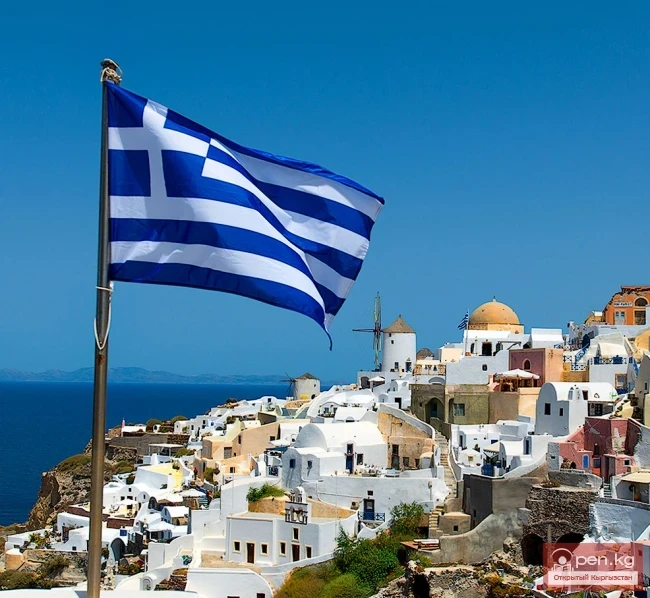
Greece
Greece officially — Hellenic Republic — is a country in Southern Europe. It is a member of the European Union and NATO. The population is over 11.3 million (estimate, 2010), and the area of the territory is 131,957 km². It ranks 84th in the world by population and 95th by area.
The capital is the city of Athens. The official language is Greek.
It is a unitary parliamentary republic. In March 2015, the presidency was assumed by Prokopis Pavlopoulos. It is divided into 13 regions.
The country is located on the Balkan Peninsula and numerous islands. It is washed by the Aegean Sea (including the Icarian Sea) and the Thracian Sea to the east, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Mediterranean and Cretan Seas to the south. It has a land border with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the northeast.
About 98% of the population adheres to Orthodoxy.
Modern Greece is the heir to the culture of Ancient Greece, considered the cradle of Western civilization, the birthplace of democracy and Western philosophy, the fundamental principles of physical and mathematical sciences, theater, and the modern Olympic Games. Its rich cultural heritage and geographical location make Greece one of the most visited countries in the world.
Greece is an industrial-agrarian country. The GDP for 2011 was $294.339 billion (about $24,543 per capita). The currency is the euro.
The country's independence was proclaimed on March 25, 1821. Before that, it was part of the Ottoman Empire.
Greece lags behind its EU partners. The Greek economy is characterized by a high degree of employment in the non-manufacturing sector (over 50% of GDP). The government's economic policy is determined by the desire to accelerate the country's adaptation to integration processes in the EU.
GDP growth in 2004 was 4%. The average annual income per capita was about 13,000 euros. Unemployment affected 10% of the economically active population. The government's economic policy aims to stabilize the economy by strengthening market regulation, extensive privatization of unprofitable state enterprises, and reforming the financial and banking systems.
Anti-inflation measures are being implemented. The government is forced to make unpopular decisions (reducing state subsidies, freezing salaries), which leads to quite painful social consequences.
The industry of Greece (share in GDP - 25%) is heavily monopolized by large local and foreign (mainly from the USA, Germany, France, and Switzerland) capital (about 200 companies receive over 50% of profits). At the same time, there is a large number of small enterprises in the country. The main industries are food, light, textile, chemical, mining, metallurgy, and cement (one of the largest exporters of cement in the world). Electrical engineering and energy, some types of machine engineering, and the production of building materials are developing.
The country has significant reserves of minerals. Lignite, bauxite, nickel ore, magnesite, marble, and others are extracted. On the island of Naxos, there is the largest deposit of emery in the world. The needs for liquid fuel are 95% covered by imports.
The share of agriculture in GDP is 13%. Arable land — 3.96 million hectares (30% of the country's total area) — is mainly distributed among small farms (with plots of up to 3.5 hectares). The main branch of agriculture is crop production. Arable land amounts to about 2.3 million hectares, of which 0.8 million hectares are irrigated; 1.2 million hectares are vineyards, olive groves, and orchards. Although the yield of major agricultural crops in Greece is lower than the EU average, the country's needs for grain, vegetable oils, vegetables, and fruits are fully met. The needs for meat are satisfied by 75%, and for butter by 70%.
Rail transport is state-owned. It is poorly developed. 60% of domestic transport is by road. Of the 40 Greek airports, 22 are international. Trade plays a significant role in the country's economy, and the fleet ranks among the top in the world (in 2004 — 3,370 ships, 18% of the total world trade fleet by tonnage), with 68% of Greek ships registered under the flags of 34 countries. The main ports are Piraeus, Thessaloniki, Patras, and Volos.
The foreign trade balance is characterized by a deficit. The volume of foreign trade turnover in 2004 was about $60 billion. The main import items are machinery and equipment, oil and petroleum products, mineral raw materials, consumer goods, and food. Exports include products from the mining industry (bauxite, nickel, manganese), agriculture (tobacco, raisins, olives and olive oil, citrus fruits, cotton), and industrial goods. The main trading partners of Greece are Germany, Italy, the USA, France, and Saudi Arabia.
The budget deficit in 2004 was 6.9% of GDP (6.5% in 2003). There was a trend towards a decrease in the inflation rate, which was 3.1% in 2004 (3.5% in 2003).
Tourism is widely developed, providing significant foreign currency inflows. The country is visited by over 10 million tourists annually, with tourism revenues amounting to about $12 billion (2004).
Greece is a country of ancient culture. The world-famous archaeological and architectural monuments of Hellas include the Acropolis of Athens, Delphi, Corinth, Mycenae, Epidaurus, and Olympia. The works of outstanding ancient Greek scholars and thinkers laid the foundation for many modern fields of knowledge. Here, European poetry and drama began.
In 1964, compulsory free 9-year education was introduced in the country. Secondary education lasts 12 years. There are 17 higher educational institutions (6 universities) in the country, the largest being the University of Athens and the University of Thessaloniki, and the Athens Polytechnic Institute.
In Greece, there are over 100 daily (central and local) and about 300 weekly newspapers. The most popular are "Kathimerini," "Rizospastis," "Ethnos," "Nea," "Eleftherotypia," and "Vima." Circulation relative to the population is higher than in most Western European countries. The Athens News Agency (ANA) was founded in 1896. National radio and television are united in the ERT broadcasting corporation. There are 1,500 radio stations and 180 television companies in the country, among which the leading ones are private television companies "Mega Channel" and "Ant1," and state channels ET-1 and ET-2. Foreign television programs from the USA, Russia, England, France, Germany, Italy, and Spain are retransmitted. Since January 2004, the "News" program in Russian has been broadcast on Channel 10.