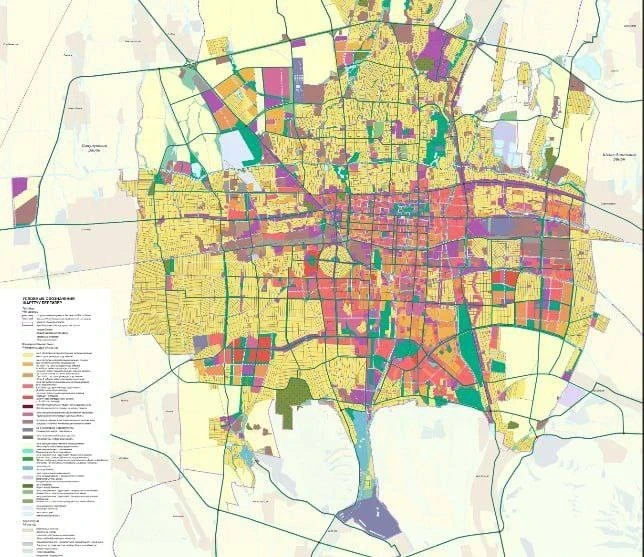
This master plan defines not only the planning structure of the city but also functional zoning, housing stock parameters, as well as the development of transport, engineering, and social infrastructure. Important aspects also include measures for environmental protection and the preservation of historical and cultural heritage.
When developing the master plan, current demographic and socio-economic trends were taken into account. According to forecasts, the population of the capital is expected to reach about 1.3 million by 2025, and may approach nearly 2 million by 2050. Considering the administrative-territorial reform, the area of Bishkek now covers about 41 thousand hectares.
The project envisions the creation of a polycentric structure with the formation of new public and business centers in each district, as well as specialized centers: administrative, medical, educational, sports, and recreational.
Particular attention is given to the Bishkek agglomeration, whose population may grow to 2.5 million. The master plan proposes the creation of a system of agglomeration centers of the first and second order, the development of transport links, and the redistribution of jobs beyond the central part of the agglomeration.
In terms of economic development, the master plan provides for:
- an increase in the labor force to 1,179.1 thousand people;
- growth in the number of employed from 593.9 thousand to 943.3 thousand;
- the creation of 349.4 thousand new jobs in the fields of industry, transport, construction, and social services.
Transport Infrastructure
The development of transport infrastructure includes:- the reconstruction of the "Manas" airport;
- the creation of a bypass road around the city;
- the construction of a railway trunk line around built-up areas;
- the development of the street network, transport interchange hubs, bus stations, and stops;
- priority attention to public passenger transport.
- intra-city rail service along the route "West - Center - East";
- light rail transport (tram);
- metrobus (BRT).
In terms of ecology, the master plan aims to create a natural-ecological infrastructure, including a system of green areas, water bodies, and ecological corridors integrated into the urban environment.
Rivers and irrigation canals play an important role in this process, contributing to the improvement of the microclimate, the restoration of shorelines, and the enhancement of the city's recreational appeal.
The preservation and development of public green spaces and protected natural areas are also a focus, as they serve as ecological cores and buffer zones.
Additionally, the plan includes measures for the ecological reorganization of industrial and transport zones, including landscaping and greening, to reduce the negative impact on the environment and optimize the use of natural resources.