlements at the End of the 20th Century
An architect in the field of management is a socially active individual, programming activities in...
Tatyana Alexandrovna Tugova
TUGOVA Tatyana Alexandrovna...

MUKSINOV Ravil Munirovich
MUKSINOV Ravil Munirovich...
TSEVMENKO Alexander Ivanovich
TSEVMENKO Alexander Ivanovich...

Urban Planning in the 1970s and 1980s in Kyrgyzstan
Urban Planning. The development of urban planning in Kyrgyzstan represents a typical picture...

Under the Sign of the Struggle Against Grayness and Uniformity
The 1970s were a period of significant professional growth and creative achievements for the...
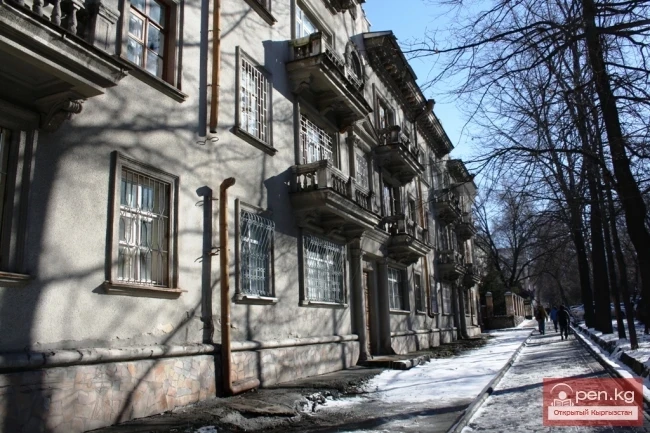

MILOV Mikhail Andreevich
MILOV Mikhail Andreevich...
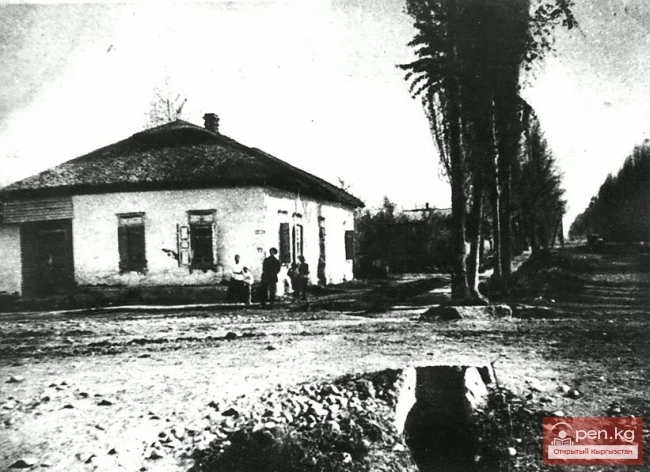

The First Stage of Developing a New Architecture
The development of new architecture began with the establishment of Soviet power in the territory...

Reported by the National Statistical Committee
National Statistical Committee: Female Population Predominates in Cities of Kyrgyzstan, While Male...
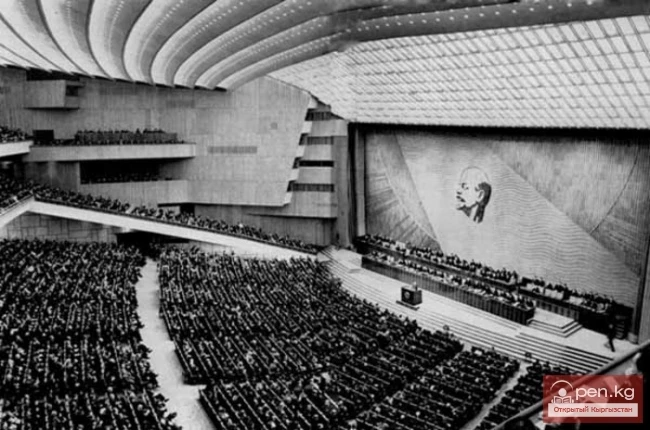

Decisions of the Congresses of the Union of Architects
The second half of the 1950s was filled with activities aimed at restructuring design methods and...
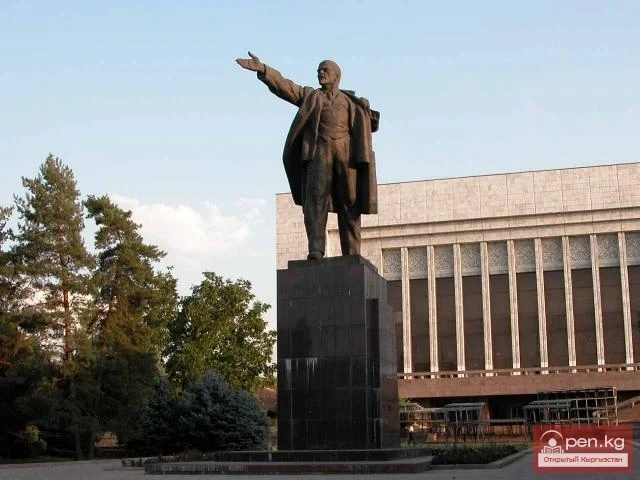

SARBANOV Kytaybek Sarbanovich
SARBANOV Kytaybek Sarbanovich...

Union of Architects of Kyrgyzstan
In connection with the adoption in 1976 by the Supreme Soviet of the USSR of the Law on the...

Maya Alexandrovna Lovushkina
Maya Alexandrovna Lovushkina...

A New Stage in the Development of Architecture
The establishment of the first design institution laid the foundation for the formation of...

Alimkulov Samsaly Amanovich
Alimkulov Samsaly Amanovich Doctor of Technical Sciences, Professor, Academician of the...

TOYBAEV Nurlanbek Beishembayevich
TOYBAEV Nurlanbek Beishembaevich...

Military Mobilization Work of Local Government Authorities in Kyrgyzstan
Activities of the Councils of Workers' Deputies in Military Conditions The Councils of...

Yudakhina Tatyana Georgievna
YUDAKHINA Tatyana Georgievna...

UMARALIEV Sanabek Kemelbekovich
UMARALIEV Sanabek Kemelbekovich...

Klimenko Anatoly Ivanovich
Klimenko Anatoly Ivanovich...

The title translates to "City-Forming Factor."
Industrial architecture. Today, the industry of Kyrgyzstan comprises 130 sectors and sub-sectors....

MUKSINOV Munir Nigmatullovich AFONIN Petr Alexandrovich
MUKSINOV Munir Nigmatullovich AFONIN Petr Alexandrovich...

GOLOVANEV Alexander Andrianovich
GOLOVANEV Alexander Andrianovich...

SHEVCHENKO Vera Georgievna
SHEVCHENKO Vera Georgievna...
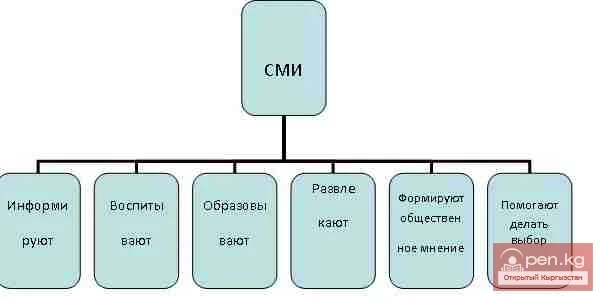
Formation and Development of the Movement of Workers and Rural Correspondents in Kyrgyzstan
From the very first days of the establishment of print media in the country as a whole, as well as...

KALINOV Nikolai Nikolaevich
KALINOV Nikolai Nikolaevich...

SHKAEB Alexey Sergeevich
SKRYABIN Alexey Sergeevich...

TURSUNOV Anvar Tursunbaevich
TURSUNOV Anvar Tursunbaevich...

ERKINBEK NURBEKOV
NURBEKOV Erkinbek...

Resolution of the Central Committee of the VKP(b) - into life
The artistic principles of constructivism were built on the basis of formal solutions to a number...

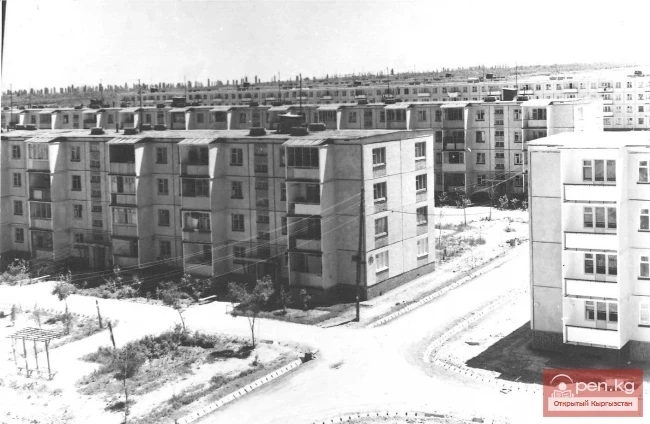
Mass Housing Construction
Housing. The new Constitution of the USSR was one of the first in the world to proclaim the right...

KUTATELADZE Gennady Platonovich
Kutateladze Gennady Platonovich Architect. Member of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union since...

Architecture of Soviet Kyrgyzstan
Soviet architects live and work in the first socialist state on the planet, whose powerful...

Muksinov Ravil Munirovich
Muksinov Ravil Munirovich (1952), Doctor of Architecture (1996), Professor (1997) Tatar. Born in...
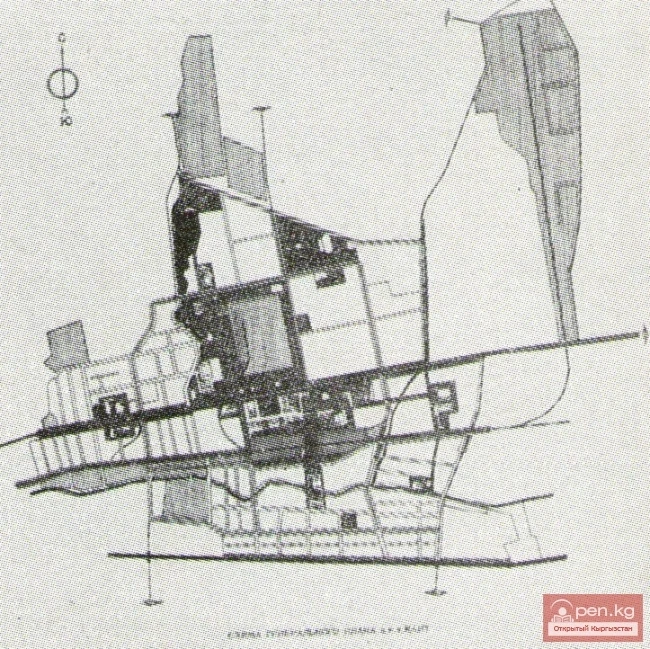
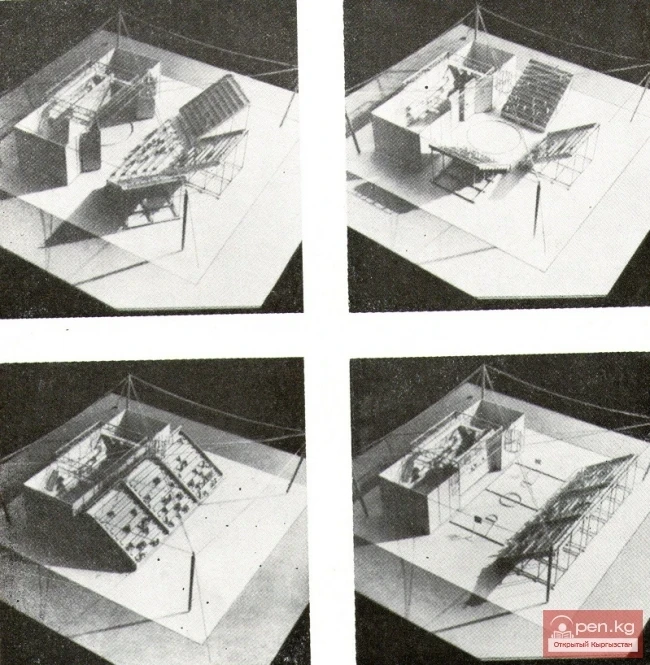
A time capsule has been laid in Ak-Tal for the construction of the first two facilities.
In the new settlement of Ak-Tilek, being established in the territory of the rural district of...

Mamatbek Sydykov
Sydykov Mamatbek...

KADYRBECOV Ishenbai Dyushenbievich
KADYRBECOV Ishenbai Dyushenbievich...

KUTSEMELov Leonid Gavrilovich
KUTSEMELLOV Leonid Gavrilovich...

SMIRNOV Yuri Nikolaevich
SMIRNOV Yuri Nikolaevich...

The title translates to "The Village of Bazar-Korgon."
BAZARKORGON AND BAZARKORGON DISTRICT Bazarkorgon (Kyrgyz: Базар-Коргон) is a village in the...

Approval of the total estimated cost of construction for the first phase of the trolleybus in the city of Frunze. Document No. 175 (September 1947)
RESOLUTION OF THE COUNCIL OF MINISTERS OF THE KYRGYZ SSR "ON APPROVAL OF THE GENERAL ESTIMATE...

ALYKULOV Kanybek Mamytovich
ALYKULOV Kanybek Mamytovich...

Abdrakhmanov's Approach to the Problems of Economic Construction in the Republic
Horse threshing with stones in the village. 1914 Difficulties in Transforming the Social...

Organization of the City Prosecutor's Office and Children's Cinema in Frunze. Documents No. 170 and No. 171 (Summer 1946).
RESOLUTION OF THE COUNCIL OF MINISTERS OF THE KYRGYZ SSR AND THE CENTRAL COMMITTEE OF THE...
The Cabinet approved the logo and the procedure for using the national symbol of the Kyrgyz Republic — the snow leopard.
The Cabinet of Ministers has officially recognized the snow leopard (irbis) as the national symbol...
Batken Region
The Batken Region was established on October 12, 1999, from the Osh Region. It includes the...

NEZHURIN Anatoly Mikhailovich
NEZHURIN Anatoly Mikhailovich...

Elena Alexandrovna Braginskaya
BRAGINSKAYA Elena Alexandrovna...

